
2.1: Density Curves, Normal Distributions, and Segmented Bar Charts
Normal Curves
Some data can be graphed on a relatively smooth curve
Detail may be lost about some specific data, but this is outweighed by the simplicity the curve allows us to analyze with
Mathematical model: an idealized description of a situation
When a curve is used to approximate a distribution, the scale is adjusted to make it into a density curve
Density curve: a distribution which is always above the x-axis and always has an area of 1
The area in any part of the curve is equal to the percent of data present in that part of the curve
Normal curve: a distribution which is symmetric, bell-shaped, and has a single peak
Defined by their means (μ) and standard deviations (σ)

Normal curves may be analyzed further using z-scores, which can be found and interpreted in relation to probabilities using a z-chart
This chart is provided on the AP exam, along with many relevant formulas
When solving z-score problems, it is always necessary to:
Show work for getting the z-score
Write a probability statement
Give the final probability
Data may be represented as N(μ, σ)
μ: mean
σ: standard deviation
Case Study: Male vs. Female Height
Who is taller relative to their gender: a 76.5-inch-tall woman or a 80-inch-tall man?
Female heights are N(64, 2.5) and male heights are N(69.1, 2.8)
Female: 76.5 inches

That means that this value is 5 standard deviations above the mean
This is where the term “off the charts” comes from → if you reference what 5 standard deviations above the mean would look like on the normal curve above in the notes, 5 standard deviations to either side is virtually unheard of and statistically very rare
Male: 80 inches
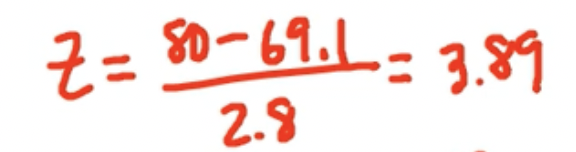
The height of an 80-inch-tall man is 3.89 standard deviations above the mean
This means that statistically, the woman is taller proportionate to her gender than the man is proportionate to his.
Segmented Bar Charts
Segmented bar chart: a display of categorical data showing such data as a percentage of the whole
Like a pie chart in bar form
Mosaic plot: segmented bar charts for comparing groups where the widths of the bars are proportional to the size of the groups
2.1: Density Curves, Normal Distributions, and Segmented Bar Charts
Normal Curves
Some data can be graphed on a relatively smooth curve
Detail may be lost about some specific data, but this is outweighed by the simplicity the curve allows us to analyze with
Mathematical model: an idealized description of a situation
When a curve is used to approximate a distribution, the scale is adjusted to make it into a density curve
Density curve: a distribution which is always above the x-axis and always has an area of 1
The area in any part of the curve is equal to the percent of data present in that part of the curve
Normal curve: a distribution which is symmetric, bell-shaped, and has a single peak
Defined by their means (μ) and standard deviations (σ)

Normal curves may be analyzed further using z-scores, which can be found and interpreted in relation to probabilities using a z-chart
This chart is provided on the AP exam, along with many relevant formulas
When solving z-score problems, it is always necessary to:
Show work for getting the z-score
Write a probability statement
Give the final probability
Data may be represented as N(μ, σ)
μ: mean
σ: standard deviation
Case Study: Male vs. Female Height
Who is taller relative to their gender: a 76.5-inch-tall woman or a 80-inch-tall man?
Female heights are N(64, 2.5) and male heights are N(69.1, 2.8)
Female: 76.5 inches

That means that this value is 5 standard deviations above the mean
This is where the term “off the charts” comes from → if you reference what 5 standard deviations above the mean would look like on the normal curve above in the notes, 5 standard deviations to either side is virtually unheard of and statistically very rare
Male: 80 inches
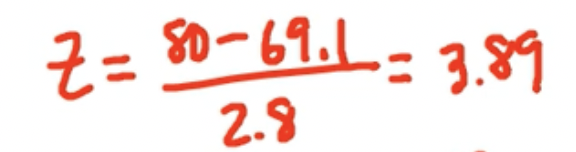
The height of an 80-inch-tall man is 3.89 standard deviations above the mean
This means that statistically, the woman is taller proportionate to her gender than the man is proportionate to his.
Segmented Bar Charts
Segmented bar chart: a display of categorical data showing such data as a percentage of the whole
Like a pie chart in bar form
Mosaic plot: segmented bar charts for comparing groups where the widths of the bars are proportional to the size of the groups
 Knowt
Knowt
