
8.1-8.3: Rate of Reactions, (Factors), graphs
Some reactions are fast and some are slow
1- Concrete setting. This is quite slow it will take a couple of days for the concrete ti fully harden
2- The precipitation of silver chloride, when u mix solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride this is a very fast reaction.
3- Rust forming on an old car is a very slow reaction.
What is rate?
Rate is a measure of how fast or slow something is, Rate is a measure of the change that happens in a single unit of time (seconds, minute and hour even a day)
We will look at factors that EFFECT the rate of reactions.
There are three things that can effect the rate of reaction
Concentration (By changing Concentration)
Temperature (By changing Temperature)
Surface Area (By changing Surface area)
Using a Catalyst
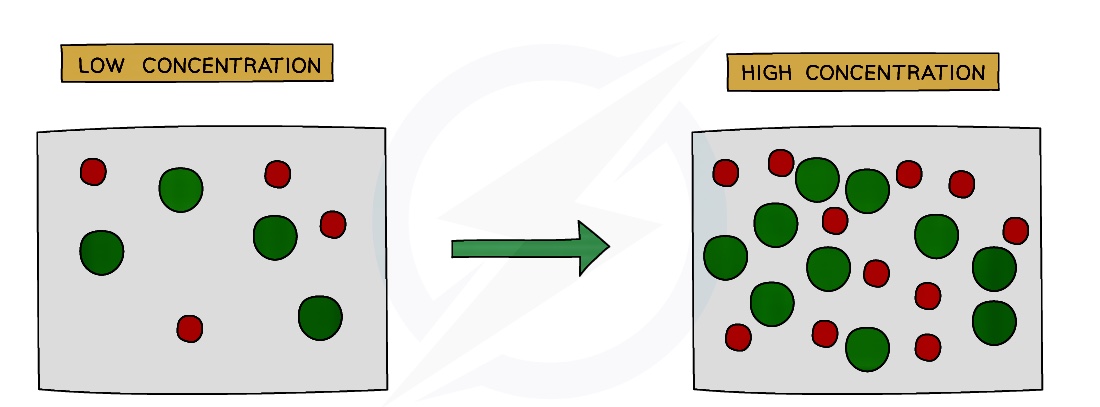
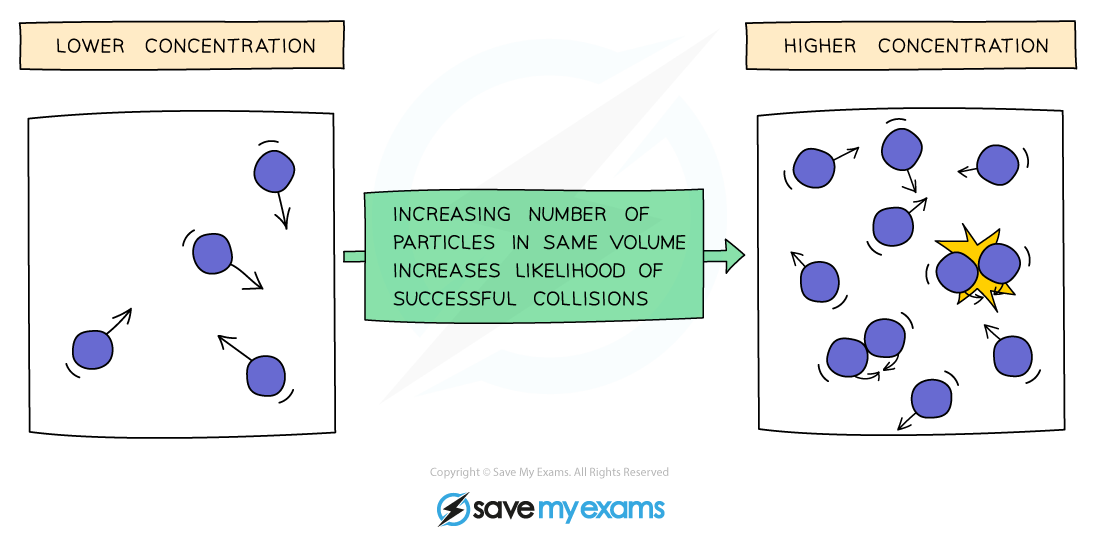
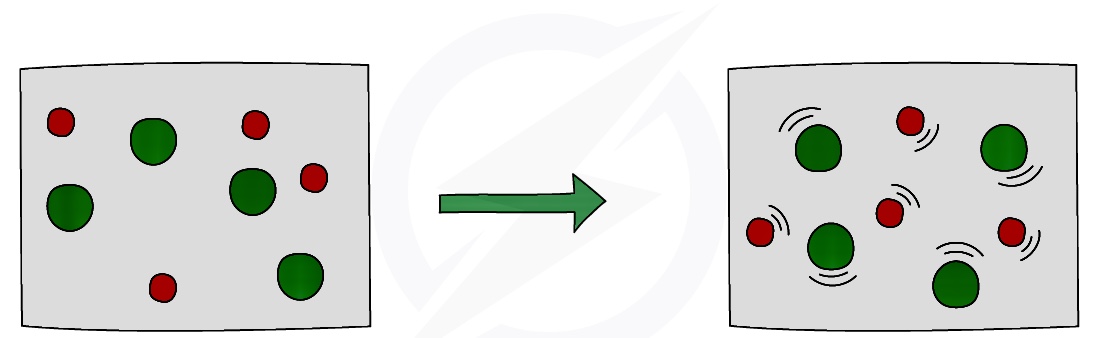
Effect of Concentration
Increasing the concentration of a solution increases the collision rate.
This is because there will be more reactant particles per unit volume, causing more frequent collisions so there are more successful collisions per second, increasing the rate of reaction.

Extended for IGCSE and a better understanding:
Increasing the concentration means there are more particles per cm3, so there is less space between the particles
Since there are more particles then it follows that there are more frequent collisions, increasing colllision rate and so the rate of the reaction increases
Effect of Temperature
Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction
This is because the particles will have more energy and move faster, therefore there will be a greater collision rate
Also, a higher proportion of particles will have greater than the required activation energy, and therefore have sufficient energy to react, meaning there will be more successful collisions per second, increasing the reaction rate
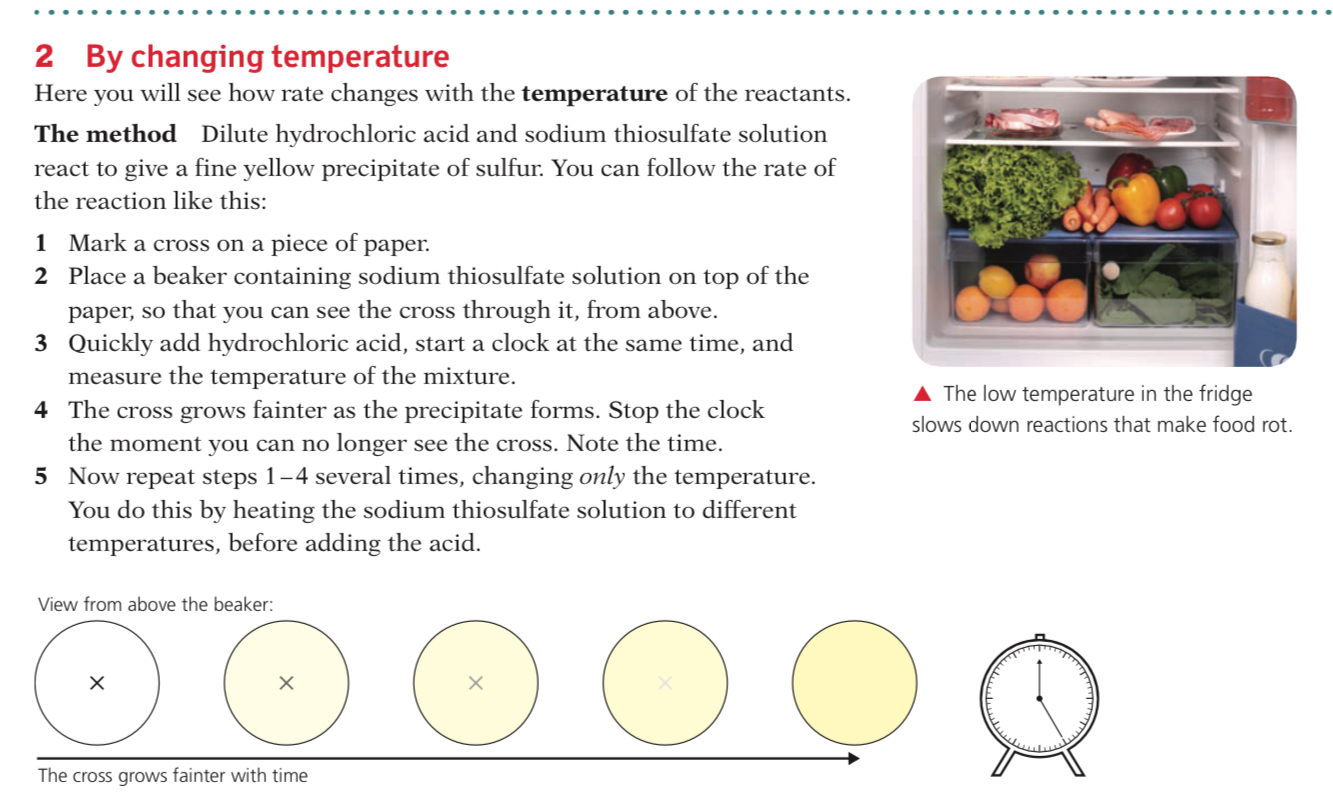
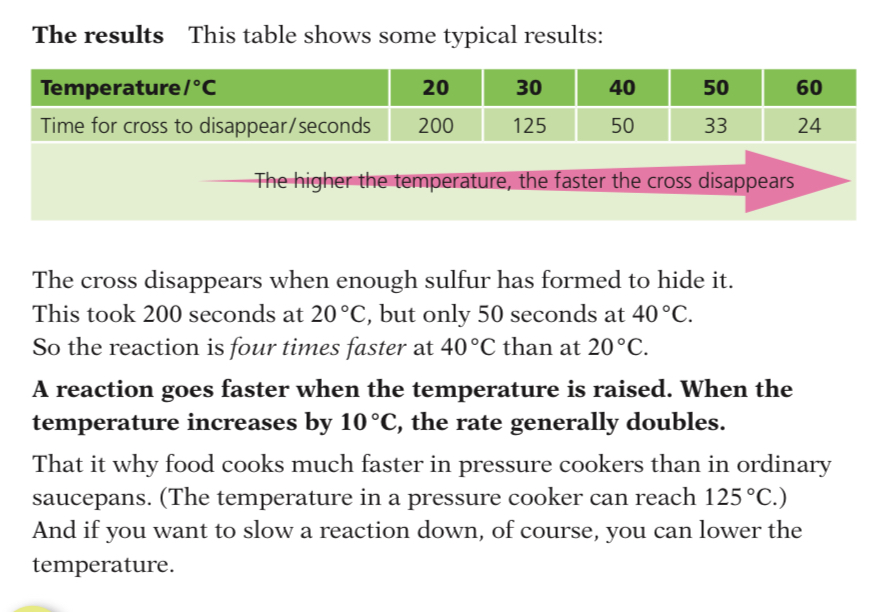
Extended for IGCSE and a better understanding:
Particles need to have sufficient energy to react when they collide
This is called the activation energy
At low temperatures only a small number of particles will have the required activation energy so the reaction will be slow
At higher temperatures the particles have more kinetic energy so they move faster and with more energy
The collisions are therefore more energetic, and there are then a greater number of particles with sufficient energy to react, so the rate of reaction increases
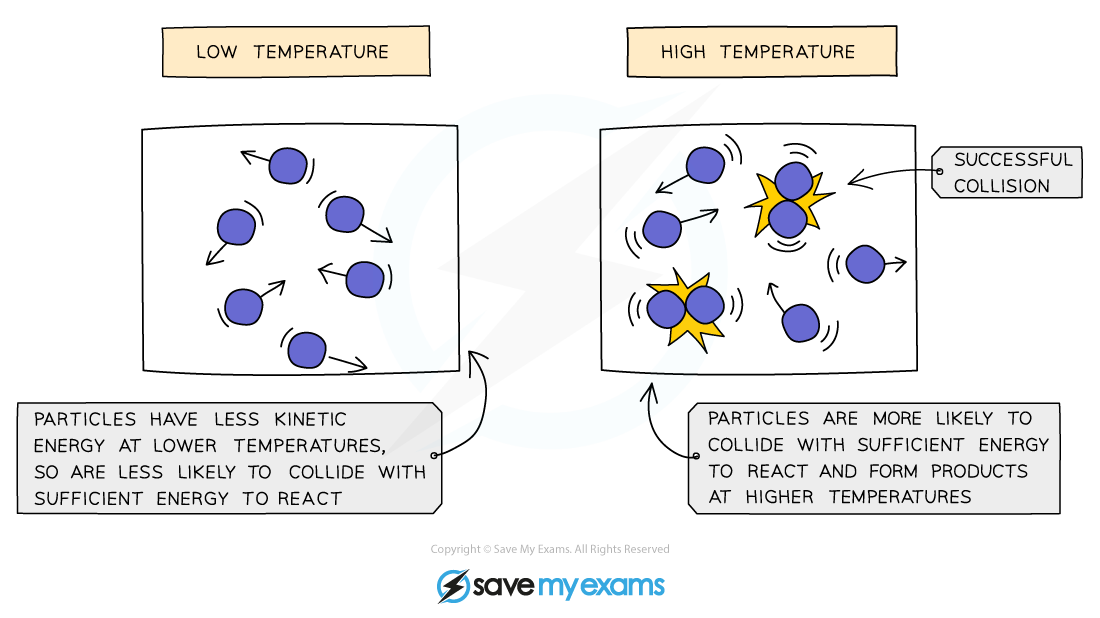
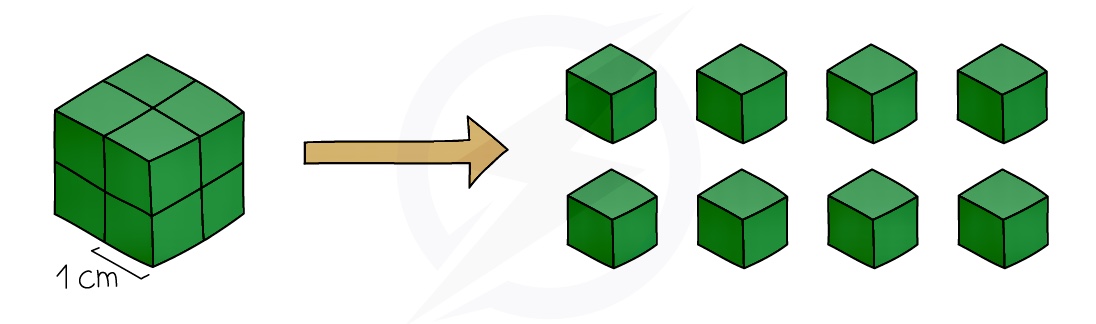
Effect of Surface area
Increasing the surface area of a solid increases the collision rate
This is because more of the solid particles will be exposed to the other reactant so there will be more frequent collisions and therefore more successful collisions per second, increasing the rate of reaction


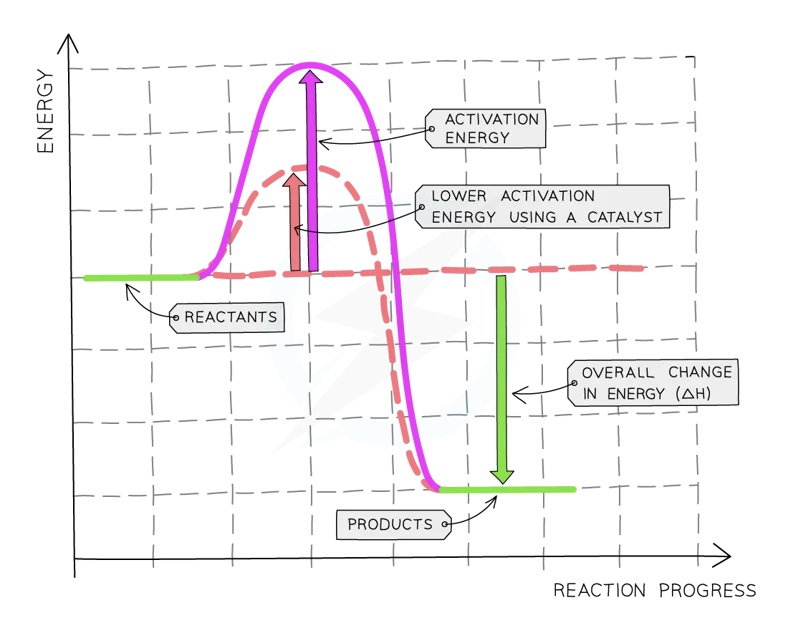
Using a Catalyst
Catalysts (including enzymes) create alternative reaction pathways which have a lower activation energy
This means that more collisions will have sufficient energy to be successful
When a catalyst is used, the rate of reaction will increase
Explosive combustion
As you’ve seen you can increase the rate of reaction by increasing the concentration, temperature and the surface area of solid reactant.
In some situation an increase in any of these can lead to a dangerously fast reaction. you can get an Explosion .
Explosive combustion occurs when there are many fine particles in the air
Many industrial processes such as metal working, coal mining or flour milling produce very fine and tiny particles
These particles have a very large surface area and are combustible in air
Even a small spark may cause them to ignite and since the surface area is so large, the rate of reaction can be incredibly fast, hence they are explosive
Methane gas mixed with air in coal mines can also form an explosive mixture
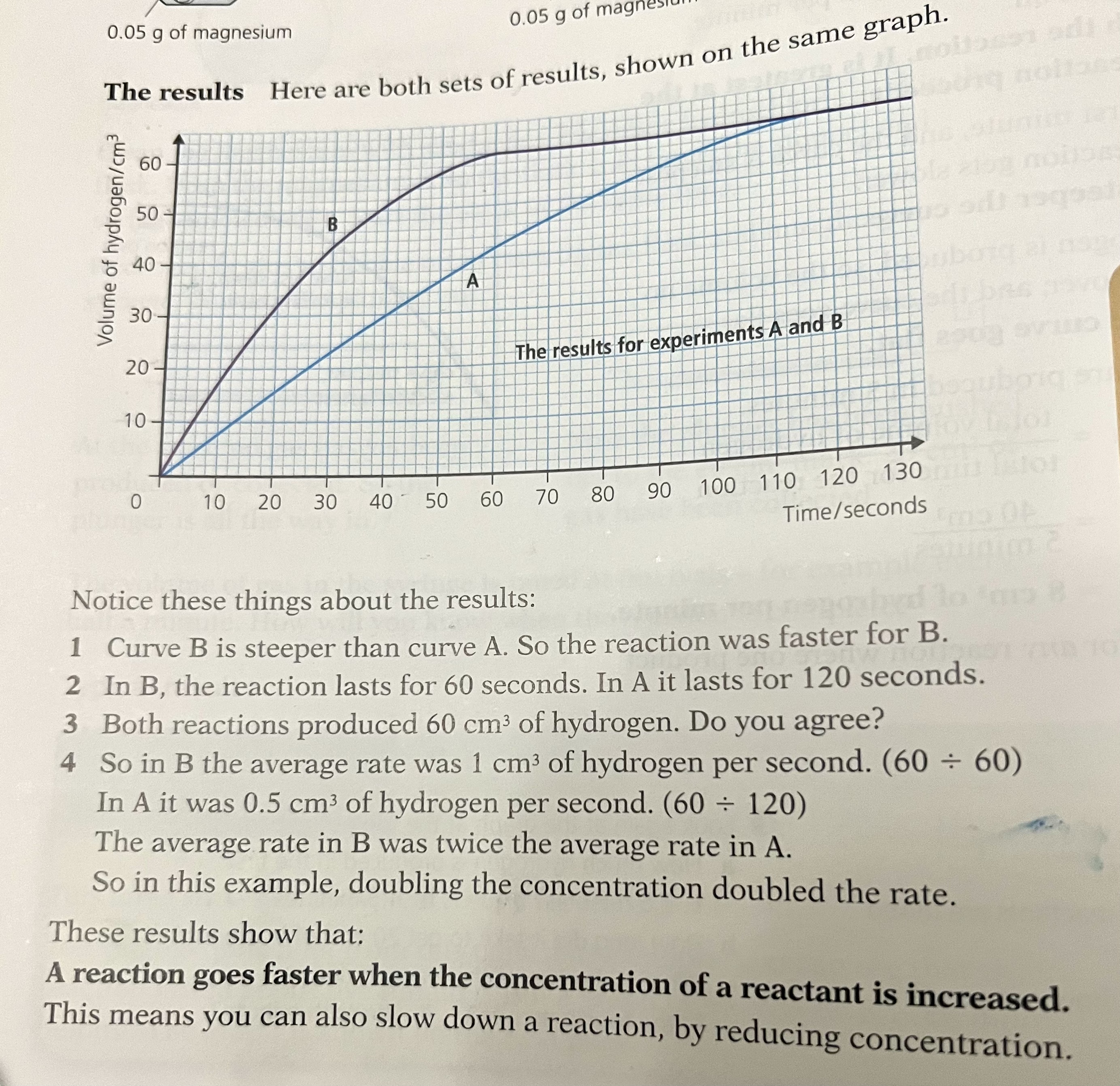
Interpreting Data from Graphs
The shape of the graph shows a lot about the reaction going on.
Concentration
Compared to a reaction with a reactant at a low concentration, the graph line for the same reaction but at a higher concentration has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that with increased concentration of a solution, the rate of reaction will increase
As long as the reactant having its concentration changed is already in excess, the amount of product formed will not change, but will simply be formed faster
Graph showing the effect of the concentration of a solution on the rate of reaction
The ending point the line should always merge with the low concentration and high concentration one
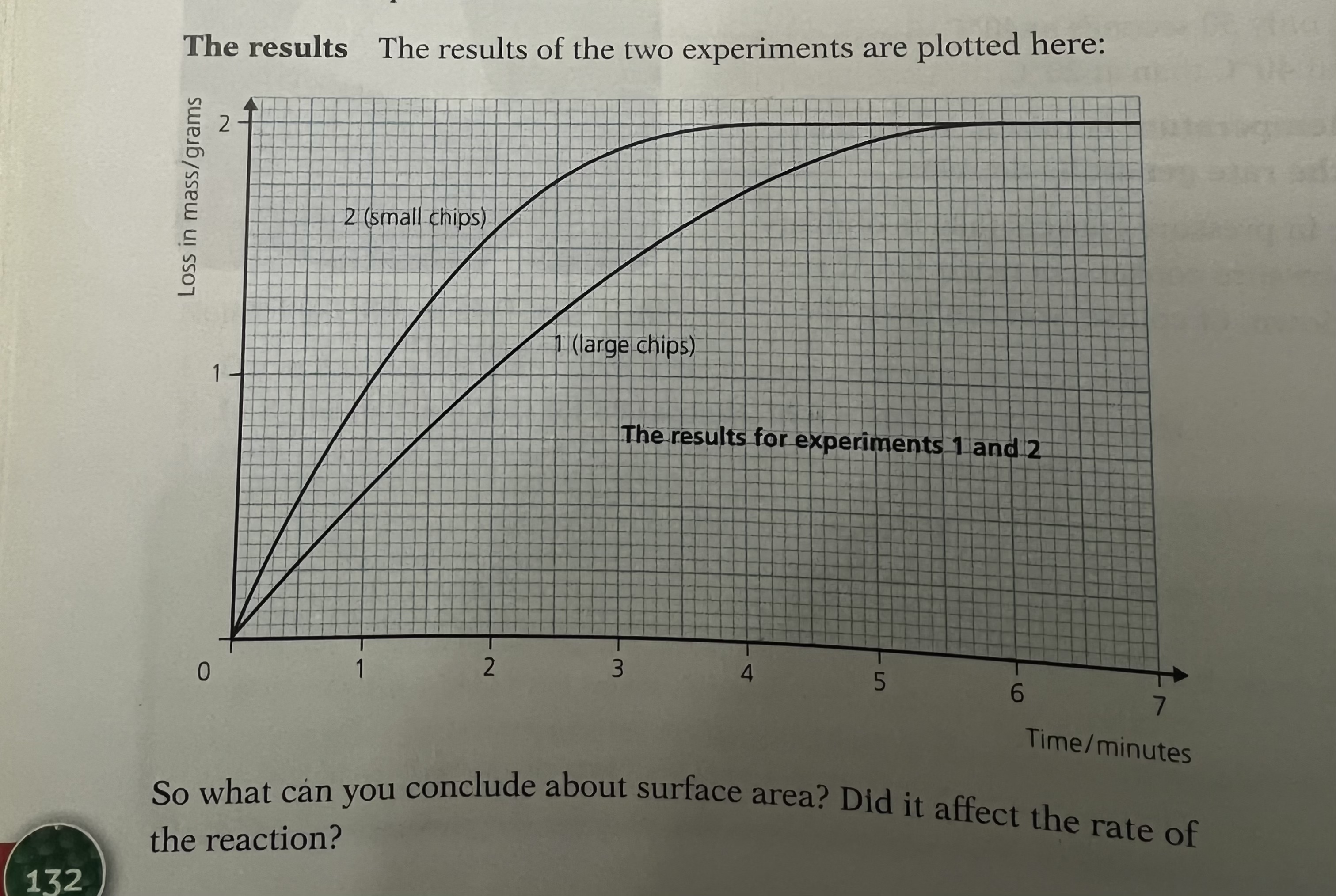
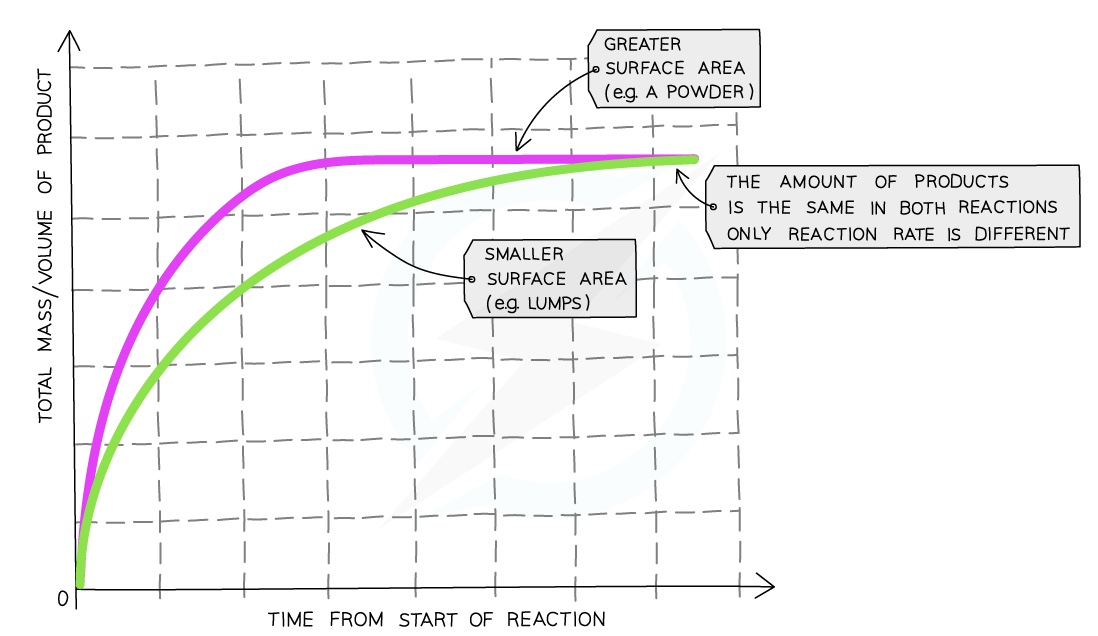
Surface Area
Compared to a reaction with lumps of reactant, the graph line for the same reaction but with powdered reactant has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that with increased surface area of the solid, the rate of reaction will increase
Catalyst
Compared to a reaction without a catalyst, the graph line for the same reaction but with a catalyst has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that when a catalyst is used, the rate of reaction will increase
A catalyst will never change how much product is made
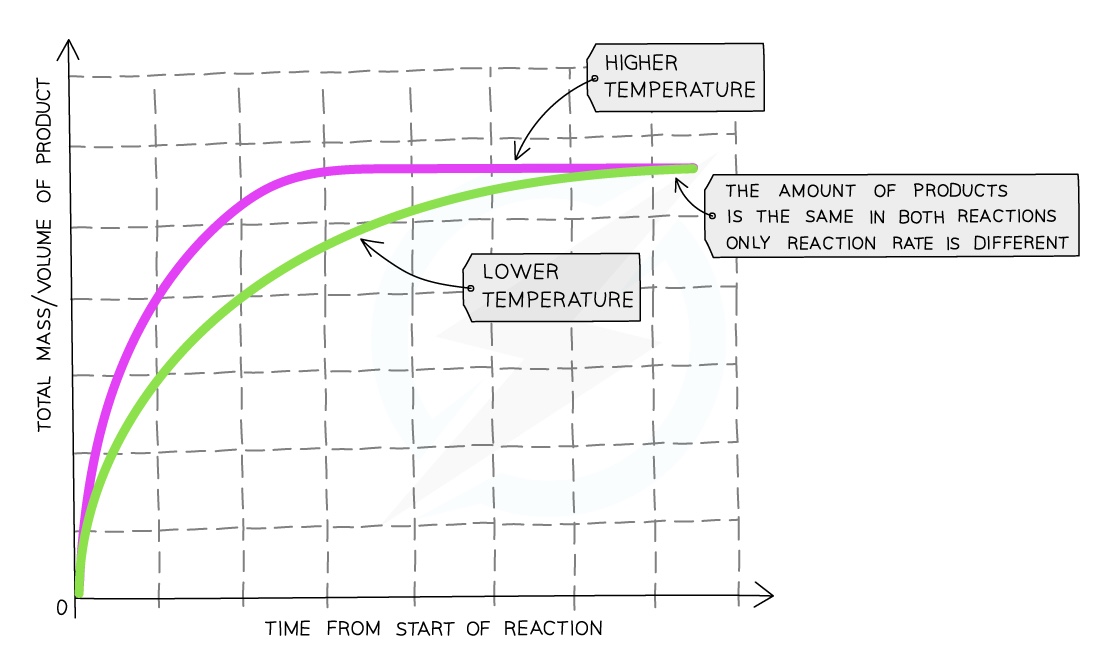
Temperature
Compared to a reaction at a low temperature, the graph line for the same reaction but at a higher temperature has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that with increased temperature, the rate of reaction will increase
Explaining the shape of the graph
The steeper the curve, the faster the rate of the reaction
The curve is steepest initially so the rate is quickest at the beginning of the reaction
As the reaction progresses, the concentration of the reactants decreases, the rate decreases shown by the curve becoming less steep
When one of the reactants is used up, the reaction stops, the rate becomes zero and the curve levels off to a horizontal line
The amount of product formed in a reaction is determined by the limiting reactant:
If the amount of limiting reactant increases, the amount of product formed increases
If the amount of the reactant in excess increases, the amount of product remains the same
8.1-8.3: Rate of Reactions, (Factors), graphs
Some reactions are fast and some are slow
1- Concrete setting. This is quite slow it will take a couple of days for the concrete ti fully harden
2- The precipitation of silver chloride, when u mix solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride this is a very fast reaction.
3- Rust forming on an old car is a very slow reaction.
What is rate?
Rate is a measure of how fast or slow something is, Rate is a measure of the change that happens in a single unit of time (seconds, minute and hour even a day)
We will look at factors that EFFECT the rate of reactions.
There are three things that can effect the rate of reaction
Concentration (By changing Concentration)
Temperature (By changing Temperature)
Surface Area (By changing Surface area)
Using a Catalyst
Effect of Concentration
Increasing the concentration of a solution increases the collision rate.
This is because there will be more reactant particles per unit volume, causing more frequent collisions so there are more successful collisions per second, increasing the rate of reaction.



Extended for IGCSE and a better understanding:
Increasing the concentration means there are more particles per cm3, so there is less space between the particles
Since there are more particles then it follows that there are more frequent collisions, increasing colllision rate and so the rate of the reaction increases

Effect of Temperature
Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction
This is because the particles will have more energy and move faster, therefore there will be a greater collision rate
Also, a higher proportion of particles will have greater than the required activation energy, and therefore have sufficient energy to react, meaning there will be more successful collisions per second, increasing the reaction rate



Extended for IGCSE and a better understanding:
Particles need to have sufficient energy to react when they collide
This is called the activation energy
At low temperatures only a small number of particles will have the required activation energy so the reaction will be slow
At higher temperatures the particles have more kinetic energy so they move faster and with more energy
The collisions are therefore more energetic, and there are then a greater number of particles with sufficient energy to react, so the rate of reaction increases

Effect of Surface area
Increasing the surface area of a solid increases the collision rate
This is because more of the solid particles will be exposed to the other reactant so there will be more frequent collisions and therefore more successful collisions per second, increasing the rate of reaction




Using a Catalyst
Catalysts (including enzymes) create alternative reaction pathways which have a lower activation energy
This means that more collisions will have sufficient energy to be successful
When a catalyst is used, the rate of reaction will increase

Explosive combustion
As you’ve seen you can increase the rate of reaction by increasing the concentration, temperature and the surface area of solid reactant.
In some situation an increase in any of these can lead to a dangerously fast reaction. you can get an Explosion .
Explosive combustion occurs when there are many fine particles in the air
Many industrial processes such as metal working, coal mining or flour milling produce very fine and tiny particles
These particles have a very large surface area and are combustible in air
Even a small spark may cause them to ignite and since the surface area is so large, the rate of reaction can be incredibly fast, hence they are explosive
Methane gas mixed with air in coal mines can also form an explosive mixture
Interpreting Data from Graphs
The shape of the graph shows a lot about the reaction going on.
Concentration
Compared to a reaction with a reactant at a low concentration, the graph line for the same reaction but at a higher concentration has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that with increased concentration of a solution, the rate of reaction will increase
As long as the reactant having its concentration changed is already in excess, the amount of product formed will not change, but will simply be formed faster
Graph showing the effect of the concentration of a solution on the rate of reaction
The ending point the line should always merge with the low concentration and high concentration one
Surface Area
Compared to a reaction with lumps of reactant, the graph line for the same reaction but with powdered reactant has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that with increased surface area of the solid, the rate of reaction will increase

Catalyst
Compared to a reaction without a catalyst, the graph line for the same reaction but with a catalyst has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that when a catalyst is used, the rate of reaction will increase
A catalyst will never change how much product is made
Temperature
Compared to a reaction at a low temperature, the graph line for the same reaction but at a higher temperature has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that with increased temperature, the rate of reaction will increase

Explaining the shape of the graph
The steeper the curve, the faster the rate of the reaction
The curve is steepest initially so the rate is quickest at the beginning of the reaction
As the reaction progresses, the concentration of the reactants decreases, the rate decreases shown by the curve becoming less steep
When one of the reactants is used up, the reaction stops, the rate becomes zero and the curve levels off to a horizontal line
The amount of product formed in a reaction is determined by the limiting reactant:
If the amount of limiting reactant increases, the amount of product formed increases
If the amount of the reactant in excess increases, the amount of product remains the same
 Knowt
Knowt
