
Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
LIGHT INTENSITY
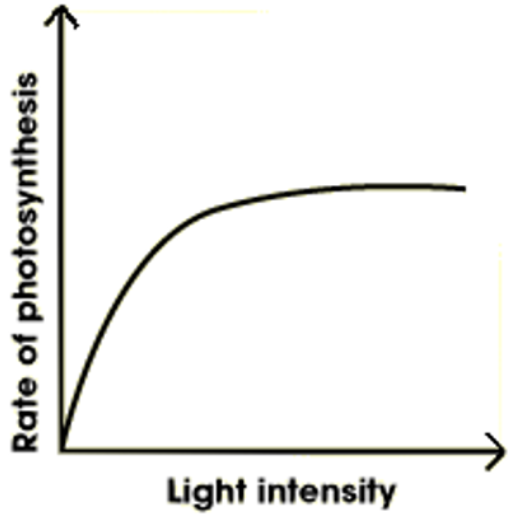
The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by changes in light intensity when the temperature and Carbon Dioxide concentration are both constant. As light intensity increases, so does photosynthesis.This is due to the increase in energy provided to the plant. Consequently, photosynthesis' light-dependent stage can take place. This results in more ATP and reduced NADP being produced for the Calvin Cycle, which allows the Calvin Cycle to proceed at a faster rate. According to the graph below, photosynthesis is thought to be limited by light intensity at this stage. The relationship above will eventually deteriorate and the rate of photosynthesis will plateau if light intensity keeps rising. During this point, photosynthesis is not limited by light intensity (another factor, like temperature or Carbon Dioxide concentration, would be limiting the rate of photosynthesis).
LIGHT WAVELENGTH
Light is necessary for the light dependent stage. This is so that they can energise electrons, which causes them to get excited. Also, it is necessary for the photolysis of water, which involves splitting water molecules. A reduced amount of ATP and NADPH would be created for the Calvin Cycle if light levels were low or absent altogether. But, only light wavelengths are absorbed. Photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophyll, absorb light. Green light is reflected rather than absorbed.
TEMPERATURE
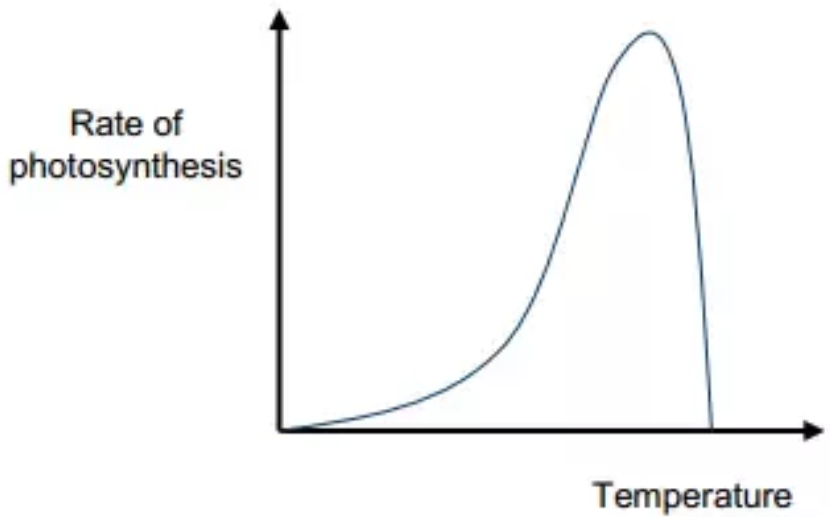
The rate of photosynthesis increases as the temperature rises. However, because the reaction is managed by enzymes, the trend only lasts until a particular temperature at which the enzymes begin to denature, which causes a decrease in the rate of photosynthesis. Temperature has a significant impact on the rate of most metabolic reactions. Since the light independent reactions in photosynthesis are fueled by light energy rather than the kinetic energy of the reacting molecules, temperature has no impact on these processes.
CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION
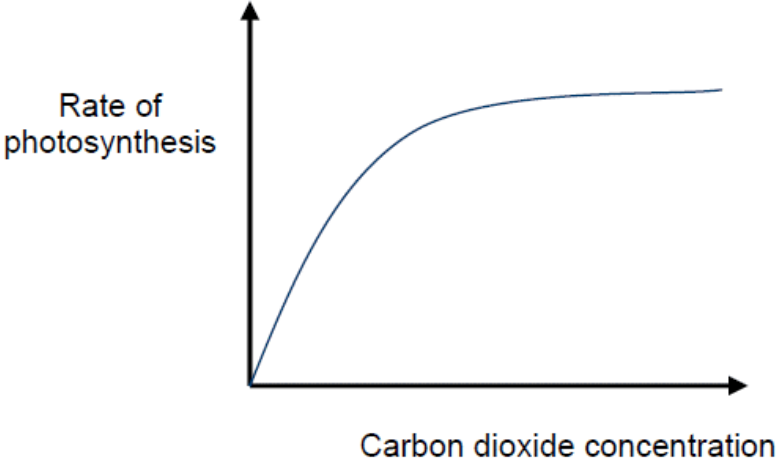
As the level of carbon dioxide rises, the rate of photosynthesis increases. In order for photosynthesis to take place, Carbon dioxide must be a reactant. It is also necessary when carbon dioxide and ribulose biphosphate are mixed during the light-independent stage of photosynthesis. This indicates that the more Carbon Dioxide present, the faster the light-independent stage of the Calvin Cycle can occur, leading to a greater total rate of photosynthesis. This trend proceeds until a deficiency in a different factor needed for photosynthesis prevents the rate from rising any further.
Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
LIGHT INTENSITY
The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by changes in light intensity when the temperature and Carbon Dioxide concentration are both constant. As light intensity increases, so does photosynthesis.This is due to the increase in energy provided to the plant. Consequently, photosynthesis' light-dependent stage can take place. This results in more ATP and reduced NADP being produced for the Calvin Cycle, which allows the Calvin Cycle to proceed at a faster rate. According to the graph below, photosynthesis is thought to be limited by light intensity at this stage. The relationship above will eventually deteriorate and the rate of photosynthesis will plateau if light intensity keeps rising. During this point, photosynthesis is not limited by light intensity (another factor, like temperature or Carbon Dioxide concentration, would be limiting the rate of photosynthesis).

LIGHT WAVELENGTH
Light is necessary for the light dependent stage. This is so that they can energise electrons, which causes them to get excited. Also, it is necessary for the photolysis of water, which involves splitting water molecules. A reduced amount of ATP and NADPH would be created for the Calvin Cycle if light levels were low or absent altogether. But, only light wavelengths are absorbed. Photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophyll, absorb light. Green light is reflected rather than absorbed.
TEMPERATURE
The rate of photosynthesis increases as the temperature rises. However, because the reaction is managed by enzymes, the trend only lasts until a particular temperature at which the enzymes begin to denature, which causes a decrease in the rate of photosynthesis. Temperature has a significant impact on the rate of most metabolic reactions. Since the light independent reactions in photosynthesis are fueled by light energy rather than the kinetic energy of the reacting molecules, temperature has no impact on these processes.

CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION
As the level of carbon dioxide rises, the rate of photosynthesis increases. In order for photosynthesis to take place, Carbon dioxide must be a reactant. It is also necessary when carbon dioxide and ribulose biphosphate are mixed during the light-independent stage of photosynthesis. This indicates that the more Carbon Dioxide present, the faster the light-independent stage of the Calvin Cycle can occur, leading to a greater total rate of photosynthesis. This trend proceeds until a deficiency in a different factor needed for photosynthesis prevents the rate from rising any further.

 Knowt
Knowt
