
Unit 2 - Understanding the Atom
The Historical Development of Atomic Theory
Democritus - Early philosopher who proposed the existence of the atom
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
First scientific theory of the atom
Based on Joseph Proust and other scientists’ research
Proust’s research: each compound contains exact proportions
Law of definite proportions
Atoms are indivisible
Elements are made of identical atoms unique to each element
Compounds are made of 2+ atoms in fixed proportion
A chemical reaction is the rearrangement of atoms
Discovery of the Electron (Cathode Ray Experiment)
By JJ Thompson
Led to the Plum Pudding Model
Oil Drop Experiment
By Millikan
Thompson found charge & mass of electron
Discovery of Nucleus (Gold Foil Experiment)
By Rutherford
Most particles pass directly through the atom, some get deflected
→ Most of the atom is empty space, with a large particle at the center
Quiz: https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/5faee2a376564d001b6fb43a/the-historical-development-of-atomic-theory
Electromagnetic Waves
Vocab
Electric Field - The area surrounding a charged object in which it can act upon another charged object
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The frequency spectrum containing all electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic Wave
A combination of electric & magnetic fields radiating from a source @ the speed of light.
The electric & magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular of each other
Caused by disturbing charged particles, which then oscillate and produce oscillating fields
Source produces an magnetic field, the magnetic field then produces an electric field, the electric field the produces another magnetic field, repeat forever
Magnetic Field - The area surrounding a magnetic object in which it can act upon an object
Polarization
Types of Waves
Mechanical - Waves that use matter to carry energy
Electromagnetic - Waves that do not use/need matter to carry energy
Are all transverse waves
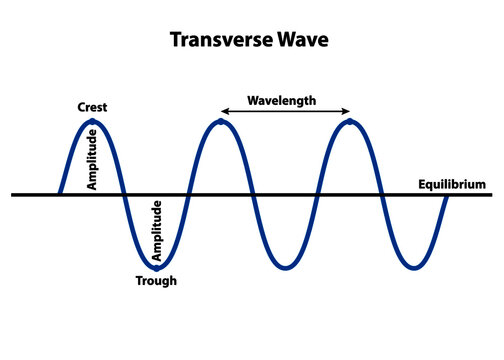
Parts of a Transverse Wave
Crest - Midline → Top
Trough - Midline → Bottom
Amplitude - Top → Midline or Midline → Bottom
Wavelength - Crest 1 → Crest 2
Frequency - Oscillations per second
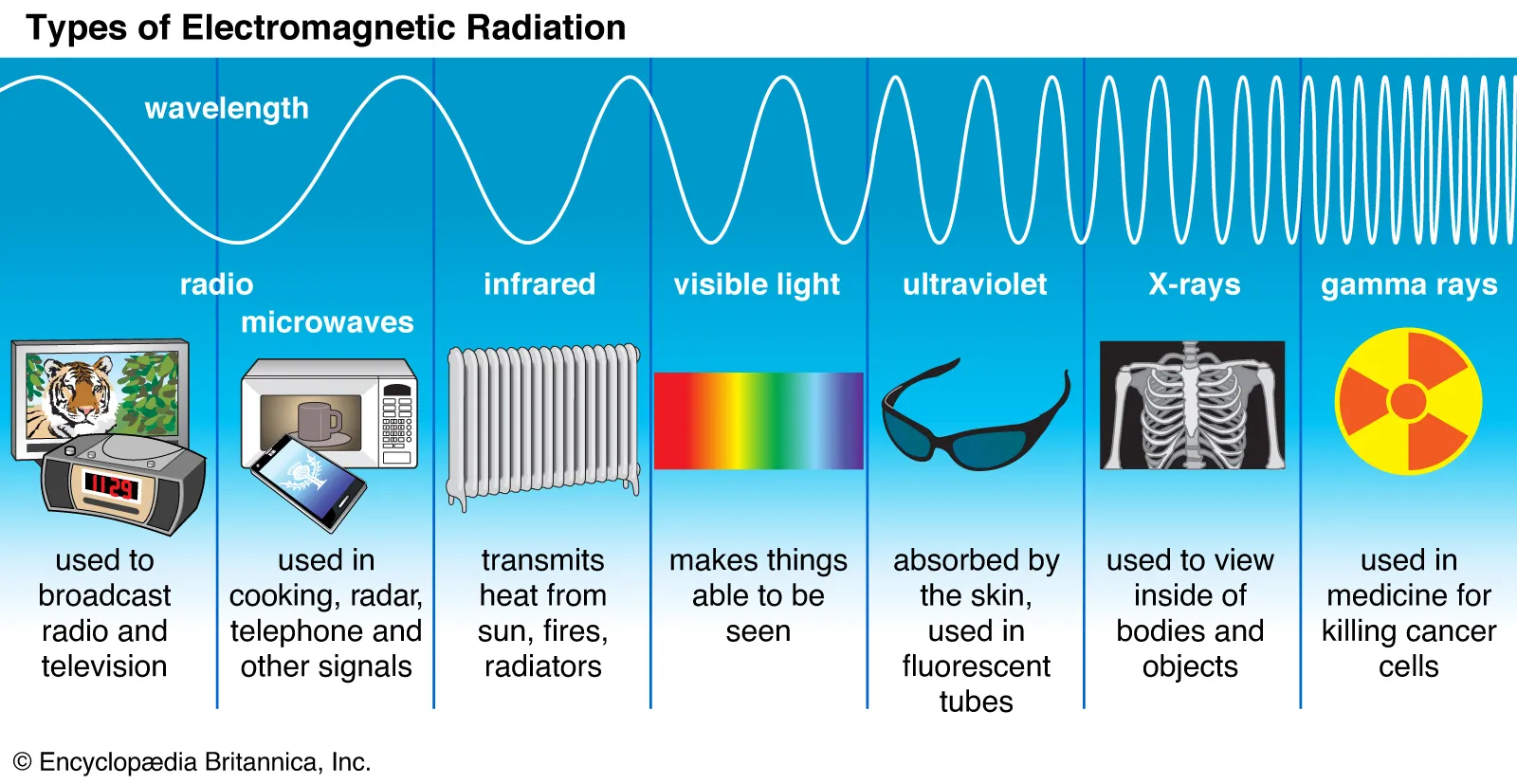
Electromagnetic Waves
Each type is contained on a different part of the electromagnetic spectrum
High frequency/low wavelength → low frequency/high wavelength:
Gamma Rays → X-Rays → Ultraviolet → Visible Light → Infrared → Microwaves → Radio waves
Energy transferred
Energy = plank’s constant * frequency
Plank’s constant ~ 6.63 * 10^-34
Frequency, Wavelength, & Speed
Speed of light = frequency(hertz) * wavelength(meters)
Slower = Smaller wavelength
Uses
Gamma Rays - Used to destroy cancer cells
Ultraviolet Rays - Disrupts DNA production in bacteria & viruses
X-Rays - Used for medical imaging
Infrared - Heat lamps, remote controls
Microwaves - Warm food
Radio waves - Long distance transmission of information
Polarization - Modifying light by forcing it to only vibrate in a singular plane
The Modern Atomic Theory
Theories of Light
Newton - Corpuscular theory; light is made of particles
Thomas Young - Diffraction double slit experiment; light behaves like waves
Heinrich Hertz - Photoelectric effect observed; also acts like a particle
Photoelectric Effect
Electrons are emitted when electromagnetic waves hit a material
Shows particle like behavior
Einstein proposes light is a stream of particles called photons
Energy = Plank’s constant * frequency
Emission Spectrum
Visible light spectrum where emitted light produce colored bands
Some metals showed up as discrete lines
Bohr Model
Electrons orbit nucleus made of protons & neutrons
Electron Cloud Model
Electrons have probable locations
Each cloud has different energy levels
The Structure of the Atom
Atom - Smallest particle of a substance
Made of a nucleus surrounded by orbitals
Consists of 3 types of particals
Protons - Positively charged
Neutrons - Particle w/o charge
Electron - Negatively charged electron
Charge of proton = negative charged of electron
If charge of atom = 0, then the atoms has == number of protons & electrons
Locations
Nucleus - Contains all the protons & neutrons
Orbitals - Contains the electrons
Atomic mass unit
1/12 of a C12 atom
~ 1.660538921 * 10^-24 g
Proton - 1 amu
Neutron - 1 amu
Electron - 0.0006 amu
Atomic Number
of Protons in an atom
Ions
Charged atoms
Changed number of electrons
Atomic Mass / Mass Number
of Protons + # of Neutrons
Isotopes
Different # of neutrons
Unit 2 - Understanding the Atom
The Historical Development of Atomic Theory
Democritus - Early philosopher who proposed the existence of the atom
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
First scientific theory of the atom
Based on Joseph Proust and other scientists’ research
Proust’s research: each compound contains exact proportions
Law of definite proportions
Atoms are indivisible
Elements are made of identical atoms unique to each element
Compounds are made of 2+ atoms in fixed proportion
A chemical reaction is the rearrangement of atoms
Discovery of the Electron (Cathode Ray Experiment)
By JJ Thompson
Led to the Plum Pudding Model
Oil Drop Experiment
By Millikan
Thompson found charge & mass of electron
Discovery of Nucleus (Gold Foil Experiment)
By Rutherford
Most particles pass directly through the atom, some get deflected
→ Most of the atom is empty space, with a large particle at the center
Quiz: https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/5faee2a376564d001b6fb43a/the-historical-development-of-atomic-theory
Electromagnetic Waves
Vocab
Electric Field - The area surrounding a charged object in which it can act upon another charged object
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The frequency spectrum containing all electromagnetic waves

Electromagnetic Wave
A combination of electric & magnetic fields radiating from a source @ the speed of light.
The electric & magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular of each other
Caused by disturbing charged particles, which then oscillate and produce oscillating fields
Source produces an magnetic field, the magnetic field then produces an electric field, the electric field the produces another magnetic field, repeat forever
Magnetic Field - The area surrounding a magnetic object in which it can act upon an object
Polarization
Types of Waves
Mechanical - Waves that use matter to carry energy
Electromagnetic - Waves that do not use/need matter to carry energy
Are all transverse waves
Parts of a Transverse Wave
Crest - Midline → Top
Trough - Midline → Bottom
Amplitude - Top → Midline or Midline → Bottom
Wavelength - Crest 1 → Crest 2
Frequency - Oscillations per second

Electromagnetic Waves
Each type is contained on a different part of the electromagnetic spectrum
High frequency/low wavelength → low frequency/high wavelength:
Gamma Rays → X-Rays → Ultraviolet → Visible Light → Infrared → Microwaves → Radio waves
Energy transferred
Energy = plank’s constant * frequency
Plank’s constant ~ 6.63 * 10^-34
Frequency, Wavelength, & Speed
Speed of light = frequency(hertz) * wavelength(meters)
Slower = Smaller wavelength
Uses
Gamma Rays - Used to destroy cancer cells
Ultraviolet Rays - Disrupts DNA production in bacteria & viruses
X-Rays - Used for medical imaging
Infrared - Heat lamps, remote controls
Microwaves - Warm food
Radio waves - Long distance transmission of information
Polarization - Modifying light by forcing it to only vibrate in a singular plane
The Modern Atomic Theory
Theories of Light
Newton - Corpuscular theory; light is made of particles
Thomas Young - Diffraction double slit experiment; light behaves like waves
Heinrich Hertz - Photoelectric effect observed; also acts like a particle
Photoelectric Effect
Electrons are emitted when electromagnetic waves hit a material
Shows particle like behavior
Einstein proposes light is a stream of particles called photons
Energy = Plank’s constant * frequency
Emission Spectrum
Visible light spectrum where emitted light produce colored bands
Some metals showed up as discrete lines
Bohr Model
Electrons orbit nucleus made of protons & neutrons
Electron Cloud Model
Electrons have probable locations
Each cloud has different energy levels
The Structure of the Atom
Atom - Smallest particle of a substance
Made of a nucleus surrounded by orbitals
Consists of 3 types of particals
Protons - Positively charged
Neutrons - Particle w/o charge
Electron - Negatively charged electron
Charge of proton = negative charged of electron
If charge of atom = 0, then the atoms has == number of protons & electrons
Locations
Nucleus - Contains all the protons & neutrons
Orbitals - Contains the electrons
Atomic mass unit
1/12 of a C12 atom
~ 1.660538921 * 10^-24 g
Proton - 1 amu
Neutron - 1 amu
Electron - 0.0006 amu
Atomic Number
of Protons in an atom
Ions
Charged atoms
Changed number of electrons
Atomic Mass / Mass Number
of Protons + # of Neutrons
Isotopes
Different # of neutrons
 Knowt
Knowt