
Examining Stained Cells
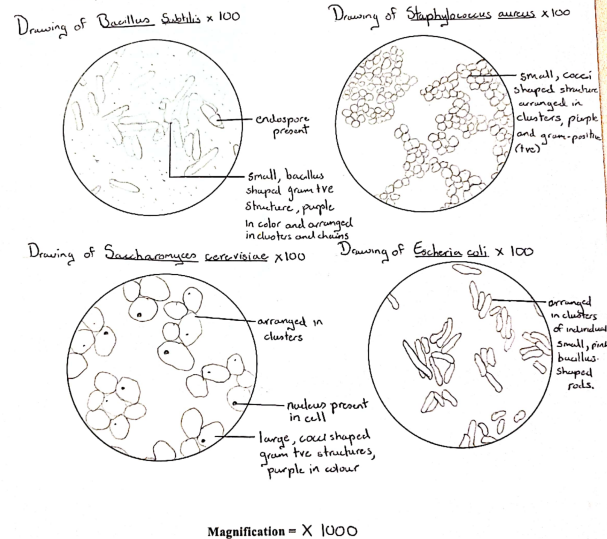
Bacillus subtilis, a small, purple, bacillus-shaped bacterium with a gram +ve structure that arranges in clusters and forms endospores
Staphylococcus aureus, a small, purple, cocci-shaped bacterium, and just like Bacillus subtilis, with a gram +ve structure and a cluster arrangement
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) is, a large, cocci-shaped cell with a gram +ve structure that is purple in colour
Escherichia coli is a small, pink, bacillus-shaped bacterium with a gram -ve structure and
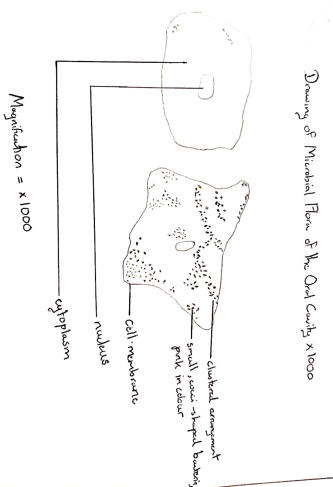
The microbial flora of the oral cavity, pink clustered, cheek cells with a large number of cocci or bacillus shaped bacteria in the cytoplasm.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a nucleus present in its cells, which the bacterial cells lack as they are single-celled prokaryotes meaning their genetic information is bound by a nucleus, unlike the yeast cells which are eukaryotes as their genetic information is bound by a nucleus.
Low power: 4×
High power: 40 or 44×
Oil immersion: 95 or 100×
Heat fixing the slides allows for the specimen to be firmly fixed on the slide so it isn't rinsed off when the liquid stain is applied. It also kills the cells in the smear making them more permeable to the dye that will be used for staining. This is done by first allowing the smear on the slide to dry then passing the entire slide through a Bunsen burner flame two or three times with the smear facing away from the flame.
Basic dye stains microorganisms because the chromophores are positive, giving the material an overall positive charge.
The component of the molecule that gives it colour is known as a chromophore.
Bacteria thrive in the mouth because the teeth provide a firm, sticky surface for them to thrive on.
The mouth is always wet and has a neutral pH, oxygen availability and warm temperature. It also has a steady input of nutrients from sources such as saliva and food.
Plaque contains the same bacteria that is present in saliva.
Bacteria such as Streptococcus sanguinis thrive on plaque, and the bacteria that contribute to plaque production are present in saliva, especially the protein contained in saliva, which creates a dental pellicle.
Examining Stained Cells


Bacillus subtilis, a small, purple, bacillus-shaped bacterium with a gram +ve structure that arranges in clusters and forms endospores
Staphylococcus aureus, a small, purple, cocci-shaped bacterium, and just like Bacillus subtilis, with a gram +ve structure and a cluster arrangement
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) is, a large, cocci-shaped cell with a gram +ve structure that is purple in colour
Escherichia coli is a small, pink, bacillus-shaped bacterium with a gram -ve structure and
The microbial flora of the oral cavity, pink clustered, cheek cells with a large number of cocci or bacillus shaped bacteria in the cytoplasm.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a nucleus present in its cells, which the bacterial cells lack as they are single-celled prokaryotes meaning their genetic information is bound by a nucleus, unlike the yeast cells which are eukaryotes as their genetic information is bound by a nucleus.
Low power: 4×
High power: 40 or 44×
Oil immersion: 95 or 100×
Heat fixing the slides allows for the specimen to be firmly fixed on the slide so it isn't rinsed off when the liquid stain is applied. It also kills the cells in the smear making them more permeable to the dye that will be used for staining. This is done by first allowing the smear on the slide to dry then passing the entire slide through a Bunsen burner flame two or three times with the smear facing away from the flame.
Basic dye stains microorganisms because the chromophores are positive, giving the material an overall positive charge.
The component of the molecule that gives it colour is known as a chromophore.
Bacteria thrive in the mouth because the teeth provide a firm, sticky surface for them to thrive on.
The mouth is always wet and has a neutral pH, oxygen availability and warm temperature. It also has a steady input of nutrients from sources such as saliva and food.
Plaque contains the same bacteria that is present in saliva.
Bacteria such as Streptococcus sanguinis thrive on plaque, and the bacteria that contribute to plaque production are present in saliva, especially the protein contained in saliva, which creates a dental pellicle.
 Knowt
Knowt