
Cognitive Approach - Cognitive Processes
Multi-Store Model of Memory
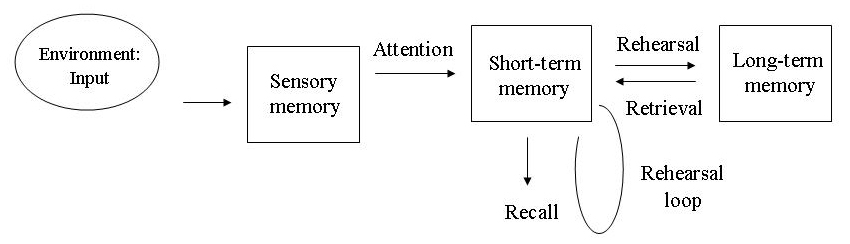
Sensory memory – iconic memory
Stores visual sensory information
Capacity: unlimited
Duration: 1/3 of a second
Short Term Memory
Capacity: 5-9 pieces
Duration: 20 seconds
Chunking can help increase the capacity
Move stuff from short term memory to long term memory through rehearsal
Maintenance rehearsal involves repeating information again and again
Elaborative rehearsal involves elaborating on the information in a meaningful way
Takes more effort, but it is more effective as it ensures that information is encoded into long term memory
Long Term Memory
Whenever we remember something we are retrieving it from what is stored in long term memory
Capacity: unlimited
Duration: unlimited
Procedural memory: “knowing how”, memory of how to do things (skills)
Declarative memory: “knowing that”, memory of information about the world (semantic memory) and personal experiences (episodic memory)
Episodic memory: stores events (episodes) involving personal experiences. Stores information about context (when and where), state (physical and psychological condition)
Semantic memory: LTM declarative memory that stores info about the world. E.g. facts (sun is a star), definitions, rules, concepts, everyday knowledge (a bus is a form of transport) and specialized knowledge (chess piece moves)
Working Memory Model
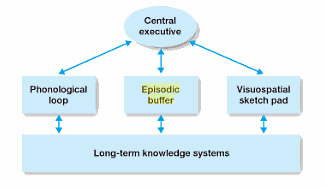
Central Executive
Replaces the sensory memory buffer
Responsible for monitoring an coordinating the operation of ‘slave systems’
The central executive directs attention to tasks
Allocates information based on modality
Phonological loop
Limited capacity (like STM in MSM of memory)
Deals with auditory info and language - both written and verbal
Baddley (1986) further divided it into the:
Phonological store; holds words for a brief period - can be thought as the inner ear
Articulatory process; holds words seen/heard and silently repeated like an inner voice
Episodic Buffer
Temporarily holds several sources of auditory, long-term and visual information active at the same time, while consideration of what is needed in present situation takes place
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Limited capacity (like STM in MSM of memory)
Visual component of short-term memory/inner eye
Temporary store for spatial and visual information about what things look like; form and colour
The inner scribe; processes spatial and movement information.
Dual Processing Model
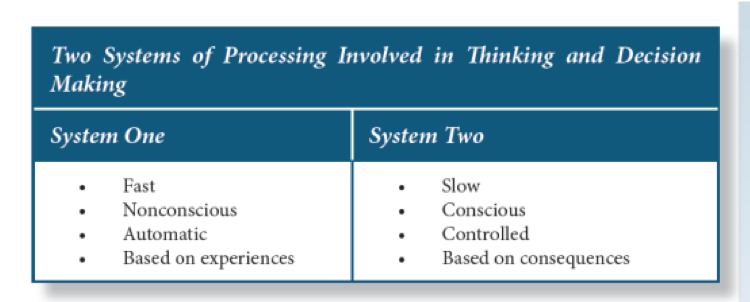
System 1 Thinking
the one that is reliant on past information and schema, makes quick and effortless decisions based on limited information.
Tend to use mental short-cuts called heuristics
90% of time we access system 1
System 1 thinking and take shortcuts - quick thinking, intuitive
System 2 Thinking
System 2 thinking - much more effortful and requires more conscious reasoning
5% of the time we access system 2 where we slow down.
System 2 thinking - rational thinking
Cognitive Approach - Cognitive Processes
Multi-Store Model of Memory

Sensory memory – iconic memory
Stores visual sensory information
Capacity: unlimited
Duration: 1/3 of a second
Short Term Memory
Capacity: 5-9 pieces
Duration: 20 seconds
Chunking can help increase the capacity
Move stuff from short term memory to long term memory through rehearsal
Maintenance rehearsal involves repeating information again and again
Elaborative rehearsal involves elaborating on the information in a meaningful way
Takes more effort, but it is more effective as it ensures that information is encoded into long term memory
Long Term Memory
Whenever we remember something we are retrieving it from what is stored in long term memory
Capacity: unlimited
Duration: unlimited
Procedural memory: “knowing how”, memory of how to do things (skills)
Declarative memory: “knowing that”, memory of information about the world (semantic memory) and personal experiences (episodic memory)
Episodic memory: stores events (episodes) involving personal experiences. Stores information about context (when and where), state (physical and psychological condition)
Semantic memory: LTM declarative memory that stores info about the world. E.g. facts (sun is a star), definitions, rules, concepts, everyday knowledge (a bus is a form of transport) and specialized knowledge (chess piece moves)
Working Memory Model

Central Executive
Replaces the sensory memory buffer
Responsible for monitoring an coordinating the operation of ‘slave systems’
The central executive directs attention to tasks
Allocates information based on modality
Phonological loop
Limited capacity (like STM in MSM of memory)
Deals with auditory info and language - both written and verbal
Baddley (1986) further divided it into the:
Phonological store; holds words for a brief period - can be thought as the inner ear
Articulatory process; holds words seen/heard and silently repeated like an inner voice
Episodic Buffer
Temporarily holds several sources of auditory, long-term and visual information active at the same time, while consideration of what is needed in present situation takes place
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Limited capacity (like STM in MSM of memory)
Visual component of short-term memory/inner eye
Temporary store for spatial and visual information about what things look like; form and colour
The inner scribe; processes spatial and movement information.
Dual Processing Model

System 1 Thinking
the one that is reliant on past information and schema, makes quick and effortless decisions based on limited information.
Tend to use mental short-cuts called heuristics
90% of time we access system 1
System 1 thinking and take shortcuts - quick thinking, intuitive
System 2 Thinking
System 2 thinking - much more effortful and requires more conscious reasoning
5% of the time we access system 2 where we slow down.
System 2 thinking - rational thinking
 Knowt
Knowt
