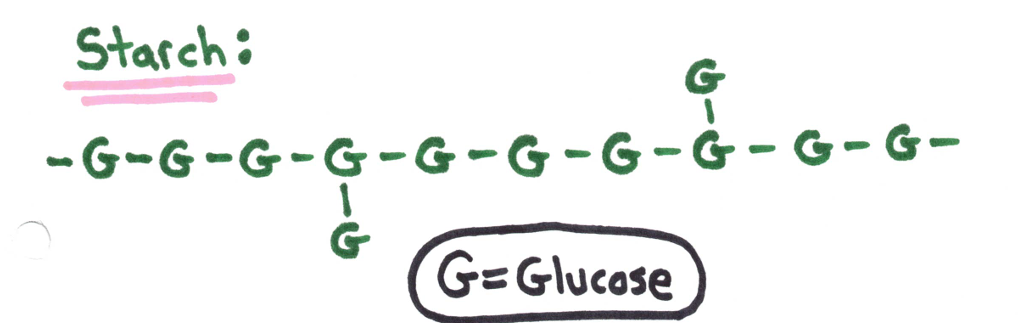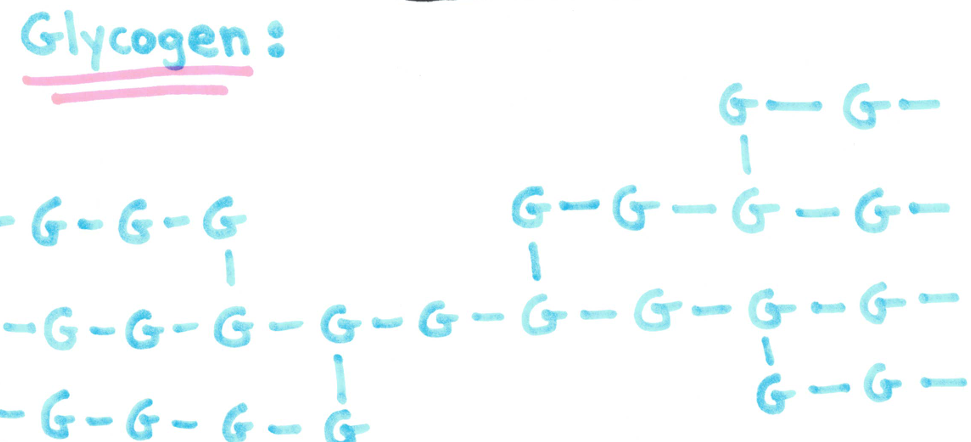The Biochemistry of Life: An Overview
The 4 groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Organic = contains carbon
Examples of the different compounds:
Carbohydrates (sugars, starch)
Examples: glycogen, starch, various sugars (-ose)
Made up of: monosaccharides (single sugars)
Lipids
Examples: fats, oils, waxes
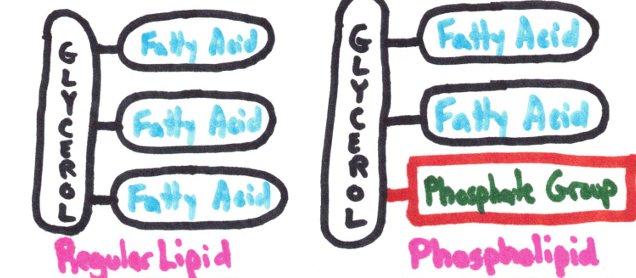
Made up of glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Proteins
Examples: collagen, keratin, enzymes
Made up of: amino acids
Nucleic Acids
Examples: DNA, RNA
Made up of: nucleotides
🍞 Carbohydrates
A carbohydrate is characterized by the presence of a H-C-OH group, in which the ratio of Hydrogen (H) atoms to Oxygen (O) atoms is ~2:1.
Monosaccharide - simple sugars having only one unit. These are the building blocks of a larger carbohydrate.
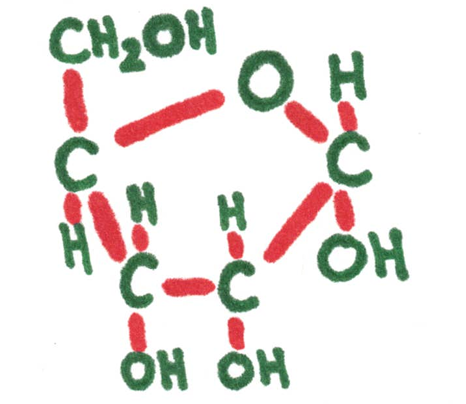
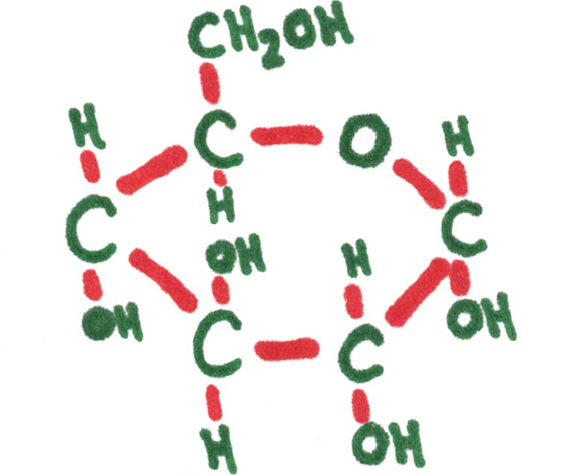
Examples: glucose, ribose, fructose
Ribose 5-carbon (pentose sugar) | Atoms need to connect to this many other ones. | Glucose 5-carbon (hextose) sugar |
|---|---|---|
| H=1 O=2 N=3 C=4 |
|
Disaccharides - 2 monosaccharides joined together
Examples: sucrose
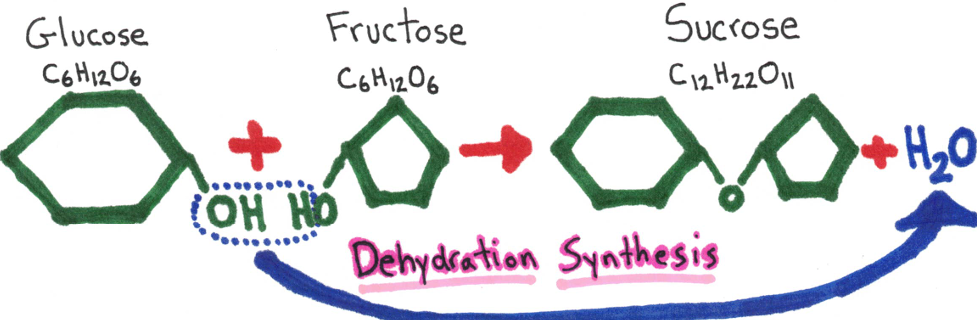
Polysaccharides - many monosaccharide units
❗ Excess sugar in living organisms is stored as polysaccharides.
Plants store sugar in the form of starch. | Animals store sugar in the form of glycogen. |
|---|---|
|
|
Cellulose - found only in plants, this carbohydrate gives strength and rigidity to plants/trees (paper)
🍗Lipids
Lipids (fats/oils) also called triglycerides.
Lipids are water-insoluble substances found in both plants and animals.
Fats are solid at room temperature.
Oils are liquid at room temperature.
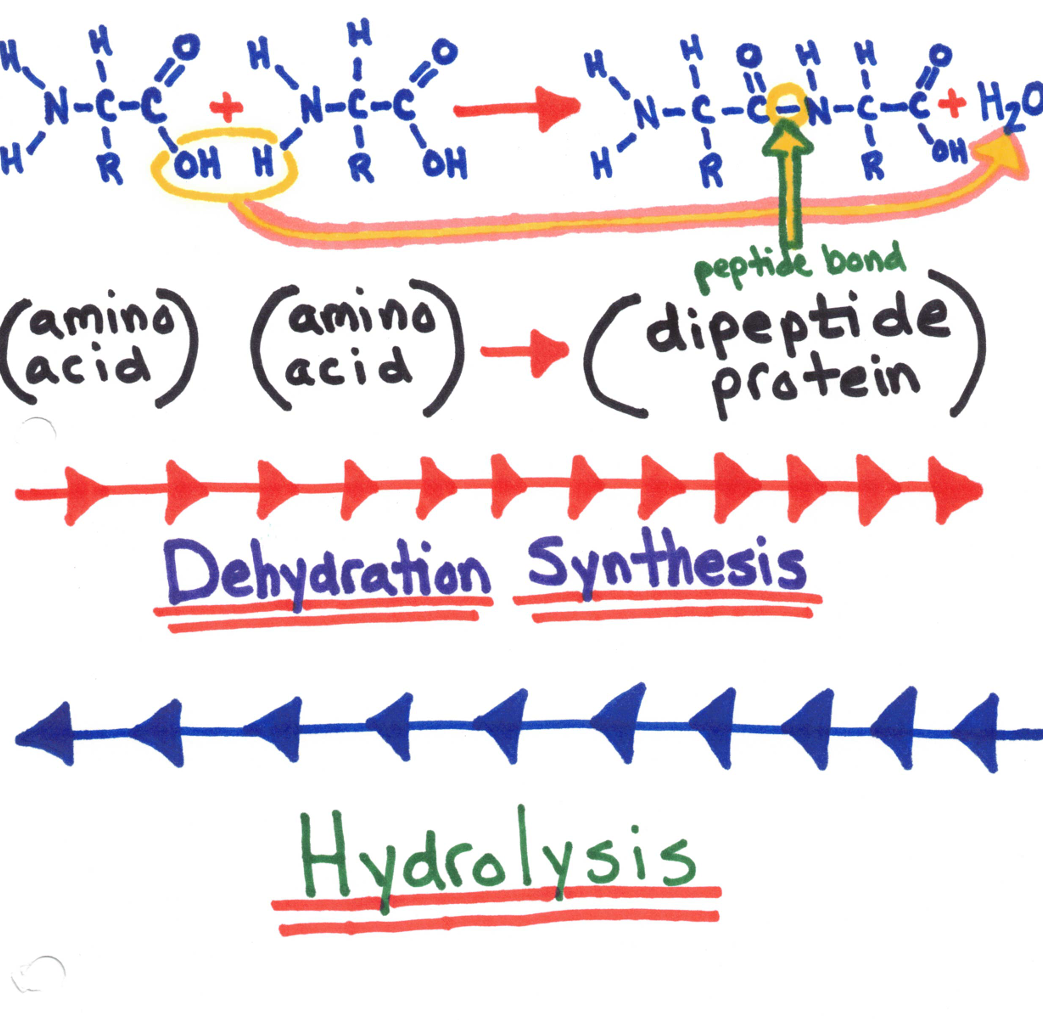
A fat is formed when one mole of glycerol bonds with 3 fatty acids (DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS.
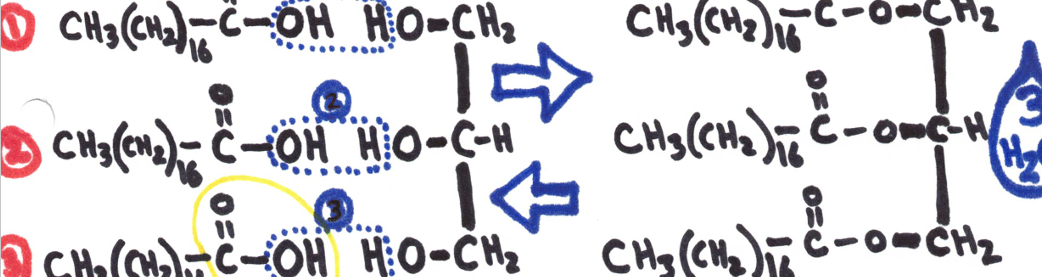
Dehydration Synthesis - 2 hydrogen and an oxygen are removed, this makes allows the substances to combine with each other.
Carboxyl group  Lipids are used as a long-term storage of energy as well as warmth and cushioning.
Lipids are used as a long-term storage of energy as well as warmth and cushioning.
Examples of fatty acids.
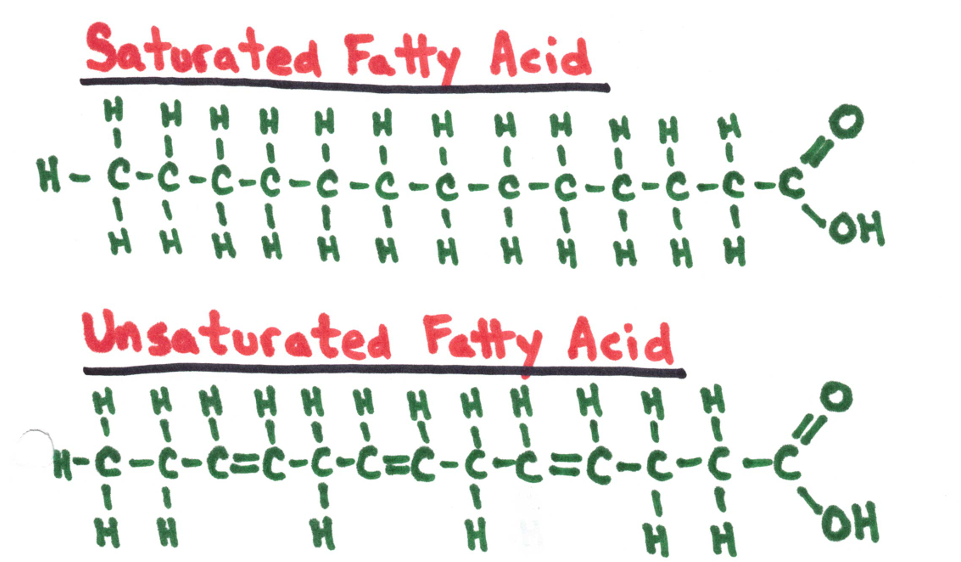 Unsaturated fats are better for you than saturated fats as they can be broken down easier.
Unsaturated fats are better for you than saturated fats as they can be broken down easier.
Major difference between the two types: saturated fats are “saturated” with plenty of hydrogen.
❗ In order for a fat to be considered unsaturated it only needs to include one unsaturated fatty acids, on the other hand for it to be considered saturated it can only include fatty acids.
Other Types of Lipids
Steroids/hormones (testosterone/estrogen)
Soap (fatty acids attached to an inorganic base)
Phospholipids
Proteins
Contain C, H, O, and N (nitrogen) CHON
Made up of amino acids.
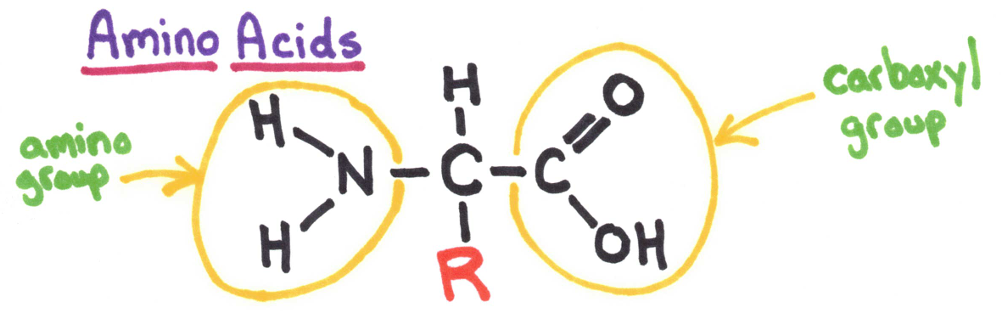 R = radical group. There are 20 different amino acids important to the body. 9 of the 20 are essential amino acids, while the others can be made with these other amino acids.
R = radical group. There are 20 different amino acids important to the body. 9 of the 20 are essential amino acids, while the others can be made with these other amino acids.
Examples of Proteins:
Collagen - makes your skin elastic-like.
Keratin - makes up fingernails, hair, and hooves.
Hemoglobin - carries oxygen CO2 in red blood cells.
Amino Acids
Amino acids join together by forming a covalent bond called a peptide bond.
 Enzymes
Enzymes
Catalyst - a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction.
Enzyme - catalysts found in living organisms
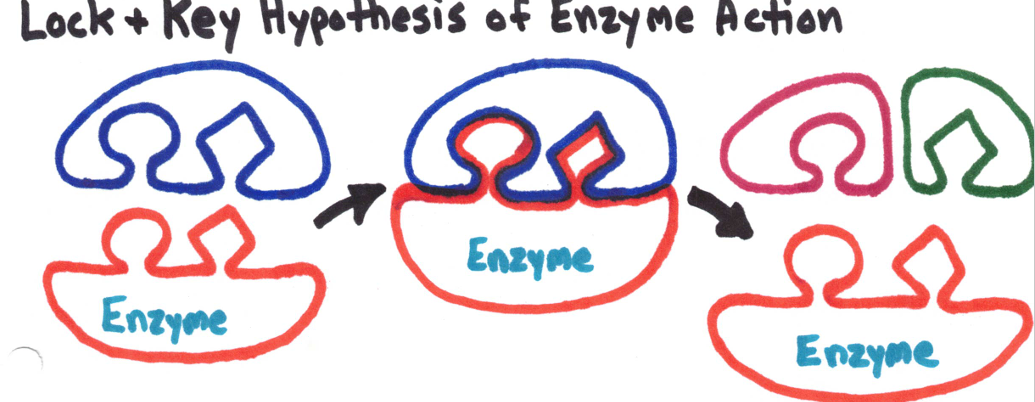 Enzymes break downs substrates down into products without being used up in the process.
Enzymes break downs substrates down into products without being used up in the process.
Enzymes are very specific
Enzymes are proteins
Enzymes work best at optimal temperatures and pH levels.
Heat denatures (destroys) enzymes.
Enzymes regulate life processes.
Nucleic Acids
Contain C, H, O, N, and P (phosphorus)
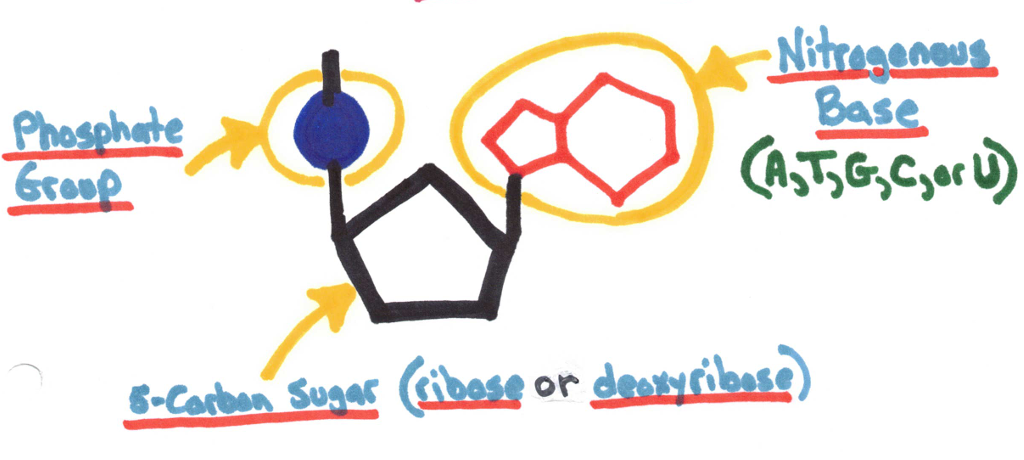
Made up of nucleotides.
Help the body store and retain information and characteristics. We need to continue consuming foods with nucleic acids to provide our bodies with the ability to use this.
 Examples:
Examples:
RNA - ribose sugar and A, U, G, C
DNA - deoxyribose sugar and A, T, G, C
The Biochemistry of Life: An Overview
The 4 groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Organic = contains carbon
Examples of the different compounds:
Carbohydrates (sugars, starch)
Examples: glycogen, starch, various sugars (-ose)
Made up of: monosaccharides (single sugars)
Lipids
Examples: fats, oils, waxes
Made up of glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Proteins
Examples: collagen, keratin, enzymes
Made up of: amino acids
Nucleic Acids
Examples: DNA, RNA
Made up of: nucleotides
🍞 Carbohydrates
A carbohydrate is characterized by the presence of a H-C-OH group, in which the ratio of Hydrogen (H) atoms to Oxygen (O) atoms is ~2:1.
Monosaccharide - simple sugars having only one unit. These are the building blocks of a larger carbohydrate.
Examples: glucose, ribose, fructose
Ribose 5-carbon (pentose sugar) | Atoms need to connect to this many other ones. | Glucose 5-carbon (hextose) sugar |
|---|---|---|
| H=1 O=2 N=3 C=4 |
|
Disaccharides - 2 monosaccharides joined together
Examples: sucrose

Polysaccharides - many monosaccharide units
❗ Excess sugar in living organisms is stored as polysaccharides.
Plants store sugar in the form of starch. | Animals store sugar in the form of glycogen. |
|---|---|
|
|
Cellulose - found only in plants, this carbohydrate gives strength and rigidity to plants/trees (paper)
🍗Lipids
Lipids (fats/oils) also called triglycerides.
Lipids are water-insoluble substances found in both plants and animals.
Fats are solid at room temperature.
Oils are liquid at room temperature.
A fat is formed when one mole of glycerol bonds with 3 fatty acids (DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS.

Dehydration Synthesis - 2 hydrogen and an oxygen are removed, this makes allows the substances to combine with each other.
Carboxyl group  Lipids are used as a long-term storage of energy as well as warmth and cushioning.
Lipids are used as a long-term storage of energy as well as warmth and cushioning.
Examples of fatty acids.
 Unsaturated fats are better for you than saturated fats as they can be broken down easier.
Unsaturated fats are better for you than saturated fats as they can be broken down easier.
Major difference between the two types: saturated fats are “saturated” with plenty of hydrogen.
❗ In order for a fat to be considered unsaturated it only needs to include one unsaturated fatty acids, on the other hand for it to be considered saturated it can only include fatty acids.
Other Types of Lipids
Steroids/hormones (testosterone/estrogen)
Soap (fatty acids attached to an inorganic base)
Phospholipids

Proteins
Contain C, H, O, and N (nitrogen) CHON
Made up of amino acids.
 R = radical group. There are 20 different amino acids important to the body. 9 of the 20 are essential amino acids, while the others can be made with these other amino acids.
R = radical group. There are 20 different amino acids important to the body. 9 of the 20 are essential amino acids, while the others can be made with these other amino acids.
Examples of Proteins:
Collagen - makes your skin elastic-like.
Keratin - makes up fingernails, hair, and hooves.
Hemoglobin - carries oxygen CO2 in red blood cells.
Amino Acids
Amino acids join together by forming a covalent bond called a peptide bond.
 Enzymes
Enzymes
Catalyst - a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction.
Enzyme - catalysts found in living organisms
 Enzymes break downs substrates down into products without being used up in the process.
Enzymes break downs substrates down into products without being used up in the process.
Enzymes are very specific
Enzymes are proteins
Enzymes work best at optimal temperatures and pH levels.
Heat denatures (destroys) enzymes.
Enzymes regulate life processes.
Nucleic Acids
Contain C, H, O, N, and P (phosphorus)
Made up of nucleotides.
Help the body store and retain information and characteristics. We need to continue consuming foods with nucleic acids to provide our bodies with the ability to use this.
 Examples:
Examples:
RNA - ribose sugar and A, U, G, C
DNA - deoxyribose sugar and A, T, G, C
 Knowt
Knowt