
Chapter 12: Linear Regression and Correlation
Introductory
Bivariate data: two variable data
Multivariate data: more than two variables
12.1 Linear Equations
y = a + bx: linear regression for two variables is based on a linear equation with one independent variable.
Independent variable: x
Dependent variable: y
Slope: b
y-intercept: a
Graph form: a straight line or linear
B > 0: slopes to the right
b = 0: horizontal line
b < 0: slopes downward to the right
12.2 Scatter Plots
Scatterplot: uses dots to represent values for two different numeric variables.
Calculator steps for scatter plot
Enter your X data into list L1 and your Y data into list L2.
Press 2nd STATPLOT ENTER to use Plot 1. On the input screen for PLOT 1, highlight On and press ENTER. (Make sure the other plots are OFF.)
For TYPE: highlight the first icon, the scatter plot, and press ENTER.
For X List, enter L1 ENTER and for Ylist: L2 ENTER.
For Mark: it does not matter which symbol you highlight, but the square is the easiest to see. Press ENTER.
Make sure there are no other equations that could be plotted. Press Y = and clear any equations out.
Press the ZOOM key and then the number 9 (for menu item "ZoomStat"); the calculator will fit the window to the data. You can press WINDOW to see the scaling of the axes.
Scatterplot Direction: High values of one variable occurring with high values of the other variable or low values of one variable occurring with low values of the other variable
Strength: Looking at how close the points are to the line
Linear regression: shows the relationship between a dependent and independent variable(s)
12.3 The Regression Equation
Least-Squares Line: You have a set of data whose scatter plot appears to "fit" a straight line
Least-squares regression line: Helps obtain a line of best fit
y hat: estimates value of y
y0 – ŷ0 = ε0: error or residual
Absolute value of a residual: measures the vertical distance between the actual value of y and the estimated value of y
ε: the Greek letter epsilon
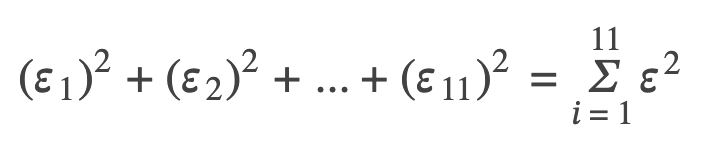
Slope equation: b = r (sy / sx)
sx = the standard deviation of the x values.
sy = the standard deviation of the y values
Interpretation of the Slope: “The slope of the best-fit line tells us how the dependent variable (y) changes for every one unit increase in the independent (x) variable, on average.”
Using the Linear Regression T Test
In the STAT list editor, enter the X data in list L1 and the Y data in list L2, paired so that the corresponding (x,y) values are next to each other in the lists.
On the STAT TESTS menu, scroll down with the cursor to select the LinRegTTest.
On the LinRegTTest input screen enter: Xlist: L1 ; Ylist: L2 ; Freq: 1
On the next line, at the prompt β or ρ, highlight "≠ 0" and press ENTER
Leave the line for "RegEq:" blank
Highlight Calculate and press ENTER.
Correlation coefficient (r): is numerical and provides a measure of strength and direction of the linear association between the independent variable x and the dependent variable y.
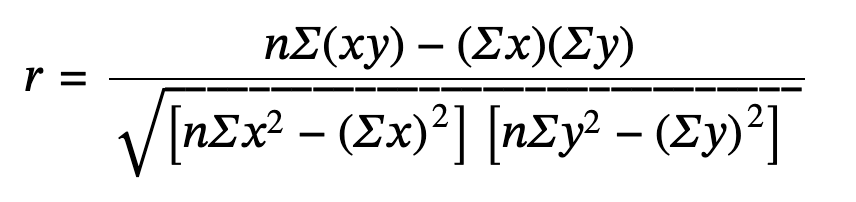
The value of r is always between –1 and +1: –1 ≤ r ≤ 1.
The size of the correlation r indicates the strength of the linear relationship between x and y. Values of r close to –1 or to +1 indicate a stronger linear relationship between x and y.
If r = 0 there is likely no linear correlation. It is important to view the scatterplot, however, because data that exhibit a curved or horizontal pattern may have a correlation of 0.
If r = 1, there is perfect positive correlation. If r = –1, there is perfect negative correlation. In both these cases, all of the original data points lie on a straight line.
Positive correlation: A positive value of r means that when x increases, y tends to increase and when x decreases, y tends to decrease.
Positive correlation: A negative value of r means that when x increases, y tends to decrease and when x decreases, y tends to increase
Correlation does not imply causation
0 < r < 1: A scatter plot showing data with a positive correlation.
–1 < r < 0: A scatter plot showing data with a negative correlation.
r = 0: A scatter plot showing data with zero correlation.
Coefficient of determination: a number between 0 and 1 that measures how well a statistical model predicts an outcome
r^2 interpretation: when expressed as a percent, represents the percent of variation in the dependent (predicted) variable y that can be explained by variation in the independent (explanatory) variable x using the regression (best-fit) line.
1 - r^2 Interpretation: when expressed as a percentage, represents the percent of the variation in y that is NOT explained by variation in x using the regression line.
12.4 Testing the Significance of the Correlation Coefficient
Significance of the correlation coefficient: to decide whether the linear relationship in the sample data is strong enough to use to model the relationship in the population.
ρ: population correlation coefficient
r: sample correlation coefficient
Conclusion for Significant: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero.
Conclusion for Not Significant: There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is not significantly different from zero.
Null Hypothesis: H0→ ρ = 0
Alternative Hypothesis: Ha→ ρ ≠ 0
Interpreting Null Hypothesis: The population correlation coefficient IS NOT significantly different from zero. There IS NOT a significant linear relationship (correlation) between x and y in the population.
Interpreting Alternate Hypothesis: The population correlation coefficient IS significantly DIFFERENT FROM zero. There IS A SIGNIFICANT LINEAR RELATIONSHIP (correlation) between x and y in the population.
To calculate the p-value using LinRegTTEST
On the LinRegTTEST input screen, on the line prompt for β or ρ, highlight "≠ 0"
The output screen shows the p-value on the line that reads "p ="
p-value is less than the significance level: We reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero
p**-value is NOT less than the significance level**: DO NOT REJECT the null hypothesis. There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is NOT significantly different from zero.
12.6 Outliers
Outliers: are observed data points that are far from the least squares line.
Influential points: observed data points that are far from the other observed data points in the horizontal direction. These points may have a big effect on the slope of the regression line.
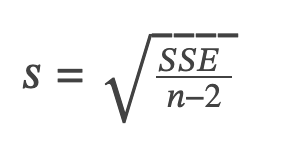
Degrees of freedom: n - 2
Examples

Chapter 12: Linear Regression and Correlation
Introductory
Bivariate data: two variable data
Multivariate data: more than two variables
12.1 Linear Equations
y = a + bx: linear regression for two variables is based on a linear equation with one independent variable.
Independent variable: x
Dependent variable: y
Slope: b
y-intercept: a
Graph form: a straight line or linear
B > 0: slopes to the right
b = 0: horizontal line
b < 0: slopes downward to the right
12.2 Scatter Plots
Scatterplot: uses dots to represent values for two different numeric variables.
Calculator steps for scatter plot
Enter your X data into list L1 and your Y data into list L2.
Press 2nd STATPLOT ENTER to use Plot 1. On the input screen for PLOT 1, highlight On and press ENTER. (Make sure the other plots are OFF.)
For TYPE: highlight the first icon, the scatter plot, and press ENTER.
For X List, enter L1 ENTER and for Ylist: L2 ENTER.
For Mark: it does not matter which symbol you highlight, but the square is the easiest to see. Press ENTER.
Make sure there are no other equations that could be plotted. Press Y = and clear any equations out.
Press the ZOOM key and then the number 9 (for menu item "ZoomStat"); the calculator will fit the window to the data. You can press WINDOW to see the scaling of the axes.
Scatterplot Direction: High values of one variable occurring with high values of the other variable or low values of one variable occurring with low values of the other variable
Strength: Looking at how close the points are to the line
Linear regression: shows the relationship between a dependent and independent variable(s)
12.3 The Regression Equation
Least-Squares Line: You have a set of data whose scatter plot appears to "fit" a straight line
Least-squares regression line: Helps obtain a line of best fit
y hat: estimates value of y
y0 – ŷ0 = ε0: error or residual
Absolute value of a residual: measures the vertical distance between the actual value of y and the estimated value of y
ε: the Greek letter epsilon
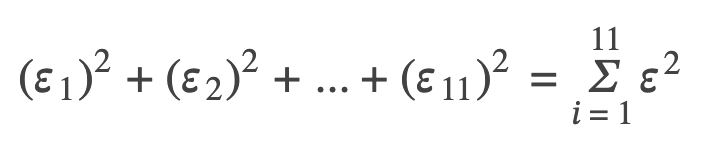
Slope equation: b = r (sy / sx)
sx = the standard deviation of the x values.
sy = the standard deviation of the y values
Interpretation of the Slope: “The slope of the best-fit line tells us how the dependent variable (y) changes for every one unit increase in the independent (x) variable, on average.”
Using the Linear Regression T Test
In the STAT list editor, enter the X data in list L1 and the Y data in list L2, paired so that the corresponding (x,y) values are next to each other in the lists.
On the STAT TESTS menu, scroll down with the cursor to select the LinRegTTest.
On the LinRegTTest input screen enter: Xlist: L1 ; Ylist: L2 ; Freq: 1
On the next line, at the prompt β or ρ, highlight "≠ 0" and press ENTER
Leave the line for "RegEq:" blank
Highlight Calculate and press ENTER.
Correlation coefficient (r): is numerical and provides a measure of strength and direction of the linear association between the independent variable x and the dependent variable y.
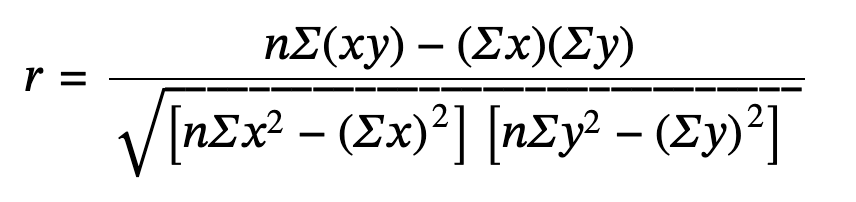
The value of r is always between –1 and +1: –1 ≤ r ≤ 1.
The size of the correlation r indicates the strength of the linear relationship between x and y. Values of r close to –1 or to +1 indicate a stronger linear relationship between x and y.
If r = 0 there is likely no linear correlation. It is important to view the scatterplot, however, because data that exhibit a curved or horizontal pattern may have a correlation of 0.
If r = 1, there is perfect positive correlation. If r = –1, there is perfect negative correlation. In both these cases, all of the original data points lie on a straight line.
Positive correlation: A positive value of r means that when x increases, y tends to increase and when x decreases, y tends to decrease.
Positive correlation: A negative value of r means that when x increases, y tends to decrease and when x decreases, y tends to increase
Correlation does not imply causation
0 < r < 1: A scatter plot showing data with a positive correlation.
–1 < r < 0: A scatter plot showing data with a negative correlation.
r = 0: A scatter plot showing data with zero correlation.
Coefficient of determination: a number between 0 and 1 that measures how well a statistical model predicts an outcome
r^2 interpretation: when expressed as a percent, represents the percent of variation in the dependent (predicted) variable y that can be explained by variation in the independent (explanatory) variable x using the regression (best-fit) line.
1 - r^2 Interpretation: when expressed as a percentage, represents the percent of the variation in y that is NOT explained by variation in x using the regression line.
12.4 Testing the Significance of the Correlation Coefficient
Significance of the correlation coefficient: to decide whether the linear relationship in the sample data is strong enough to use to model the relationship in the population.
ρ: population correlation coefficient
r: sample correlation coefficient
Conclusion for Significant: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero.
Conclusion for Not Significant: There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is not significantly different from zero.
Null Hypothesis: H0→ ρ = 0
Alternative Hypothesis: Ha→ ρ ≠ 0
Interpreting Null Hypothesis: The population correlation coefficient IS NOT significantly different from zero. There IS NOT a significant linear relationship (correlation) between x and y in the population.
Interpreting Alternate Hypothesis: The population correlation coefficient IS significantly DIFFERENT FROM zero. There IS A SIGNIFICANT LINEAR RELATIONSHIP (correlation) between x and y in the population.
To calculate the p-value using LinRegTTEST
On the LinRegTTEST input screen, on the line prompt for β or ρ, highlight "≠ 0"
The output screen shows the p-value on the line that reads "p ="
p-value is less than the significance level: We reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero
p**-value is NOT less than the significance level**: DO NOT REJECT the null hypothesis. There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is NOT significantly different from zero.
12.6 Outliers
Outliers: are observed data points that are far from the least squares line.
Influential points: observed data points that are far from the other observed data points in the horizontal direction. These points may have a big effect on the slope of the regression line.
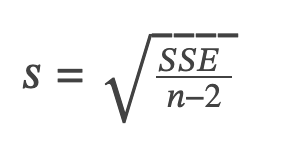
Degrees of freedom: n - 2
Examples

 Knowt
Knowt
