
Bio Chapter 2 - The Cell
“But the plans of the Lord stand firm forever, the purposes of his heart through all generations” - Psalm 33:11
Lesson 2.1 - Atoms + Other Building Blocks of Life
Electron - a negative charge on the outside of an atom
Neutron - no charge and insideof the atom
Proton - a positive charge inside the atom and bonded to neutrons
Compound - consisting of two or more simple parts or individuals in combination
What is the compound H2SO4 made of - two hydrogen atoms, one sulfur atom, and four oxygen atoms
Why Does Ice Float - Ice floats because when it freezes, it expands and binds to other water molecules doing the same. These stick together and work to form ice, which is less dense than water. This is important to the organisms underneath because they are protected from the harsh elements by this ice and therefore can live through the winter.
Adhesion - The act of water sticking to other surfaces
Cohesion - The act of water sticking to itself
Capillary Action - The act of water using both cohesion and adhesion to supply water to the leaves of a plant
Surface Tension - Tension created by tension inflicted upon the bonds of water molecules
Differences - Water sticking to itself versus other surfaces, water using this to perform an action, and the use of cohesion in surface tension
Lesson 2.2 - Water Molecule
Polar Covalent Bond - These are formed when there is an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms
Covalent Bond - These are formed when there is an equal sharing of electrons between atoms
Why is Water a Polar Molecule - Water is polar because the hydrogen and oxygen atoms share electrons. However, the oxygen atom has more protons in its nucleus (which are positive) and therefore attracts more electrons (making it negative), although the hydrogen keeps some (making it positive). These uneven amounts of electrons create poles, which makes water polar.
How Hydrogen Bonds Form with Water Molecules - Since oxygen atoms have slightly negative charges and hydrogen atoms have slightly positive charges, the two can attach to one another. This is essentially the bonding of two water molecules
Solution - A type of homogenous mixture in which the particles of one or more substances (the solute) are distributed uniformly throughout another substance (the solvent). The particles are too small to be seen by the naked eye, unlike in a suspension, where the particles don’t settle are big enough for the naked eye to see
Solute - A substance that is dissolved in a solution - Sugar in Tea
Solvent - A liquid that is able to dissolve a solid - Acetone
Acid - A compound that forms H+ ions in a solution. pH scale range 0-6, weak 4-6, strong 0-3
Base - A compound that produces hydroxide ions in a solution. pH scale range 8-14, weak 8-10, strong 11-14
Neutral - A compound with a pH of 7, or perfectly neutral, without leaning acidic or basic
Homeostasis - The tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements
Buffer - Weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH. These help the body to remain in homeostasis
Lesson 2.3 - Carbon Compounds
Carbohydrates - Compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Used as a main source of energy in living things
Plants use it for structural purposes
Breakdown of carbs (sugars) provide immediate energy to cells
Store extra sugar as complex carbs called starches
Monosaccharides - anything that ends in “ose”, and includes sugars and starches
Lipid - Compounds made from carbon and hydrogen atoms
Not soluble in water
Fats, oils, waxes, and steroids
Used to store energy and create waterproof cell membranes
Formed when glycerol molecules are combined with fatty acids
Fatty acids chains are formed when a carbon molecule is joined with two carbon molecules
A satured fatty acid is formed when a chain is joined with a single bond
An unsatured fatty acid is formed when a chain is joined with another chain or if there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond
Protein - Macromolcues that contain oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur
Made of amino acid monomers
Amino acids have an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other
There are 20 different amino groups
Instructions for amino acids to form are found in DNA
Control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes
Used to form bones and muscles
Used to transport other substances and fight diseases
There are four steps to forming proteins
1: Amino acids form a chain
2: Amino acids are twisted to form a helix or a pleated sheet
3: The chain is then folded into a 3D object
4: If there is more than 1 object, the two can join and create another object
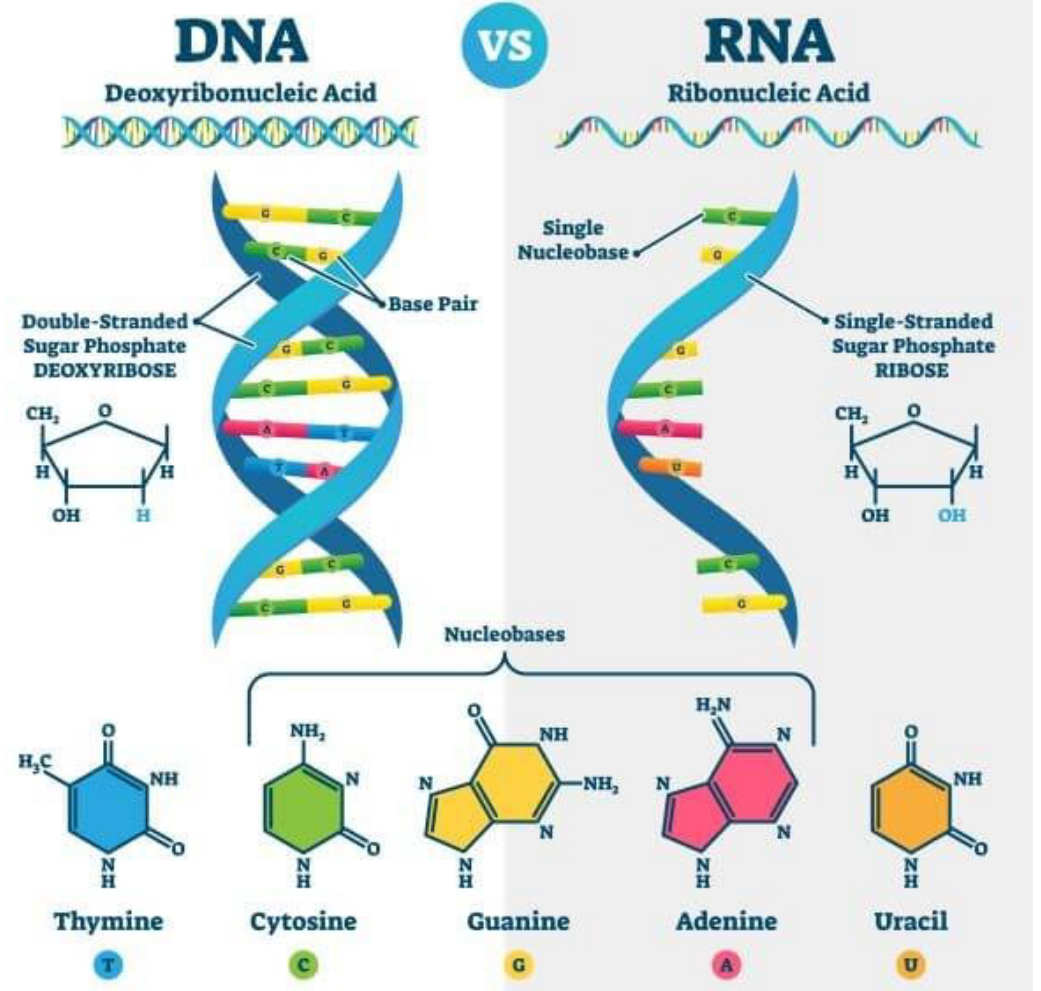
Nucleic Acid - Macromoclues that contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphours
Made of nucleotide monomers
Nucleotides contain/are made of:
A 5-carbon sugar
A phosphate group
A nitrogen base
When multiple nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds, they create nucleic acids
Used to store and transmit genetic info to cells
RNA - Single helix & DNA - double helix
Lesson 2.4 - Chemical Reactions + Enzymes
Chemical Reaction - A process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals
During a Reaction Energy Can Be Released In - The form of energy
Energy - Cannot be created or destroyed, but is transferred each time a chemical reaction is carried out. It is also needed in each and every chemical reaction, as it is used to activate it
Plants - Get their energy from the sun (this is their activation energy)
Humans - Get their energy from eating plants and animals (this is their activation energy)
Endergonic - Energy absorbed in a reaction
Exergonic - Energy released in a reaction
What Happens to ___ During a Chemical Reaction:
Atoms - They are rearranged
Compounds - They are also rearranged to fit the new set of chemicals
Product and Reactants of 2H + O > H2O:
Products - The element H2O
Reactants - 2 Hydrogen molecules, 1 oxygen molecule
Activation Energy - The energy that is needed to get a reaction started
Catalyst - A substrate that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. These work by lowering the nesscary amount of activation energy
Enzymes: “Ase”
Proteins that act as biological catalysts
Speed up chemical reactions in cells
Lowering the activation energy
Are very specific and only responsible for carrying out one reaction
Lactase - Lactose
Inhibitor - Something that prevents the action of an enzyme by blocking the active site so a substrate cannot enter as easily
Temperature and Enzymes - If enzymes are put in conditions that are too hot or cold for them to work easily, it will take them longer to produce new molecules and do their jobs properly
Hotter Temp - Molecules move too fast
Lower Temp - Molecules move too slow
Denaturation - 3D proteins losing their shape and size
2 Things Enzymes Do During Chemical Reactions:
Enzymes lower activation energy
Enzymes speed up a chemical reaction
The Steps an Enzyme Undergoes During A Chemical Reaction -
Substrates bind to active site on enzyme
Bond in substrate break/new bonds are created
Products are formed and released
Enzyme is free to be used again
Enzymes Play Essential Roles In:
Regulating cell pathways
Making materials cells need
Releasing energy
Transferring information
“But as for you, be strong and do not give up, for your work will be rewarded” - 2 Chronicles 15:7
Bio Chapter 2 - The Cell

“But the plans of the Lord stand firm forever, the purposes of his heart through all generations” - Psalm 33:11
Lesson 2.1 - Atoms + Other Building Blocks of Life
Electron - a negative charge on the outside of an atom
Neutron - no charge and insideof the atom
Proton - a positive charge inside the atom and bonded to neutrons
Compound - consisting of two or more simple parts or individuals in combination
What is the compound H2SO4 made of - two hydrogen atoms, one sulfur atom, and four oxygen atoms
Why Does Ice Float - Ice floats because when it freezes, it expands and binds to other water molecules doing the same. These stick together and work to form ice, which is less dense than water. This is important to the organisms underneath because they are protected from the harsh elements by this ice and therefore can live through the winter.
Adhesion - The act of water sticking to other surfaces
Cohesion - The act of water sticking to itself
Capillary Action - The act of water using both cohesion and adhesion to supply water to the leaves of a plant
Surface Tension - Tension created by tension inflicted upon the bonds of water molecules
Differences - Water sticking to itself versus other surfaces, water using this to perform an action, and the use of cohesion in surface tension
Lesson 2.2 - Water Molecule
Polar Covalent Bond - These are formed when there is an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms
Covalent Bond - These are formed when there is an equal sharing of electrons between atoms
Why is Water a Polar Molecule - Water is polar because the hydrogen and oxygen atoms share electrons. However, the oxygen atom has more protons in its nucleus (which are positive) and therefore attracts more electrons (making it negative), although the hydrogen keeps some (making it positive). These uneven amounts of electrons create poles, which makes water polar.
How Hydrogen Bonds Form with Water Molecules - Since oxygen atoms have slightly negative charges and hydrogen atoms have slightly positive charges, the two can attach to one another. This is essentially the bonding of two water molecules
Solution - A type of homogenous mixture in which the particles of one or more substances (the solute) are distributed uniformly throughout another substance (the solvent). The particles are too small to be seen by the naked eye, unlike in a suspension, where the particles don’t settle are big enough for the naked eye to see
Solute - A substance that is dissolved in a solution - Sugar in Tea
Solvent - A liquid that is able to dissolve a solid - Acetone
Acid - A compound that forms H+ ions in a solution. pH scale range 0-6, weak 4-6, strong 0-3
Base - A compound that produces hydroxide ions in a solution. pH scale range 8-14, weak 8-10, strong 11-14
Neutral - A compound with a pH of 7, or perfectly neutral, without leaning acidic or basic
Homeostasis - The tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements
Buffer - Weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH. These help the body to remain in homeostasis
Lesson 2.3 - Carbon Compounds
Carbohydrates - Compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Used as a main source of energy in living things
Plants use it for structural purposes
Breakdown of carbs (sugars) provide immediate energy to cells
Store extra sugar as complex carbs called starches
Monosaccharides - anything that ends in “ose”, and includes sugars and starches
Lipid - Compounds made from carbon and hydrogen atoms
Not soluble in water
Fats, oils, waxes, and steroids
Used to store energy and create waterproof cell membranes
Formed when glycerol molecules are combined with fatty acids
Fatty acids chains are formed when a carbon molecule is joined with two carbon molecules
A satured fatty acid is formed when a chain is joined with a single bond
An unsatured fatty acid is formed when a chain is joined with another chain or if there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond
Protein - Macromolcues that contain oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur
Made of amino acid monomers
Amino acids have an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other
There are 20 different amino groups
Instructions for amino acids to form are found in DNA
Control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes
Used to form bones and muscles
Used to transport other substances and fight diseases
There are four steps to forming proteins
1: Amino acids form a chain
2: Amino acids are twisted to form a helix or a pleated sheet
3: The chain is then folded into a 3D object
4: If there is more than 1 object, the two can join and create another object
Nucleic Acid - Macromoclues that contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphours
Made of nucleotide monomers
Nucleotides contain/are made of:
A 5-carbon sugar
A phosphate group
A nitrogen base
When multiple nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds, they create nucleic acids
Used to store and transmit genetic info to cells
RNA - Single helix & DNA - double helix

Lesson 2.4 - Chemical Reactions + Enzymes
Chemical Reaction - A process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals
During a Reaction Energy Can Be Released In - The form of energy
Energy - Cannot be created or destroyed, but is transferred each time a chemical reaction is carried out. It is also needed in each and every chemical reaction, as it is used to activate it
Plants - Get their energy from the sun (this is their activation energy)
Humans - Get their energy from eating plants and animals (this is their activation energy)
Endergonic - Energy absorbed in a reaction
Exergonic - Energy released in a reaction
What Happens to ___ During a Chemical Reaction:
Atoms - They are rearranged
Compounds - They are also rearranged to fit the new set of chemicals
Product and Reactants of 2H + O > H2O:
Products - The element H2O
Reactants - 2 Hydrogen molecules, 1 oxygen molecule
Activation Energy - The energy that is needed to get a reaction started
Catalyst - A substrate that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. These work by lowering the nesscary amount of activation energy
Enzymes: “Ase”
Proteins that act as biological catalysts
Speed up chemical reactions in cells
Lowering the activation energy
Are very specific and only responsible for carrying out one reaction
Lactase - Lactose
Inhibitor - Something that prevents the action of an enzyme by blocking the active site so a substrate cannot enter as easily
Temperature and Enzymes - If enzymes are put in conditions that are too hot or cold for them to work easily, it will take them longer to produce new molecules and do their jobs properly
Hotter Temp - Molecules move too fast
Lower Temp - Molecules move too slow
Denaturation - 3D proteins losing their shape and size
2 Things Enzymes Do During Chemical Reactions:
Enzymes lower activation energy
Enzymes speed up a chemical reaction
The Steps an Enzyme Undergoes During A Chemical Reaction -
Substrates bind to active site on enzyme
Bond in substrate break/new bonds are created
Products are formed and released
Enzyme is free to be used again
Enzymes Play Essential Roles In:
Regulating cell pathways
Making materials cells need
Releasing energy
Transferring information
“But as for you, be strong and do not give up, for your work will be rewarded” - 2 Chronicles 15:7
 Knowt
Knowt
