
Chapter 2: The Market System and the Circular Flow
Economic system - A particular set of institutional arrangements + coordinating mechanism used to respond to the economizing problem
Determine what goods produced, how goods are produced, who gets them, etc.
Command system - Socialism/communism; gov’t owns most property + economic decision-making occurs through central economic plan
Central planning board makes all major decisions
Firms produce according to gov’t directives
Some private ownership
Market system - Capitalism; private ownership of resources + use of markets/prices to coordinate economic activity
Acting in own self-interest
Competition among independently acting buyers + sellers
Laissez-faire capitalism - Limited gov’t interference w/ economy
Characteristics
Private property - Private individuals + firms own most property resources; encourages investment, innovation, economic growth
Freedom of enterprise - Entrepreneurs + businesses can obtain resources to produce + sell goods
Freedom of choice - Owners can employ property/money as they see fit; consumers can buy goods and services that best satisfy their wants
Self-interest - Each economic unit tries to achieve its own particular goal, usually delivering something of value to others
Competition - Between economic units; based on freedom of choice in pursuit of monetary return; spreads economic power between businesses + households
Markets - Institution/mechanism that brings buyers + sellers into contact
Technology and capital goods
Specialization - Use of resources to produce a few goods instead of an entire range
Division of labor - Human specialization
Medium of exchange - Function of money; makes trade easier
Barter - Swapping goods and services for each other; requires coincidence of wants between buyers and sellers
Money - Convenient social invention to facilitate exchanges of goods and services
Active but limited government
Five fundamental questions
What goods and services will be produced?
Only goods and services produced at continuing profit will be produced
Consumer sovereignty - Consumers spend income on goods they are willing + able to buy
“Dollar votes” - Consumers using dollars to show what goods + services they want in the market; determine which industries survive and fail
How will the goods and services be produced?
Least-cost production - Most economically efficient techniques of production
Who will get the goods and services?
Products distributed to consumers based on who is willing and able to pay
Depends on income, prices, and preferences
How will the system accommodate change?
Changes as consumer preferences, production techniques, and resource supplies change
Directs expansion/contraction of industries
How will the system promote progress?
Technological advance
Creative destruction - Creation of new products + production methods destroys market positions of firms relying on existing products and older business ways
Capital accumulation (dollar votes for capital goods)
“Invisible hand” - As firms seek to further their own self-interest in a market system, they simultaneously promote social interests
Efficiency - Efficient use of resources by guiding them to production of wanted goods + services
Incentives - Skill acquisition, hard work, innovation
Freedom - Economic activity without coercion
Problems with command systems
Coordination problem
Central planners coordinating millions of individual decisions
Failure of single industry → Affected several other industries
Planning techniques ineffective for large economies
Incentive problem
Persistent shortages + surpluses
No incentive to adjust production to fluctuations
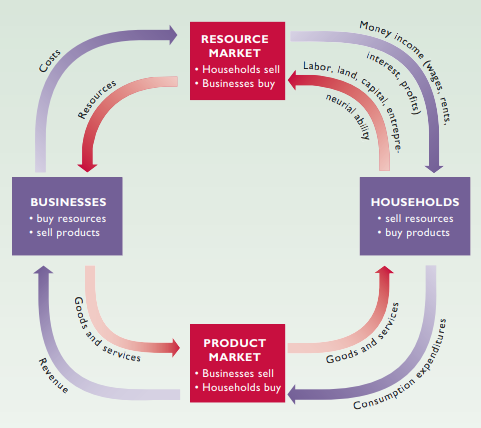
Circular flow diagram - Shows repetitive flows of goods, services, resources, and money through the economy
Resource market - Where resources by households sold to businesses
Product market - Where goods and services produced by businesses sold to households
Chapter 2: The Market System and the Circular Flow
Economic system - A particular set of institutional arrangements + coordinating mechanism used to respond to the economizing problem
Determine what goods produced, how goods are produced, who gets them, etc.
Command system - Socialism/communism; gov’t owns most property + economic decision-making occurs through central economic plan
Central planning board makes all major decisions
Firms produce according to gov’t directives
Some private ownership
Market system - Capitalism; private ownership of resources + use of markets/prices to coordinate economic activity
Acting in own self-interest
Competition among independently acting buyers + sellers
Laissez-faire capitalism - Limited gov’t interference w/ economy
Characteristics
Private property - Private individuals + firms own most property resources; encourages investment, innovation, economic growth
Freedom of enterprise - Entrepreneurs + businesses can obtain resources to produce + sell goods
Freedom of choice - Owners can employ property/money as they see fit; consumers can buy goods and services that best satisfy their wants
Self-interest - Each economic unit tries to achieve its own particular goal, usually delivering something of value to others
Competition - Between economic units; based on freedom of choice in pursuit of monetary return; spreads economic power between businesses + households
Markets - Institution/mechanism that brings buyers + sellers into contact
Technology and capital goods
Specialization - Use of resources to produce a few goods instead of an entire range
Division of labor - Human specialization
Medium of exchange - Function of money; makes trade easier
Barter - Swapping goods and services for each other; requires coincidence of wants between buyers and sellers
Money - Convenient social invention to facilitate exchanges of goods and services
Active but limited government
Five fundamental questions
What goods and services will be produced?
Only goods and services produced at continuing profit will be produced
Consumer sovereignty - Consumers spend income on goods they are willing + able to buy
“Dollar votes” - Consumers using dollars to show what goods + services they want in the market; determine which industries survive and fail
How will the goods and services be produced?
Least-cost production - Most economically efficient techniques of production
Who will get the goods and services?
Products distributed to consumers based on who is willing and able to pay
Depends on income, prices, and preferences
How will the system accommodate change?
Changes as consumer preferences, production techniques, and resource supplies change
Directs expansion/contraction of industries
How will the system promote progress?
Technological advance
Creative destruction - Creation of new products + production methods destroys market positions of firms relying on existing products and older business ways
Capital accumulation (dollar votes for capital goods)
“Invisible hand” - As firms seek to further their own self-interest in a market system, they simultaneously promote social interests
Efficiency - Efficient use of resources by guiding them to production of wanted goods + services
Incentives - Skill acquisition, hard work, innovation
Freedom - Economic activity without coercion
Problems with command systems
Coordination problem
Central planners coordinating millions of individual decisions
Failure of single industry → Affected several other industries
Planning techniques ineffective for large economies
Incentive problem
Persistent shortages + surpluses
No incentive to adjust production to fluctuations
Circular flow diagram - Shows repetitive flows of goods, services, resources, and money through the economy
Resource market - Where resources by households sold to businesses
Product market - Where goods and services produced by businesses sold to households

 Knowt
Knowt