
Chapter 20 - Money, price & financial intermediaries
The banking system and the allocation of saving to productive uses
Financial intermediaries: firms that extend credit to borrowers using funds raised from savers.
Money: any asset that can be used in making purchases.
Medium of exchange: asset used in purchasing goods and services.
Barter: direct trade of goods or services for other goods/services.
Unit of account: basic measure of economic value.
Store of value: asset that serves as a means of holding wealth.
M1: sum of currency outstanding and balances held in checking accounts.
M2: all the assets in M1 plus some additional assets that are usable in making payments but at greater cost or inconvenience than currency or checks.
Commercial banks and the creating of money
Bank reserves: cash or similar assets held by commercial banks for the purpose of meeting depositor withdrawals and payments.
100% reserve banking: situation in which banks' reserves equal 100% of their deposits.
Reserve-deposit ratio: bank reserves divided by deposits.
Fractional-reserve banking system: banking system in which bank reserves are less than deposits so that the reserve-deposit ratio is less than 100%.
Central banks, the money supply and the prices
Federal Reserve System (or the Fed): central bank of the United States.
Monetary policy: determination of the nation's money supply.
Open-market purchase: purchase of government bonds from the public by the Fed for the purpose of increasing the supply of bank reserves and the money supply.
Open-market sale: sale by the Fed of government bonds to the public for the purpose of reducing bank reserves and the money supply.
Open-market operations: open-market purchases and open-market sales.
Velocity: measure of the speed at which money changes hands in transactions involving final goods and services, or, equivalently, nominal GDP divided by the stock of money.
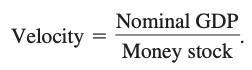
Quantity equation: money times velocity equals nominal GDP.
Chapter 20 - Money, price & financial intermediaries
The banking system and the allocation of saving to productive uses
Financial intermediaries: firms that extend credit to borrowers using funds raised from savers.
Money: any asset that can be used in making purchases.
Medium of exchange: asset used in purchasing goods and services.
Barter: direct trade of goods or services for other goods/services.
Unit of account: basic measure of economic value.
Store of value: asset that serves as a means of holding wealth.
M1: sum of currency outstanding and balances held in checking accounts.
M2: all the assets in M1 plus some additional assets that are usable in making payments but at greater cost or inconvenience than currency or checks.
Commercial banks and the creating of money
Bank reserves: cash or similar assets held by commercial banks for the purpose of meeting depositor withdrawals and payments.
100% reserve banking: situation in which banks' reserves equal 100% of their deposits.
Reserve-deposit ratio: bank reserves divided by deposits.
Fractional-reserve banking system: banking system in which bank reserves are less than deposits so that the reserve-deposit ratio is less than 100%.
Central banks, the money supply and the prices
Federal Reserve System (or the Fed): central bank of the United States.
Monetary policy: determination of the nation's money supply.
Open-market purchase: purchase of government bonds from the public by the Fed for the purpose of increasing the supply of bank reserves and the money supply.
Open-market sale: sale by the Fed of government bonds to the public for the purpose of reducing bank reserves and the money supply.
Open-market operations: open-market purchases and open-market sales.
Velocity: measure of the speed at which money changes hands in transactions involving final goods and services, or, equivalently, nominal GDP divided by the stock of money.
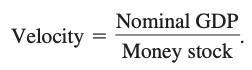
Quantity equation: money times velocity equals nominal GDP.
 Knowt
Knowt