
BUSN 311: Final Exam Review Terms
First 20 Questions
Needs, Wants, and Demand
Needs
States of felt deprivation
Wants
The form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality
Demands
Human wants that are backed by buying power
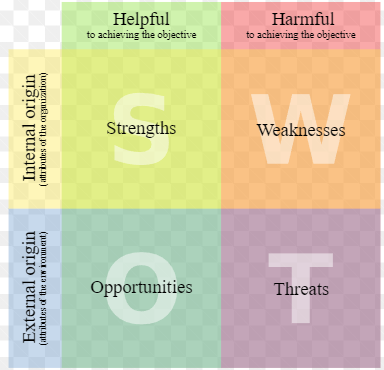
SWOT
Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
An overall analysis of a company
Benchmarking
Comparing the companies products and processes to those of competitors or leading firms in other industries to identify best practices and find ways to improve quality and performance
Segmentation
Market Segmentation
Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors and who might require separate marketing strategies or mixes
Age and Life-Cycle Segmentation
Dividing a market into different age and life-cycle groups.
Behavioral Segmentation
Dividing a market into segments based on consumer knowledge, attitudes, uses of a product, or responses to a product.
Benefit Segmentation
Dividing the market into segments according to the different benefits that consumers seek from the product.
Cross-market Segmentation
Forming segments of consumers who have similar needs and buying behaviors even though they are located in different countries
Demographic Segmentation
Diving the market into segments based on variables such as age, life-cycle stage, gender, income, occupation, education, religion, ethnicity, and generation.
Gender Segmentation
Dividing a market into different segments based on gender
Geographic Segmentation
Dividing a market into different geographical units, such as nations, states, regions, countries, cities, or even neighborhoods.
Income Segmentation
Diving the market into different income segments
Intermarket Segmentation (Cross-market)
Forming segments of consumers who have similar needs and buying behavior even though they are located in different countries
Market Segmentation
Diving the market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors and who might require separate marketing strategies or mixes.
Occasion Segmentation
Dividing the market into segments according to occasions when buyers get the idea to buy, actually make their purchase, or use the purchased item.
Psychographic Segmentation
Dividing a market into different segments based on lifestyle or personality characteristics
Target Market
A set of buyers who share common needs or characteristics that a company decides to serve
Positioning
Arranging for a product to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target customers
Differentiation (product, customer, channel, price)
Actually differentiating the market offering to create superior customer value
Value Proposition
The full mix of benefits upon which a brand is positioned
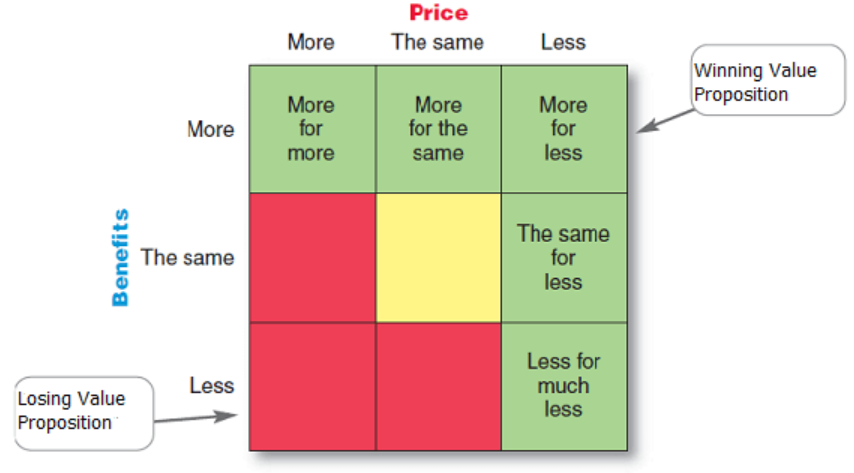
Competitive Advantage
An advantage over competitors gained by offering greater customer value either by having lower prices or providing more benefits that justify higher prices.
Direct Marketing
Engaged directly with carefully targeted individual consumers and customer communities to both obtain an immediate response and build lasting customer relationships
Product adaptation
The process of changing a product to meet the needs of customers in a market other than the one in which it is made for.
Customer Relationship Management
The overall process of building and maintaining profitable relationships with customers by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction
Promotional Mix (Marketing Communications Mix)
The specific blend of promotional tools that the company uses to persuasively communicate customer value and build customer relationships
Marketing Mix
The set of tactical marketing tools-- Product, place, price, promotion -- that the firm blends to produce the response it wants in the target market
Cause Related Marketing
Marketing that is carried out by a for-profit business to advance a charitable cause or better society.
Advertising Appeal
Communication strategies that marketing and advertising professionals use to grab attention and persuade people to buy or act.
Advertising
Any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor
Channel Differentiation
Companies can achieve competitive advantage through the way they design their distribution channels' coverage, expertise and performance.
Word of Mouth Marketing
The impact of the personal words and recommendations of trusted friends, family, associates, and other consumers on buying behavior
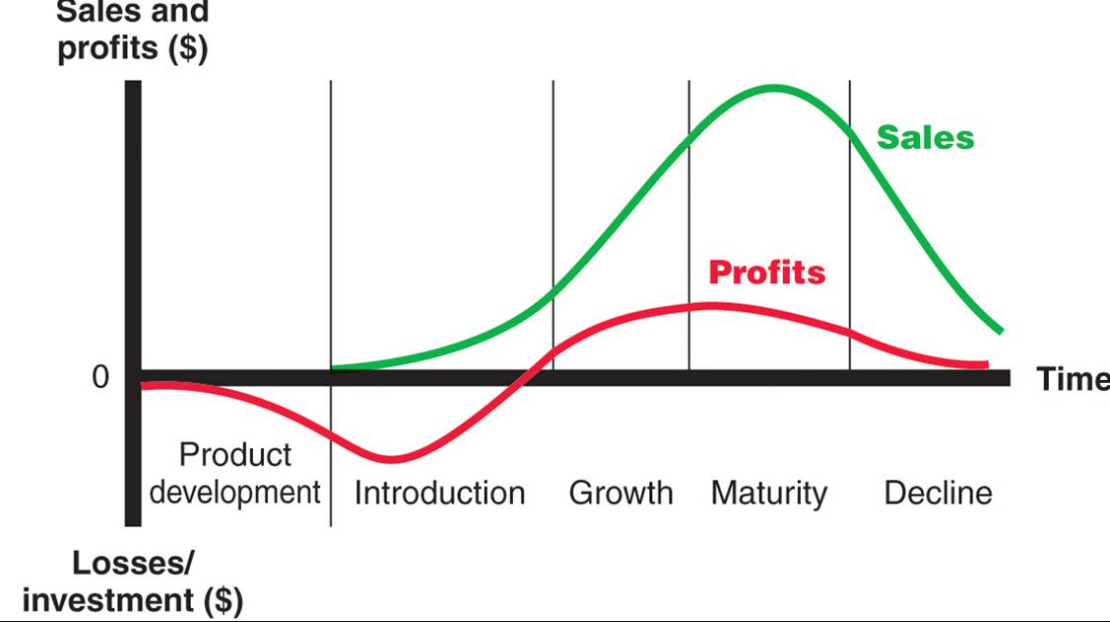
PLC (product life cycle) •
The amount of time spent in each stage will vary from product to product, and different companies have different strategic approaches to transitioning from one phase to the next.
IMC: Integrated Marketing Communications
Carefully integrating and coordinating the companies many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message about the organization and its products
Pricing Strategies
Break-Even Pricing
Setting price to break even on the costs of making and marketing a product, or setting price to make a target return.
Competition-Based Pricing
Setting prices based on competitors strategies, prices, costs, and market offerings.
Cost-Based Pricing
Setting prices based on the costs of producing, distributing, and selling the product plus a fair rate of return for effort and risk.
Cost-Plus Pricing
Adding a standard markup to the cost of the product
Customer Value-Based Pricing
Setting price based on buyers perceptions of value rather than on the seller's cost.
Good-Value Pricing
Offering just the right combination of quality and good service at a fair price.
Markup Pricing
Adding a standard markup to the cost of the product
Target Return Pricing
Setting price to break even on the costs of making and marketing a product, or setting price to make a target return.
Value-Added Pricing
Attaching value-added features and services to differentiate a company’s offers and charging higher prices.
Based-Point Pricing
Pricing in which the seller designates some city as a basing point and charges all customers the freight cost from that city to the customer.
Dynamic Pricing
Adjusting prices continually to meet changing conditions and situations in the marketplace
FOB-Origin Pricing
Pricing in which goods are placed free on board a carrier; the customer pays the freight from the factory to the destination
Freight-Absorption Pricing
Pricing in which the seller absorbs all of part of the freight charges in order to get the desired business.
Geographical Pricing
Setting prices for customers located in different parts of the country or world.
Market-Penetration Pricing
Setting a low price for a new product in order to attract a large number of buyers and a large market share.
Market-Skimming Pricing (Price Skimming)
Setting a high price for a new product to skim maximum revenues layer by layer from the segments willing to pay the high price; the company makes fewer but profitable sales
Optional-Product Pricing
The pricing of optional or accessory products along with a main product
Personalized Pricing
Adjusting prices in real time to fit individual customer needs, situations, locations, and buying behaviors.
Product Bundle Pricing
Combining several products and offering the bundle at a reduced price.
Product Line Pricing
Setting the price steps between various products in a product line based on cost differences between the products, customer evaluations, of different features, features, and competitors prices.
Promotional Pricing
Temporarily pricing products below the list price, and sometimes even below cost, to increase short-run sales.
Psychological Pricing
Pricing that considers the psychology of process and not simply the economics; the price is used to say something about the product.
Reference prices
Prices that buyers carry in their minds and refer to when they look at a given product.
Segmented Pricing
Selling a product or service at two or more prices, where difference in prices is not based on differences in costs.
Uniform-Delivered Pricing
Pricing in which the company charges the same price plus freight to all customers, regardless of their location.
Zone Pricing
Pricing in which the company sets up two or more zones. All customers within a zone pay the same total price; the more distant the zone, the higher the price
Marketing Research Methods
The systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing an organization
Observational research
Gathering primary data by observing relevant people, actions, and situations
Online focus group
Gathering a small group of people online with a trained moderator to chat about a product, service, or organization and gain qualitative insights about consumer attitudes and behavior
Online marketing research
Collecting primary data through internet and mobile surveys, online focus groups, consumer tracking, experiments, and online panels and brand communities
Survey research
Gathering primary data by asking people questions about their knowledge, attitudes, preferences, and buying behavior
Market-penetration Pricing: Setting a low price for a new product in order to attract a large number of buyers and a large market share.
Chapter 14-17 Vocab
Intermediaries
Offer producers greater efficiency in making goods available to target markets. Through contracts, experience, specialization, and scale of operations, intermediaries usually offer the firm more than it can achieve on its own.
Advertising
Any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor
Affordable Method
Setting the promotion budget at the level management thinks the company can afford
Buzz Marketing
Cultivating opinion leaders and getting them to spread information about a product or a service to others in their communities
Competitive-Parity Method
Setting the promotion budget to match competitors outlays
Content Marketing
Creating, inspiring, and sharing brand messages and conversations with and among consumers across a fluid mix of paid, owned, earned, and shared channels
Direct and digital marketing
Engaged directly with carefully targeted individual consumers and customer communities to both obtain an immediate response and build lasting customer relationships
Five A’s
The five customer journey stages on the path from awareness of a brand to advocating it to others: awareness, appeal, ask, act, and advocacy
Integrated marketing communications (IMC)
Carefully integrating and coordinating the companies many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message about the organization and its products
Nonpersonal communication channels
Media that carry messages without personal contact or feedback, including major media, atmospheres, and events
Objective-and-task method
Developing the promotion budget by (1) defining specific promotion objectives, (2) determining the tasks needed to achieve these objectives, and (3) estimating the costs of performing these tasks. The sum of these costs is the proposed promotion budget
Percentage-of-sales method
Setting the promotion budget at a certain percentage of current or forecasted sales or as a percentage of the unit sales price
Personal communication channels
Channels through which two or more people communicate directly with each other, including face-to-face, on the phone, via mail or email, or even through an internet “chat”
Personal Selling
Personal presentation by the firms sales force or the purpose of engaging customers, making sales, and building customer relationships
Promotional mix (Marketing communications mix)
The specific blend of promotional tools that the company uses to persuasively communicate customer value and build customer relationships
Public Relations
Building good relations with the company's various publics by obtaining favorable publicity, building a good corporate image, and creating favorable events, stories, and other marketing content
Pull Strategy
A promotional strategy that calls for spending a lot on consumer advertising, -promotion, and other content to induce final consumers to engage with and buy the product, creating a demand vacuum that “pulls” the product through the channel
Push Strategy
A promotion strategy that calls for using the salesforce and trade promotion to push the product through channels. The produced promotes the product to channel members who in turn promote it to final consumers
Sales Promotion
Short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sale of a product or a service
Advertising agency
A marketing services firm assists companies in planning, preparing, implementing, and evaluating all or portions of their advertising programs
Advertising Budget
The dollars and other resources allocated to a product or a company advertising program
Advertising media
The vehicles through which advertising messages are delivered to their intended audiences
Advertising objective
A specific communication task to be accomplished with a specific target audience during a specific period of time
Advertising strategy
The strategy by which the company accomplishes its advertising objectives. It consists of two major elements: creating advertising messages and selecting advertising media
Creative concept
The compelling “big idea” that will bring an advertising message strategy to life in a distinctive and memorable way
Execution styles
The approach, style, tone, words, and format used for executing an advertising message
Native advertising
Advertising or other brand-produced online content that looks in form and function like the other natural content surrounding it on a web or social media platform
Return on advertising investment
The net return on advertising investment divided by the costs of the advertising investment
Approach
The sales step in which a salesperson meets the customer for the first
Business Promotions
Sales promotion tools used to generate business leads, stimulate purchases, reward customers, and motivate salespeople
Closing
The sakes step in which a salesperson asks the customer for an older
Consumer promotions
Sales promotion tools used to boost short-term customer buying and engagement or enhance long-term customers relationships
Customer sales force structure
A sales force organization in which salespeople specialize in selling only to certain customers or industries
Event marketing (sponsorships)
Creating a brand-marketing event or serving as a sole or participating sponsor of events created by others
Follow-up
The sales step in which a salesperson follows up after the sale to ensure customer satisfaction and repeat business
Handling objections
The sales step in which a salesperson seeks out, clarifies, and overcomes any customer objections to buying
Inside Sales force
Salespeople who conduct business from their offices via telephone, online and social media interactions, or visits from prospective buyers
Outside Sales force (field sales force)
Salespeople who travel to call on customers in the field
Preapproach
The sales step in which a salesperson learns as much as possible about a prospective customer before making a sales call
Presentation
The sales step in which a salesperson tells the “value story” to the buyer, showing how the companies offer solves the customers problems
Product sales force structure
A sales force organization in which salespeople specialize in selling only a portion of the companies product or lines when
Prospecting
The sales step in which a salesperson or company identifies qualified potential customers
Sales force management
Analyzing, planning, implementing, and controlling sales force activities
Salesperson
An individual who represents a company to customers by performing one or more of the following activities: Prospecting, communicating, selling, servicing, information gathering, and relationship building
Sales Quota
A standard that states the amount a salesperson should sell and how sales should be divided among the companies products
Selling Process
The steps that salespeople follow when selling, which include prospecting and qualifying, preapproach, approach, presentation, and demonstration, handling objections, closing, and follow-up
Social Selling
Using online, mobile, and social media to engage customers, build stronger customer relationships, and augment sales performance
Team selling
Using teams of people from sales, marketing, engineering, finance, technical support, and even upper management to service large, complex accounts
Territorial Sales force structure
A sales force organization that assigns each salesperson to an exclusive geographic territory in which that salesperson sells the companies full line
Trade promotions
Sales promotion tools used to persuade resellers to carry a brand, give it self space, and promote it in advertising
BUSN 311: Final Exam Review Terms
First 20 Questions
Needs, Wants, and Demand
Needs
States of felt deprivation
Wants
The form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality
Demands
Human wants that are backed by buying power
SWOT
Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
An overall analysis of a company

Benchmarking
Comparing the companies products and processes to those of competitors or leading firms in other industries to identify best practices and find ways to improve quality and performance
Segmentation
Market Segmentation
Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors and who might require separate marketing strategies or mixes
Age and Life-Cycle Segmentation
Dividing a market into different age and life-cycle groups.
Behavioral Segmentation
Dividing a market into segments based on consumer knowledge, attitudes, uses of a product, or responses to a product.
Benefit Segmentation
Dividing the market into segments according to the different benefits that consumers seek from the product.
Cross-market Segmentation
Forming segments of consumers who have similar needs and buying behaviors even though they are located in different countries
Demographic Segmentation
Diving the market into segments based on variables such as age, life-cycle stage, gender, income, occupation, education, religion, ethnicity, and generation.
Gender Segmentation
Dividing a market into different segments based on gender
Geographic Segmentation
Dividing a market into different geographical units, such as nations, states, regions, countries, cities, or even neighborhoods.
Income Segmentation
Diving the market into different income segments
Intermarket Segmentation (Cross-market)
Forming segments of consumers who have similar needs and buying behavior even though they are located in different countries
Market Segmentation
Diving the market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors and who might require separate marketing strategies or mixes.
Occasion Segmentation
Dividing the market into segments according to occasions when buyers get the idea to buy, actually make their purchase, or use the purchased item.
Psychographic Segmentation
Dividing a market into different segments based on lifestyle or personality characteristics
Target Market
A set of buyers who share common needs or characteristics that a company decides to serve
Positioning
Arranging for a product to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target customers
Differentiation (product, customer, channel, price)
Actually differentiating the market offering to create superior customer value
Value Proposition
The full mix of benefits upon which a brand is positioned

Competitive Advantage
An advantage over competitors gained by offering greater customer value either by having lower prices or providing more benefits that justify higher prices.
Direct Marketing
Engaged directly with carefully targeted individual consumers and customer communities to both obtain an immediate response and build lasting customer relationships
Product adaptation
The process of changing a product to meet the needs of customers in a market other than the one in which it is made for.
Customer Relationship Management
The overall process of building and maintaining profitable relationships with customers by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction
Promotional Mix (Marketing Communications Mix)
The specific blend of promotional tools that the company uses to persuasively communicate customer value and build customer relationships
Marketing Mix
The set of tactical marketing tools-- Product, place, price, promotion -- that the firm blends to produce the response it wants in the target market
Cause Related Marketing
Marketing that is carried out by a for-profit business to advance a charitable cause or better society.
Advertising Appeal
Communication strategies that marketing and advertising professionals use to grab attention and persuade people to buy or act.
Advertising
Any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor
Channel Differentiation
Companies can achieve competitive advantage through the way they design their distribution channels' coverage, expertise and performance.
Word of Mouth Marketing
The impact of the personal words and recommendations of trusted friends, family, associates, and other consumers on buying behavior
PLC (product life cycle) •
The amount of time spent in each stage will vary from product to product, and different companies have different strategic approaches to transitioning from one phase to the next.

IMC: Integrated Marketing Communications
Carefully integrating and coordinating the companies many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message about the organization and its products
Pricing Strategies
Break-Even Pricing
Setting price to break even on the costs of making and marketing a product, or setting price to make a target return.
Competition-Based Pricing
Setting prices based on competitors strategies, prices, costs, and market offerings.
Cost-Based Pricing
Setting prices based on the costs of producing, distributing, and selling the product plus a fair rate of return for effort and risk.
Cost-Plus Pricing
Adding a standard markup to the cost of the product
Customer Value-Based Pricing
Setting price based on buyers perceptions of value rather than on the seller's cost.
Good-Value Pricing
Offering just the right combination of quality and good service at a fair price.
Markup Pricing
Adding a standard markup to the cost of the product
Target Return Pricing
Setting price to break even on the costs of making and marketing a product, or setting price to make a target return.
Value-Added Pricing
Attaching value-added features and services to differentiate a company’s offers and charging higher prices.
Based-Point Pricing
Pricing in which the seller designates some city as a basing point and charges all customers the freight cost from that city to the customer.
Dynamic Pricing
Adjusting prices continually to meet changing conditions and situations in the marketplace
FOB-Origin Pricing
Pricing in which goods are placed free on board a carrier; the customer pays the freight from the factory to the destination
Freight-Absorption Pricing
Pricing in which the seller absorbs all of part of the freight charges in order to get the desired business.
Geographical Pricing
Setting prices for customers located in different parts of the country or world.
Market-Penetration Pricing
Setting a low price for a new product in order to attract a large number of buyers and a large market share.
Market-Skimming Pricing (Price Skimming)
Setting a high price for a new product to skim maximum revenues layer by layer from the segments willing to pay the high price; the company makes fewer but profitable sales
Optional-Product Pricing
The pricing of optional or accessory products along with a main product
Personalized Pricing
Adjusting prices in real time to fit individual customer needs, situations, locations, and buying behaviors.
Product Bundle Pricing
Combining several products and offering the bundle at a reduced price.
Product Line Pricing
Setting the price steps between various products in a product line based on cost differences between the products, customer evaluations, of different features, features, and competitors prices.
Promotional Pricing
Temporarily pricing products below the list price, and sometimes even below cost, to increase short-run sales.
Psychological Pricing
Pricing that considers the psychology of process and not simply the economics; the price is used to say something about the product.
Reference prices
Prices that buyers carry in their minds and refer to when they look at a given product.
Segmented Pricing
Selling a product or service at two or more prices, where difference in prices is not based on differences in costs.
Uniform-Delivered Pricing
Pricing in which the company charges the same price plus freight to all customers, regardless of their location.
Zone Pricing
Pricing in which the company sets up two or more zones. All customers within a zone pay the same total price; the more distant the zone, the higher the price
Marketing Research Methods
The systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing an organization
Observational research
Gathering primary data by observing relevant people, actions, and situations
Online focus group
Gathering a small group of people online with a trained moderator to chat about a product, service, or organization and gain qualitative insights about consumer attitudes and behavior
Online marketing research
Collecting primary data through internet and mobile surveys, online focus groups, consumer tracking, experiments, and online panels and brand communities
Survey research
Gathering primary data by asking people questions about their knowledge, attitudes, preferences, and buying behavior
Market-penetration Pricing: Setting a low price for a new product in order to attract a large number of buyers and a large market share.
Chapter 14-17 Vocab
Intermediaries
Offer producers greater efficiency in making goods available to target markets. Through contracts, experience, specialization, and scale of operations, intermediaries usually offer the firm more than it can achieve on its own.
Advertising
Any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor
Affordable Method
Setting the promotion budget at the level management thinks the company can afford
Buzz Marketing
Cultivating opinion leaders and getting them to spread information about a product or a service to others in their communities
Competitive-Parity Method
Setting the promotion budget to match competitors outlays
Content Marketing
Creating, inspiring, and sharing brand messages and conversations with and among consumers across a fluid mix of paid, owned, earned, and shared channels
Direct and digital marketing
Engaged directly with carefully targeted individual consumers and customer communities to both obtain an immediate response and build lasting customer relationships
Five A’s
The five customer journey stages on the path from awareness of a brand to advocating it to others: awareness, appeal, ask, act, and advocacy
Integrated marketing communications (IMC)
Carefully integrating and coordinating the companies many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message about the organization and its products
Nonpersonal communication channels
Media that carry messages without personal contact or feedback, including major media, atmospheres, and events
Objective-and-task method
Developing the promotion budget by (1) defining specific promotion objectives, (2) determining the tasks needed to achieve these objectives, and (3) estimating the costs of performing these tasks. The sum of these costs is the proposed promotion budget
Percentage-of-sales method
Setting the promotion budget at a certain percentage of current or forecasted sales or as a percentage of the unit sales price
Personal communication channels
Channels through which two or more people communicate directly with each other, including face-to-face, on the phone, via mail or email, or even through an internet “chat”
Personal Selling
Personal presentation by the firms sales force or the purpose of engaging customers, making sales, and building customer relationships
Promotional mix (Marketing communications mix)
The specific blend of promotional tools that the company uses to persuasively communicate customer value and build customer relationships
Public Relations
Building good relations with the company's various publics by obtaining favorable publicity, building a good corporate image, and creating favorable events, stories, and other marketing content
Pull Strategy
A promotional strategy that calls for spending a lot on consumer advertising, -promotion, and other content to induce final consumers to engage with and buy the product, creating a demand vacuum that “pulls” the product through the channel
Push Strategy
A promotion strategy that calls for using the salesforce and trade promotion to push the product through channels. The produced promotes the product to channel members who in turn promote it to final consumers
Sales Promotion
Short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sale of a product or a service
Advertising agency
A marketing services firm assists companies in planning, preparing, implementing, and evaluating all or portions of their advertising programs
Advertising Budget
The dollars and other resources allocated to a product or a company advertising program
Advertising media
The vehicles through which advertising messages are delivered to their intended audiences
Advertising objective
A specific communication task to be accomplished with a specific target audience during a specific period of time
Advertising strategy
The strategy by which the company accomplishes its advertising objectives. It consists of two major elements: creating advertising messages and selecting advertising media
Creative concept
The compelling “big idea” that will bring an advertising message strategy to life in a distinctive and memorable way
Execution styles
The approach, style, tone, words, and format used for executing an advertising message
Native advertising
Advertising or other brand-produced online content that looks in form and function like the other natural content surrounding it on a web or social media platform
Return on advertising investment
The net return on advertising investment divided by the costs of the advertising investment
Approach
The sales step in which a salesperson meets the customer for the first
Business Promotions
Sales promotion tools used to generate business leads, stimulate purchases, reward customers, and motivate salespeople
Closing
The sakes step in which a salesperson asks the customer for an older
Consumer promotions
Sales promotion tools used to boost short-term customer buying and engagement or enhance long-term customers relationships
Customer sales force structure
A sales force organization in which salespeople specialize in selling only to certain customers or industries
Event marketing (sponsorships)
Creating a brand-marketing event or serving as a sole or participating sponsor of events created by others
Follow-up
The sales step in which a salesperson follows up after the sale to ensure customer satisfaction and repeat business
Handling objections
The sales step in which a salesperson seeks out, clarifies, and overcomes any customer objections to buying
Inside Sales force
Salespeople who conduct business from their offices via telephone, online and social media interactions, or visits from prospective buyers
Outside Sales force (field sales force)
Salespeople who travel to call on customers in the field
Preapproach
The sales step in which a salesperson learns as much as possible about a prospective customer before making a sales call
Presentation
The sales step in which a salesperson tells the “value story” to the buyer, showing how the companies offer solves the customers problems
Product sales force structure
A sales force organization in which salespeople specialize in selling only a portion of the companies product or lines when
Prospecting
The sales step in which a salesperson or company identifies qualified potential customers
Sales force management
Analyzing, planning, implementing, and controlling sales force activities
Salesperson
An individual who represents a company to customers by performing one or more of the following activities: Prospecting, communicating, selling, servicing, information gathering, and relationship building
Sales Quota
A standard that states the amount a salesperson should sell and how sales should be divided among the companies products
Selling Process
The steps that salespeople follow when selling, which include prospecting and qualifying, preapproach, approach, presentation, and demonstration, handling objections, closing, and follow-up
Social Selling
Using online, mobile, and social media to engage customers, build stronger customer relationships, and augment sales performance
Team selling
Using teams of people from sales, marketing, engineering, finance, technical support, and even upper management to service large, complex accounts
Territorial Sales force structure
A sales force organization that assigns each salesperson to an exclusive geographic territory in which that salesperson sells the companies full line
Trade promotions
Sales promotion tools used to persuade resellers to carry a brand, give it self space, and promote it in advertising
 Knowt
Knowt