
Period 8: 1945-1980
 8.1 Contextualizing Period 8
8.1 Contextualizing Period 8
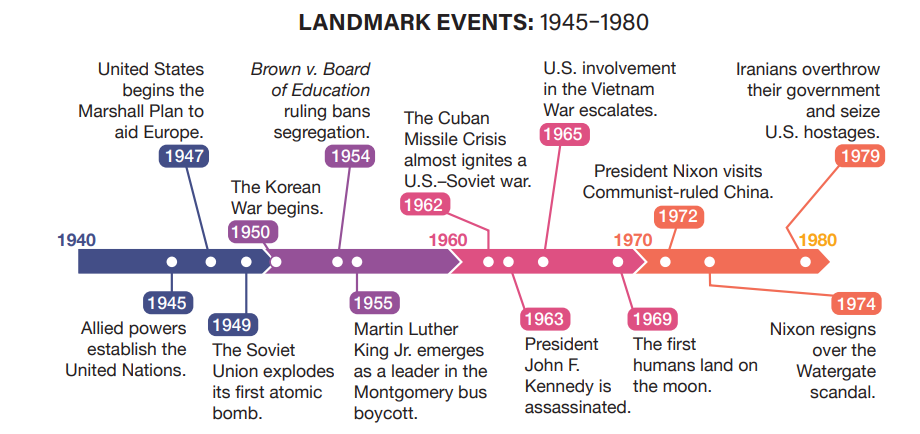
U.S. emerged from WWII w/ the world’s largest & strongest economy
Cold War lasted b/t the U.S. and Soviet Union from 1945-80
Shown in U.S. involvement in Korean + Vietnam Wars & Cuban Missile Crisis
Second Red Scare, due to spies giving communists secrets about the atomic bomb
Communists were hunted down throughout American institutions & gov’t
Economic growth from 1950s-60s: little overseas competition & ppl moved to Sun Belt states
Civil rights movement & push for equality
Frustration over Vietnam & opposition to civil rights → turn toward Conservatism
Many lost confidence in the U.S. gov’t
8.2 The Cold War from 1945-80
Origins of the Cold War
WWII alliance b/t USA & USSR was a temporary halt in their poor relations in the past (USSR wasn’t recognized by the US until 1933)
UN was founded in 1945 → Soviets rejected the Baruch Plan, which aimed to eliminate atomic weapons
Also rejected invitation to the World Bank - they viewed it as an instrument of capitalism
Soviets held occupation in countries in Central + E. Europe & held elections that favored Communist candidates
Many argued for satellites/buffer states, to protect from another Hitler-like invasion
Eastern Germany → German Democratic Republic, a Communist state under Soviet occupation
Soviets believed in war reparations; U.S. & GB didn’t to allow for economic recovery
Iron Curtain: the division b/t the U.S. allies in W. Europe & Soviet allies in E. Europe
Containment in Europe
1947: Truman adopted a containment policy to prevent Soviet expansion w/o starting a war
In response to: Communist-led uprising in Greece & Soviet demands for some control of a water route in Turkey
Truman Doctrine: Truman asked Congress for $400 million to assist the “free people” of Greece and Turkey against “totalitarian” regimes → bipartisan support
European discontent → growth of the Communist party
Marshall Plan: U.S. economic aid to help European nations revive their economies & strengthen democratic governments → $12 billion in aid was granted
Ended most Communist threats & encouraged U.S. prosperity, BUT deepened the right b/t non-Communist West and Communist East
Berlin Airlift: Soviets cut off all land access to Berlin, so Truman ordered U.S. planes to fly in supplies to the people of W. Berlin → 11-month long blockage led to E. & W. Berlin
NATO: Ten European nations + U.S. & Canada, defending all members from outside attack
Soviets countered w/ the Warsaw Pact to defend Communist states of E. Europe
U.S. passed the National Security Act, which helped w/ foreign policy & gathering information on foreign governments
Soviets developed their first atomic bomb in 1949 & Truman developed the H-bomb, which was more powerful than the bomb dropped on Hiroshima
NSC-68: measures necessary to fight the Cold War (e.g. increase U.S. defense spending and form alliances with non-Communist countries around the world)
Cold War in Asia
Japan was under the control of U.S. General Douglas MacArthur
A parliamentary democracy was set up + new constitution made Japan dependent on the U.S. for military protection
1951: Japan gave up claims to Korea + some Pacific islands → U.S. ended occupation, but stayed in Japan to protect against Communism
1946: Philippines became independent, but the U.S. retained important naval + air bases
China was divided between nationalists and communists → civil war
U.S. gave $400 million to the nationalists → 80% of U.S. military supplies ended up in Communist hands
Mainland China became Communist & Taiwan was where nationalists retreated to
After the defeat of Japan, Korea was split into North (ruled by Soviets) & South (ruled by U.S.)
June 1950: N. Korea invaded S. Korea
The UN + Truman sent troops to help S. Korea → N. Koreans initially pushed forces to the tip of the peninsula
UN forces pushed too far North toward the Chinese border, so China drove them out of N. Korea
Peace talks began in July 1951
Truman’s containment policy worked in Korea
His admin used this war to push for military expansion
Republicans attacked him as being “soft on communism” due to the success of Communists in China + Korea
Eisenhower and the Cold War
Focused on foreign policy + international crises throughout his 2 terms
Secretary of State Dulles criticized Truman’s containment policy as being too passive
He believed in challenging Communism - brinkmanship - which pleased conservatives
Dulles advocated for relying on nuclear weapons to save money
The U.S. developed a hydrogen bomb, but the Soviets caught up
Massive retaliation seemed like mutual annihilation to many
Korean Armistice: fighting stopped, most U.S. troops were withdrawn, and Korea was divided near the 38th parallel
U.S.-Soviet Relations
Spirit of Geneva: a slowdown in the arms race — “atoms of peace” presented to the UN
Soviets withdrew troops from Austria & had peaceful relations w/ Greece & Turkey
New Soviet leader supported “peaceful coexistence” in 1956
Hungarian Revolt: uprising that overthrew a gov’t back by Moscow — wanted to pull out of the Warsaw Pact
Soviet tanks crushed this uprising & restored control over Hungary — U.S. took no action
1957: Soviet Union launched Sputnik I and II → American embarrassment
Intensified fears of nuclear war
NASA created to compete with Russia + NDEA passed to improve funding for schools
Second Berlin Crisis: Soviet leader gave the West 6 months to pull its troops out of W. Berlin, before turning over the city to E. Germans
U.S. refused & invited Soviet to the U.S. — put off the crisis
U-2 Incident: Russians shot down a U.S. spy plane (learn about Soviets missile program)
Soviet leader denounced the U.S. → ending the “thaw” to the Cold War
Communism in Cuba
Rise of Fidel Castro → nationalized American owned businesses & properties in Cuba
Eisenhower cut off U.S. trade with Cuba
Castro turned to Soviets → Eisenhower allowed the CIA to train anti-communist Cuban exiles
Eisenhower’s Legacy
Helped reduce Cold War tensions → first arms limitations in 1958
Military-Industrial Complex: Eisenhower discussed negative impact of Cold War in his farewell address - he warned against acquiring unwarranted influence
To the Brink of War and Back
JFK elected in 1960 for attacking recession & allowing Soviets to lead the arms race during Eisenhower’s administration
Bay of Pigs Invasion: plan to use Cuban exiles to overthrow Castro’s regime
Failed to set off an uprising & Kennedy didn’t use additional U.S. forces to save them
Castro used this to get more Soviet aid
JFK met with the Soviet leader in 1961, who demanded the U.S. pulled its troop out Berlin
Kennedy refused → E. Germans + Soviets built a wall around W. Berlin to stop E. Germans from fleeing to the West
Soviet & U.S. tanks faced off & Kennedy assured W. Germany that they had U.S support
Cuban Missile Crisis (1962): Soviets built underground missile sites that would attack the U.S. in Cuba
Kennedy set up a naval blockade of Cuba until the weapons were removed
After 13 days of tension: Soviet leader removed the missile from Cuba, IF the U.S. agreed not to invade the island
Established a telecommunications network b/t Washington & Moscow
Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (1963): signed by Soviets, U.S., and almost 100 other nations
JFK implemented the flexible-response policy to reduce the risk of using nuclear weapons
Lyndon Johnson Becomes President
Focused on domestic reforms, but:
Continued containment policy → block spread of Communism
Escalated the Vietnam War & engage the Soviets
Negotiated agreements with Soviets to control nuclear weapons
Outer Space Treaty
Non-Proliferation Treaty: agreed to not help other countries develop/acquire nuclear weapons
Nixon’s Detente Diplomacy
Bring Americans together & focused on int’l relations
Ended Vietnam War + reduced Cold War tensions
Detente: took advantage of rivalry b/t China and the Soviets → reduced Cold War tensions
Nixon’s relationship with China led to arms control with the Soviets
Treaty that limited certain missiles
Another Chill in the Cold War
1979: U.S. recognized the People’s Republic of China as the official gov’t of China
Soviets invade Afghanistan (1979): ended the improvement of U.S.-Soviet relations
U.S. feared USSR controlling the oil-rich gulf
Pres. Carter placed an embargo on grain exports + sale of high tech to the USSR & boycotted the 1980 Olympics in Moscow
8.3 The Red Scare
Rooting Out Communists
Loyalty Review Board (1947): investigated the background of 3 mil+ federal employees
Thousands lost jobs
Smith Act: illegal to advocate or teach the overthrow of the gov’t by force/belong to an organization with this objective
e.g.) Leaders of the American Communist Party were jailed
McCarran Internal Security Act (1950): unlawful to advocate/support the establishment of totalitarian gov’t → created detention camps for subversives
HUAC: searched for Communists in gov’t & its influence throughout various organizations
Limited freedom of expression — loyalty oaths were common for writers + teachers
Espionage Cases
Hiss Case: Alger Hiss was convicted of perjury and sent to prison for being a communist
Due to a communist testimony + investigative work of Nixon
Rosenberg Case: found guilty of treason + executed in 1953
The Rise and Fall of Joseph McCarthy
Republican senator who advanced his career over the growing concern of communism
Used unsupported accusations about Communists in gov’t to discredit the Truman admin
Exposed in 1954 for his “reckless cruelty”
Fear of Communist takeover was overblown
8.4 Economy after 1945
Military members needed to find jobs after WWII → increased consumer demand for autos + housing + gov’t roadbuilding → economic growth
Postwar Economy
Employment Act of 1946: created the Council of Economic Advisers, who advised the president + Congress on promoting nat’l economic welfare
GI Bill of Rights: helps 2 mil+ GIs attend college & 5 mil more receive other training
Veterans received low-interest, gov’t-backed loans to buy homes, farms, & start businesses
Increased racial gap → mainly benefited White veterans
Baby Boom: 50 million babies b/t 1945-60 — due to more marriages + births
1960: 1/3 of all married women worked outside the home
Levittown: 17k mass-produced, low-priced family homes → suburban growth
Only for white families
Rise of the Sun Belt: warm climate, lower taxes, & economic opportunities in defense-related industries
Inflation post WWII → workers + unions demanding higher wages
Truman vs. the Republican Congress
22nd amendment (1951): president had a maximum of 2 full terms in office
Taft-Hartley Act (1947): probusiness act passed by Congress, which checked the power of growing unions
e.g.) Outlawing secondary boycotts
Election of 1948: though Truman’s popularity was at a low point, he won the election
The Fair Deal: ambitious reform program (e.g. nat’l health insurance & civil rights legislation)
Congress blocked most reforms EXCEPT for an increase in minimum wage
Most bills defeated due to: Truman’s conflicts w/ Congress & foreign policy concerns of the Cold War
Eisenhower in the White House (1953-61)
Eisenhower had a style of leadership that emphasized the delegation of authority → he filled his cabinet w/ successful corporate executives
Prioritized balancing the budget
He accepted many New Deal reforms & even expanded some (e.g. extending social security & increasing minimum wage)
Created the Department of HEW & soil-bank program for farmers (reduce farm production, to increase farm income)
Opposed nat’l health insurance and nat’l aid to education
Highway Act: authorized 42k miles of interstate highways linking all the nation’s major cities
New taxes on fuel, tires, & vehicles → improve nat’l defense
Hurts railroads + environment
Steady economic growth
Economy under the Democrats (1961-69)
New Frontier Programs: JFK called for education aid, nat’l support to healthcare, & civil rights
Few passed under JFK’s administration; most passed under Johnson
Trade Expansion Act (1962): authorized tariff reductions w/ W. european nations
Stimulated economy by increasing spending on defense + space exploration
Johnson’s Domestic Reforms: persuaded Congress to pass an expanded version of JFK’s civil rights bill & JFK’s proposal for an income tax cut
Nixon’s Domestic Policy
The New Federalism
Nixon tried to slow down the growth of Johnson’s Great Society by proposing the Family Assistance Plan — Congress defeated this
Shifted some responsibility for social programs from the nat’l to state & local levels
Revenue sharing/New Federalism: local gov’ts could block grants to address local needs
Nixon’s Economic Policies
1970 recession = stagflation: economic slowdown + high inflation
Tried cutting federal spending (didn’t work) → Keynesian economic and deficit spending
Took the $ off the gold standard & additional 10% tax on all imports
Recession ended in 1972 → Congress increased social security benefits
Ford and Carter Confront Inflation
Inflation slowed economic growth → consumers + business could no longer afford high interest rates w/ high prices
Middle-class taxpayers got pushed into higher tax brackets → “taxpayers revolt”
Chairman of the Federal Reserve Board pushed higher interest rates → hurt the automobile + business industries, which laid off thousands of workers
Ultimately helped reduce inflation
Economic recovery of other nations challenged the U.S. position as the world’s strongest economy
8.5 Culture after 1945
1950s: consensus about political issues and conformity
Consumer Culture and Conformity
Television became a center of family life → viewers watched westerns, sports, comedies, etc
Certain shows emphasized conservative values by depicting suburb stereotypes
Advertising promoted material wants → suburban shopping centers + credit cards
Rise of franchise operations → new marketing techniques + standardized products
Paperback books were extremely popular
LP records were popular → teenagers listened to rock and roll
Conglomerates with diversified holdings dominated various industries (e.g. hotels & banking)
More Americans held white-collar jobs than blue-collar jobs
Large corporations promoted conformity (e.g. dress code)
Post WWII: organized religions expanded — new religious tolerance
Women’s Roles
Baby boom + running a home in the suburbs → most women did homemaking
Women’s role in the home was reaffirmed in mass media
Well-educated women in the middle class + middle aged women entered the workforce
Lower wages
Social Critics
Books & media created to address conformist society & failures of wealthy Americans
e.g) Catcher in the Rye
Beatniks: rebellious writers + intellectuals who advocated being spontaneous, using drugs, and rebelling against societal standards
Assassination and the End of the Postwar Era
JFK was assassinated in 1963
Counterculture emerged in the late 1960s due to: the war’s failures, conspiracy theories of JFK’s death, conflicts over the civil rights movement, and materialism
8.6 Early Steps in the Civil Rights Movement, 1945-60
Origins of the Movement
1950s: African Americans focused on fighting racial segregation
South was segregated by law & there were poll taxes, literacy test, etc.
Truman’s Leadership: established the Committee on Civil Rights & desegregated the armed forces
Cold War: U.S. reputation for freedom + democracy weren’t represented in racial segregation + discrimination
Desegregating the Schools and Public Places
NAACP had been fighting to overturn the decision made in Plessy v. Ferguson
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka: segregation of public schools violated the 14th amendment
Resistance in the South: 101 members of Congress signed the “Southern Manifesto,” condemning the Supreme Court for abuse of power
KKK made a comeback
Little Rock Nine: Arkansas’ governor used the national guard to prevent 9 African American students from attending a previously all-white high school
Eisenhower sent federal troops to protect the Black students
Montgomery Bus Boycott: Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat on a bus → police were called and she was arrested
African Americans boycotted city buses
MLK Jr. emerged as leader of the nonviolent movement to end segregation
Supreme Court eventually ruled segregation laws were unconstitutional
Nonviolent protest:
Southern Christian Leadership Conference (1957): ministers and churches to get behind the civil rights struggle
Sit-in movement rose to call attention to injustice of segregated facilities
Growing impatience in the 1960s → violent confrontations
President Eisenhower signed civil rights laws in 1957 & 1960
Provided for a Civil Rights Commission & protected voting rights of African Americans
8.7 America as a World Power
Post WW2 = decolonisation / the collapse of colonial empires
Unrest in the “Third World”
New developing nations often lacked stable political + economic institutions
Need for foreign aid made them pawns of the Cold War
1960: more than 90% of U.S. foreign aid went to 3rd World nations
The Middle East
Eisenhower’s administration conducted foreign policy with covert action / undercover intervention of politics of other nations
Suez Crisis: Egypt seized the British and French owned Suez Canal, which threatened W. Europe’s oil supply from the Middle East
Britain + France retook the canal, but Eisenhower sponsored a UN resolution condemning the invasion of Egypt
Eisenhower Doctrine: U.S. pledged economic + military aid to any Middle Eastern country threatened by communism
Middle eastern countries + Venezuela formed OPEC to expand political power based on oil policies
Yom Kippur War: Syrians + Egyptians attacked Israel to recover previously lost lands
Nixon ordered provided Israel with arms, allowing them to win → Arab members of OPEC placed an embargo on oil sold to Israel’s supporters
Worldwide oil shortage + inflation
Camp David Accords: President Carter arranged a peace settlement b/t Egypt and Israel
Anti-American sentiment grew in Iran → Iranian militants seizing the U.S. Embassy there & holding 50+ staff members as hostages
Latin America
U.S. oppositions to communism often led Washington to support corrupt + ruthless dictators, esp. in Latin America
JFK set up the Peace Corps (technical aid to developing countries) & the Alliance of Progress (land reform + economic development in Latin America)
President Johnson judged neighbors based on their commitment against communism
Deployed troops to prevent Communist takeover in the Dominican Republic
Similar to “Big Stick” policy — preventing Communist gov’ts from coming to power in the W. hemisphere
Carter’s administration negotiated a new treaty for the Panama Canal — granting people of Panama to have control of the canal
Policies in Africa
Civil War broke out in the Congo after gaining freedom → U.S. helped UN stop the insurrection
Nixon admin. strengthened ties w/ White minority gov’ts & the CIA spent millions to prevent Black rebels from overthrowing control in Angola
U.S. decided to no longer back White minority gov’ts
Carter focused on human rights for foreign policy — appointed Andrew Young as U.S. ambassador for the UN
Championed the cause worldwide
Limits of a Superpower
By the 1970s the U.S. began to lose its competitive edge gained from WW2
8.8 The Vietnam War
Eisenhower’s Domino Theory
1954: France gave up Indochina (Laos, Cambodia, & Vietnam)
Vietnam was divided until a general election: North = communist; South = anti-Communist & led by Diem
Domino theory: if S. Vietnam fell under Communist control, so would other nations in SE Asia
SEATO: regional defense pact b/t 8 nations to defend one another in case of an attack within the region
Escalation of the Vietnam War in the 1960s
JFK adopted Eisenhower’s Domino Theory → continued U.S. military aid to S. Vietnam
Diem was unpopular → assassinated
Vietnam had 7 different governments in 1964
Tonkin Gulf Resolution: passed by Johnson + Congress & allowed LBJ to take ‘all necessary measures’ to protect U.S. interests in Vietnam
America’s War
Operation Rolling Thunder: authorized by Johnson - prolonged air attack against N. Vietnam
1965: Johnson used U.S. combat troops to fight
Credibility gap: Misinformation from military + civilian leaders & Johnson’s reluctance to discuss the scope + costs of the war
“Hawks”: supporters of the war - believed the war was an act of Soviet-backed communism against S. Vietnam
“Doves”: opponents of the war - viewed the conflict as a civil war b/t Vietnamese nationalists v. communists
Most opposition from college students, who would be drafted after graduation
Tet Offensive: Vietcong launched a surprise attack on every American base in S. Vietnam
U.S. inflicted heavier losses on Vietcong + recovered lost territory
Millions viewed this as a setback for Johnson’s Vietnam policy
Peace talks took place in 1968 → deadlocked over minor issues
Coming Apart at Home, 1968
Election was divided: Nixon, Hubert Humphrey (Dem), George Wallace (Ind.)
Nixon won majority of electoral votes, but popular vote was close
Richard Nixon’s Vietnam Policy
Vietnamization: reduce U.S. involvement in the war while avoiding the appearance of defeat
Gradually withdrew troops, but gave S. Vietnam money, weapons, & training
Nixon Doctrine: future Asian allies would get U.S. support w/o extensive ground forces
April 1970: U.S. forces invaded Cambodia to destroy Vietnamese Communist bases there
Kent State protest: 4 students died — U.S. Senate repealed Gulf of Tonkin resolution
My Lai massacre: U.S. troops killed women and children here in 1968
Pentagon Papers: secret gov’t study documenting mistakes + deceptions of policymakers in dealing with Vietnam
U.S. & N. Vietnam couldn’t reach a deal → Nixon ordered a massive bombing of N. Vietnam
Paris Accords: U.S. would withdraw the last of its troops in return for 500+ prisoners of war, cease-fire, and free elections in Vietnam
War Power Act: passed by Congress that required the president to report to Congress within 48 hours after taking military action + Congress had to approve military action that last more than 60 days
Defeat in SE Asia
Fail of Saigon (1975): Vietnam was reunified under the Communist gov’t → low point of American prestige overseas
Genocide in Cambodia: Cambodia fell to a Communist faction that killed millions to rid the country of Western influence
8.9 The Great Society
Johnson wanted to expand social reforms of the New Deal → “Great Society”
The War on Poverty
Brought to attention by “The Other America” book
Johnson created: the OEO w/ a billion dollar budget
Self-help programs for the poor: Head Start for preschoolers & Job Corps for vocational education
The Election of 1964
Democratic Congress + President → LBJ won re-election
Great Society Reforms
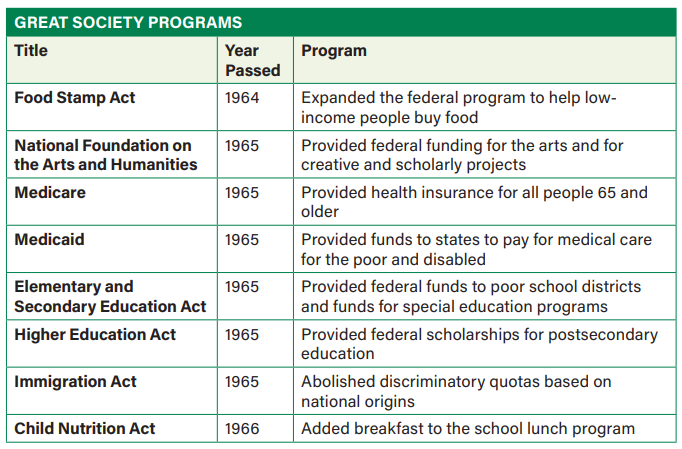
Congress increased funding for: mass transit, public housing, & crime prevention
Passed automotive industry regulations + Johnson created the Department of Transportation
Clean air + water laws enacted & federal parks + wilderness areas were expanded
Johnson jeopardized his domestic achievements by escalating the war in Vietnam
Changes in Immigration
1980s: Most immigrants from Latin America + Asia → escaping Communist takeovers
Immigration Act of 1965: opened the U.S. to immigration from all parts of the world
Rise of undocumented immigrants → employers were penalized for hiring illegal immigrants
8.10 The African American Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s
The Leadership of Dr. MLK Jr.
“Leader of the civil rights movement” → nonviolent protests against segregation
“Letter from Birmingham Jail” moved JFK to support a tougher civil rights bill
March on Washington (1963): 200k+ people joined this peaceful march to support jobs + the civil rights bill
“I Have a Dream” speech
Federal Civil Rights Acts of 1964 and 1965
Civil Rights Act (1964): made segregation illegal in all public facilities (e.g. hotels & restaurants)
Set up Equal Employment Opportunity Commission
24th amendment ratified → abolished poll taxes
March to Montgomery: met with beating & tear gas → televised pictures sent LBJ to send federal troops to protect King + other marchers
Voting Rights Act of 1965: ended literacy tests & federal registrars where Black people had been kept from voting since Reconstruction
Black Muslims and Malcolm X
Preached black nationalism, separatism, and self-improvement
Malcolm X criticized King as “Uncle Tom” & advocated self-defense against white people
Race Riots and Black Power
Malcolm X’s radicalism inspired groups like: Black Panthers, SNCC, & CORE
Race riots erupted in black neighborhoods of major cities w/ increasing casualties + destruction of property
Mid-1960s: civil rights spread to “de facto segregation” & discrimination caused by racist attitudes
King was assassinated in 1968 → nationwide rioting
Revealed anger + frustrations of Black people nationwide
8.11 The Civil Rights Movement Expands
The Women’s Movement
Due to: increased education + employment, civil rights movement, & sexual revolution
The Feminine Mystique (1963): a book encouraging middle-class women to seek fulfillment in professional careers in addition to being a wife/mother
Helped found the Nat’l Organization for Women (NOW)
Congress passed: Equal Pay Act (1963), Civil Rights Act (1964), & Title IX (1972- ended sex discrimination in schools)
Equal Rights Amendment: passed by Congress, but missed ratification by all 38 states
Latino Americans
Many were forced to take low-paying agricultural jobs → exploitation
Cesar Chavez led the United Farm Workers Association
Victories: bilingual education in schools & elections to public office
American Indian Movement
Eisenhower admin made an unsuccessful attempt at assimilation
AIM had militant actions (e.g. takeover of the abandoned Alcatraz Prison)
Indian Self-Determination Act 1975: gave reservations + tribal lands greater control over internal programs, education, and law enforcement
Gay Rights Movement
Police raid at Stonewall → riot & the gay rights movement
Mid-1970s: homosexuality was no longer classified a mental illness
1993: President Clinton settled for “don’t ask, don’t tell” for gays in the military
The Warren Court and Individual Rights
Earl Warren = chief justice of Supreme Court (1953-69)
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka (1954)
Gideon v. Wainwright = state courts must provide counsel for poor defendants (1963)
Miranda v. Arizona (1966) = police inform an arrest person of their right to remain silent
Baker v. Carr (1962): “one man, one vote” election districts needed to be redrawn for equal representation of all citizens
Yates v. USA (1957): 1st amendment protected radical & revolutionary speech, unless it was a clear danger
8.12 Youth Culture of the 1960s
1960s: Baby Boomer generation was going to college → university enrollments increased
Influenced by: civil rights movement & other groups demanding equality
Student Movement and the New Left
Students for a Democratic Society: university students that rebelled against authority
Called for university decisions to be made by a participatory democracy
Free Speech Movement (1964): took place at UC-Berkeley & demanded an end to university restrictions on students’ political activities
Students Against the Vietnam War
Grew w/ the escalation of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War & increase of young men into the draft
Student could usually claim a deferment, but faced draft after college
Draft-card burning, sit-ins, & protests
Chicago Convention: mix of peaceful & radical antiwar protestors damaged property & taunted police
Weather Underground: embraced violence & vandalism → riots, bombings, stealing weapons
Discredit idealism of New Left to many Americans
The Counterculture
Rebellious styles of dress, music, & drug use
Emergence of “hippies” & singers like Bob Dylan
Woodstock Music Festival: hundreds of thousands attended → represented this culture
Sexual Revolution: changed attitudes about casual sex & sexual themes in media
8.13 The Environment and Natural Resources from 1968-80
Origins of the Environmental Movement
Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring explained the negative side effects of insecticide in American agriculture
Barry Commoner found a cancer-causing substance in children’s teeth due to nuclear weapon tests
Public Awareness
Ohio’s Cuyahoga River burst into flames due to oil on the surface
Three Mile Island nuclear power plant accident
Earth Day (1970): reflected growing concerns over air + water pollution & destruction of the natural environment
The Apollo Crew took photos of Earth from space → “Earthrise” images for the environmental movement
The Environmental movement grew extensively by the late 1960s — many organizations (e.g. the Sierra Club) established operations in Washington D.C.
Government Environmental Protection
President Johnson signed almost 300 conservation + beautification bills
Wilderness Act: set aside some federal lands from commercial economic development to preserve their natural state
Environmental Protection Agency: created by Nixon; responsible for enforcing federal policies on various environmental issues (e.g. air + water pollution)
Clean Air Act (1970): regulated air emissions + authorized the EPA to regulate emissions of harmful air pollutants
Endangered Species Act: aimed to protect ecosystems that wildlife depend on
Congress reduced speed limits + many Americans bought more fuel-efficient cars from Japan
1970s were a high point of this movement
8.14 Society in Transition
1970s was marked by many losses → transition to a more conservative Republican government
The Nixon Presidency
Aimed to appeal to the conservative “silent majority” that was disaffected by: civil rights, liberal court rulings, counterculture, etc.
Asked federal courts in the South to delay integration plans & nominated 2 conservative judges to the Supreme Court
Helped Nixon win re-election + his foreign policy success in China + USSR
Watergate Scandal
June 1972: a group of men hired by Nixon’s reelection committee broke into the offices of the Democratic national headquarters — only part of a series of illegal activities
Nixon had ordered wire taps on gov’t employees + reporters to prevent news leaks
Nixon’s aides were called “plumbers” to discredit opponents
There wasn’t solid proof that Nixon ordered these activities, but there was proof of his attempt of an illegal cover up
Nixon chose to resign in Aug. 1974 → Ford became president
Gerald Ford in the White House (1974-77)
Granted Nixon a full & unconditional pardon
Democratic Congress investigated abuse in the executive branch (esp. the CIA)
An Outsider in the White House
The Iranian hostage crisis + economic crisis hurt Carter’s approval by Americans
“National malaise” speech: blamed U.S. problems on a “moral and spiritual crisis”
The Burger Court
Nixon appointed conservative Warren Burger to the Supreme Court
Made several decisions that upset conservatives
Roe v. Wade: protected abortion rights in a 7-2 vote
Conservative Resurgence
Protest movements, a slowing economy, & declining standard of living → many Americans had a conservative reaction to liberal policies
Moral Majority: campaigns to unseat liberal members of Congress
Business interests influenced federal + state gov’ts to lower taxes & weaken labor unions
“Think tanks” promoted free-market ideas
President Johnson implemented affirmative action to ensure minorities had equal access to education
Regents of the University of California v. Bakke ruled while race could be considered, racial quotas were unconstitutional
Conservatives intensified campaigns to end preferences on race + ethnicity
Period 8: 1945-1980
 8.1 Contextualizing Period 8
8.1 Contextualizing Period 8
U.S. emerged from WWII w/ the world’s largest & strongest economy
Cold War lasted b/t the U.S. and Soviet Union from 1945-80
Shown in U.S. involvement in Korean + Vietnam Wars & Cuban Missile Crisis
Second Red Scare, due to spies giving communists secrets about the atomic bomb
Communists were hunted down throughout American institutions & gov’t
Economic growth from 1950s-60s: little overseas competition & ppl moved to Sun Belt states
Civil rights movement & push for equality
Frustration over Vietnam & opposition to civil rights → turn toward Conservatism
Many lost confidence in the U.S. gov’t
8.2 The Cold War from 1945-80
Origins of the Cold War
WWII alliance b/t USA & USSR was a temporary halt in their poor relations in the past (USSR wasn’t recognized by the US until 1933)
UN was founded in 1945 → Soviets rejected the Baruch Plan, which aimed to eliminate atomic weapons
Also rejected invitation to the World Bank - they viewed it as an instrument of capitalism
Soviets held occupation in countries in Central + E. Europe & held elections that favored Communist candidates
Many argued for satellites/buffer states, to protect from another Hitler-like invasion
Eastern Germany → German Democratic Republic, a Communist state under Soviet occupation
Soviets believed in war reparations; U.S. & GB didn’t to allow for economic recovery
Iron Curtain: the division b/t the U.S. allies in W. Europe & Soviet allies in E. Europe
Containment in Europe
1947: Truman adopted a containment policy to prevent Soviet expansion w/o starting a war
In response to: Communist-led uprising in Greece & Soviet demands for some control of a water route in Turkey
Truman Doctrine: Truman asked Congress for $400 million to assist the “free people” of Greece and Turkey against “totalitarian” regimes → bipartisan support
European discontent → growth of the Communist party
Marshall Plan: U.S. economic aid to help European nations revive their economies & strengthen democratic governments → $12 billion in aid was granted
Ended most Communist threats & encouraged U.S. prosperity, BUT deepened the right b/t non-Communist West and Communist East
Berlin Airlift: Soviets cut off all land access to Berlin, so Truman ordered U.S. planes to fly in supplies to the people of W. Berlin → 11-month long blockage led to E. & W. Berlin
NATO: Ten European nations + U.S. & Canada, defending all members from outside attack
Soviets countered w/ the Warsaw Pact to defend Communist states of E. Europe
U.S. passed the National Security Act, which helped w/ foreign policy & gathering information on foreign governments
Soviets developed their first atomic bomb in 1949 & Truman developed the H-bomb, which was more powerful than the bomb dropped on Hiroshima
NSC-68: measures necessary to fight the Cold War (e.g. increase U.S. defense spending and form alliances with non-Communist countries around the world)
Cold War in Asia
Japan was under the control of U.S. General Douglas MacArthur
A parliamentary democracy was set up + new constitution made Japan dependent on the U.S. for military protection
1951: Japan gave up claims to Korea + some Pacific islands → U.S. ended occupation, but stayed in Japan to protect against Communism
1946: Philippines became independent, but the U.S. retained important naval + air bases
China was divided between nationalists and communists → civil war
U.S. gave $400 million to the nationalists → 80% of U.S. military supplies ended up in Communist hands
Mainland China became Communist & Taiwan was where nationalists retreated to
After the defeat of Japan, Korea was split into North (ruled by Soviets) & South (ruled by U.S.)
June 1950: N. Korea invaded S. Korea
The UN + Truman sent troops to help S. Korea → N. Koreans initially pushed forces to the tip of the peninsula
UN forces pushed too far North toward the Chinese border, so China drove them out of N. Korea
Peace talks began in July 1951
Truman’s containment policy worked in Korea
His admin used this war to push for military expansion
Republicans attacked him as being “soft on communism” due to the success of Communists in China + Korea
Eisenhower and the Cold War
Focused on foreign policy + international crises throughout his 2 terms
Secretary of State Dulles criticized Truman’s containment policy as being too passive
He believed in challenging Communism - brinkmanship - which pleased conservatives
Dulles advocated for relying on nuclear weapons to save money
The U.S. developed a hydrogen bomb, but the Soviets caught up
Massive retaliation seemed like mutual annihilation to many
Korean Armistice: fighting stopped, most U.S. troops were withdrawn, and Korea was divided near the 38th parallel
U.S.-Soviet Relations
Spirit of Geneva: a slowdown in the arms race — “atoms of peace” presented to the UN
Soviets withdrew troops from Austria & had peaceful relations w/ Greece & Turkey
New Soviet leader supported “peaceful coexistence” in 1956
Hungarian Revolt: uprising that overthrew a gov’t back by Moscow — wanted to pull out of the Warsaw Pact
Soviet tanks crushed this uprising & restored control over Hungary — U.S. took no action
1957: Soviet Union launched Sputnik I and II → American embarrassment
Intensified fears of nuclear war
NASA created to compete with Russia + NDEA passed to improve funding for schools
Second Berlin Crisis: Soviet leader gave the West 6 months to pull its troops out of W. Berlin, before turning over the city to E. Germans
U.S. refused & invited Soviet to the U.S. — put off the crisis
U-2 Incident: Russians shot down a U.S. spy plane (learn about Soviets missile program)
Soviet leader denounced the U.S. → ending the “thaw” to the Cold War
Communism in Cuba
Rise of Fidel Castro → nationalized American owned businesses & properties in Cuba
Eisenhower cut off U.S. trade with Cuba
Castro turned to Soviets → Eisenhower allowed the CIA to train anti-communist Cuban exiles
Eisenhower’s Legacy
Helped reduce Cold War tensions → first arms limitations in 1958
Military-Industrial Complex: Eisenhower discussed negative impact of Cold War in his farewell address - he warned against acquiring unwarranted influence
To the Brink of War and Back
JFK elected in 1960 for attacking recession & allowing Soviets to lead the arms race during Eisenhower’s administration
Bay of Pigs Invasion: plan to use Cuban exiles to overthrow Castro’s regime
Failed to set off an uprising & Kennedy didn’t use additional U.S. forces to save them
Castro used this to get more Soviet aid
JFK met with the Soviet leader in 1961, who demanded the U.S. pulled its troop out Berlin
Kennedy refused → E. Germans + Soviets built a wall around W. Berlin to stop E. Germans from fleeing to the West
Soviet & U.S. tanks faced off & Kennedy assured W. Germany that they had U.S support
Cuban Missile Crisis (1962): Soviets built underground missile sites that would attack the U.S. in Cuba
Kennedy set up a naval blockade of Cuba until the weapons were removed
After 13 days of tension: Soviet leader removed the missile from Cuba, IF the U.S. agreed not to invade the island
Established a telecommunications network b/t Washington & Moscow
Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (1963): signed by Soviets, U.S., and almost 100 other nations
JFK implemented the flexible-response policy to reduce the risk of using nuclear weapons
Lyndon Johnson Becomes President
Focused on domestic reforms, but:
Continued containment policy → block spread of Communism
Escalated the Vietnam War & engage the Soviets
Negotiated agreements with Soviets to control nuclear weapons
Outer Space Treaty
Non-Proliferation Treaty: agreed to not help other countries develop/acquire nuclear weapons
Nixon’s Detente Diplomacy
Bring Americans together & focused on int’l relations
Ended Vietnam War + reduced Cold War tensions
Detente: took advantage of rivalry b/t China and the Soviets → reduced Cold War tensions
Nixon’s relationship with China led to arms control with the Soviets
Treaty that limited certain missiles
Another Chill in the Cold War
1979: U.S. recognized the People’s Republic of China as the official gov’t of China
Soviets invade Afghanistan (1979): ended the improvement of U.S.-Soviet relations
U.S. feared USSR controlling the oil-rich gulf
Pres. Carter placed an embargo on grain exports + sale of high tech to the USSR & boycotted the 1980 Olympics in Moscow
8.3 The Red Scare
Rooting Out Communists
Loyalty Review Board (1947): investigated the background of 3 mil+ federal employees
Thousands lost jobs
Smith Act: illegal to advocate or teach the overthrow of the gov’t by force/belong to an organization with this objective
e.g.) Leaders of the American Communist Party were jailed
McCarran Internal Security Act (1950): unlawful to advocate/support the establishment of totalitarian gov’t → created detention camps for subversives
HUAC: searched for Communists in gov’t & its influence throughout various organizations
Limited freedom of expression — loyalty oaths were common for writers + teachers
Espionage Cases
Hiss Case: Alger Hiss was convicted of perjury and sent to prison for being a communist
Due to a communist testimony + investigative work of Nixon
Rosenberg Case: found guilty of treason + executed in 1953
The Rise and Fall of Joseph McCarthy
Republican senator who advanced his career over the growing concern of communism
Used unsupported accusations about Communists in gov’t to discredit the Truman admin
Exposed in 1954 for his “reckless cruelty”
Fear of Communist takeover was overblown
8.4 Economy after 1945
Military members needed to find jobs after WWII → increased consumer demand for autos + housing + gov’t roadbuilding → economic growth
Postwar Economy
Employment Act of 1946: created the Council of Economic Advisers, who advised the president + Congress on promoting nat’l economic welfare
GI Bill of Rights: helps 2 mil+ GIs attend college & 5 mil more receive other training
Veterans received low-interest, gov’t-backed loans to buy homes, farms, & start businesses
Increased racial gap → mainly benefited White veterans
Baby Boom: 50 million babies b/t 1945-60 — due to more marriages + births
1960: 1/3 of all married women worked outside the home
Levittown: 17k mass-produced, low-priced family homes → suburban growth
Only for white families
Rise of the Sun Belt: warm climate, lower taxes, & economic opportunities in defense-related industries
Inflation post WWII → workers + unions demanding higher wages
Truman vs. the Republican Congress
22nd amendment (1951): president had a maximum of 2 full terms in office
Taft-Hartley Act (1947): probusiness act passed by Congress, which checked the power of growing unions
e.g.) Outlawing secondary boycotts
Election of 1948: though Truman’s popularity was at a low point, he won the election
The Fair Deal: ambitious reform program (e.g. nat’l health insurance & civil rights legislation)
Congress blocked most reforms EXCEPT for an increase in minimum wage
Most bills defeated due to: Truman’s conflicts w/ Congress & foreign policy concerns of the Cold War
Eisenhower in the White House (1953-61)
Eisenhower had a style of leadership that emphasized the delegation of authority → he filled his cabinet w/ successful corporate executives
Prioritized balancing the budget
He accepted many New Deal reforms & even expanded some (e.g. extending social security & increasing minimum wage)
Created the Department of HEW & soil-bank program for farmers (reduce farm production, to increase farm income)
Opposed nat’l health insurance and nat’l aid to education
Highway Act: authorized 42k miles of interstate highways linking all the nation’s major cities
New taxes on fuel, tires, & vehicles → improve nat’l defense
Hurts railroads + environment
Steady economic growth
Economy under the Democrats (1961-69)
New Frontier Programs: JFK called for education aid, nat’l support to healthcare, & civil rights
Few passed under JFK’s administration; most passed under Johnson
Trade Expansion Act (1962): authorized tariff reductions w/ W. european nations
Stimulated economy by increasing spending on defense + space exploration
Johnson’s Domestic Reforms: persuaded Congress to pass an expanded version of JFK’s civil rights bill & JFK’s proposal for an income tax cut
Nixon’s Domestic Policy
The New Federalism
Nixon tried to slow down the growth of Johnson’s Great Society by proposing the Family Assistance Plan — Congress defeated this
Shifted some responsibility for social programs from the nat’l to state & local levels
Revenue sharing/New Federalism: local gov’ts could block grants to address local needs
Nixon’s Economic Policies
1970 recession = stagflation: economic slowdown + high inflation
Tried cutting federal spending (didn’t work) → Keynesian economic and deficit spending
Took the $ off the gold standard & additional 10% tax on all imports
Recession ended in 1972 → Congress increased social security benefits
Ford and Carter Confront Inflation
Inflation slowed economic growth → consumers + business could no longer afford high interest rates w/ high prices
Middle-class taxpayers got pushed into higher tax brackets → “taxpayers revolt”
Chairman of the Federal Reserve Board pushed higher interest rates → hurt the automobile + business industries, which laid off thousands of workers
Ultimately helped reduce inflation
Economic recovery of other nations challenged the U.S. position as the world’s strongest economy
8.5 Culture after 1945
1950s: consensus about political issues and conformity
Consumer Culture and Conformity
Television became a center of family life → viewers watched westerns, sports, comedies, etc
Certain shows emphasized conservative values by depicting suburb stereotypes
Advertising promoted material wants → suburban shopping centers + credit cards
Rise of franchise operations → new marketing techniques + standardized products
Paperback books were extremely popular
LP records were popular → teenagers listened to rock and roll
Conglomerates with diversified holdings dominated various industries (e.g. hotels & banking)
More Americans held white-collar jobs than blue-collar jobs
Large corporations promoted conformity (e.g. dress code)
Post WWII: organized religions expanded — new religious tolerance
Women’s Roles
Baby boom + running a home in the suburbs → most women did homemaking
Women’s role in the home was reaffirmed in mass media
Well-educated women in the middle class + middle aged women entered the workforce
Lower wages
Social Critics
Books & media created to address conformist society & failures of wealthy Americans
e.g) Catcher in the Rye
Beatniks: rebellious writers + intellectuals who advocated being spontaneous, using drugs, and rebelling against societal standards
Assassination and the End of the Postwar Era
JFK was assassinated in 1963
Counterculture emerged in the late 1960s due to: the war’s failures, conspiracy theories of JFK’s death, conflicts over the civil rights movement, and materialism
8.6 Early Steps in the Civil Rights Movement, 1945-60
Origins of the Movement
1950s: African Americans focused on fighting racial segregation
South was segregated by law & there were poll taxes, literacy test, etc.
Truman’s Leadership: established the Committee on Civil Rights & desegregated the armed forces
Cold War: U.S. reputation for freedom + democracy weren’t represented in racial segregation + discrimination
Desegregating the Schools and Public Places
NAACP had been fighting to overturn the decision made in Plessy v. Ferguson
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka: segregation of public schools violated the 14th amendment
Resistance in the South: 101 members of Congress signed the “Southern Manifesto,” condemning the Supreme Court for abuse of power
KKK made a comeback
Little Rock Nine: Arkansas’ governor used the national guard to prevent 9 African American students from attending a previously all-white high school
Eisenhower sent federal troops to protect the Black students
Montgomery Bus Boycott: Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat on a bus → police were called and she was arrested
African Americans boycotted city buses
MLK Jr. emerged as leader of the nonviolent movement to end segregation
Supreme Court eventually ruled segregation laws were unconstitutional
Nonviolent protest:
Southern Christian Leadership Conference (1957): ministers and churches to get behind the civil rights struggle
Sit-in movement rose to call attention to injustice of segregated facilities
Growing impatience in the 1960s → violent confrontations
President Eisenhower signed civil rights laws in 1957 & 1960
Provided for a Civil Rights Commission & protected voting rights of African Americans
8.7 America as a World Power
Post WW2 = decolonisation / the collapse of colonial empires
Unrest in the “Third World”
New developing nations often lacked stable political + economic institutions
Need for foreign aid made them pawns of the Cold War
1960: more than 90% of U.S. foreign aid went to 3rd World nations
The Middle East
Eisenhower’s administration conducted foreign policy with covert action / undercover intervention of politics of other nations
Suez Crisis: Egypt seized the British and French owned Suez Canal, which threatened W. Europe’s oil supply from the Middle East
Britain + France retook the canal, but Eisenhower sponsored a UN resolution condemning the invasion of Egypt
Eisenhower Doctrine: U.S. pledged economic + military aid to any Middle Eastern country threatened by communism
Middle eastern countries + Venezuela formed OPEC to expand political power based on oil policies
Yom Kippur War: Syrians + Egyptians attacked Israel to recover previously lost lands
Nixon ordered provided Israel with arms, allowing them to win → Arab members of OPEC placed an embargo on oil sold to Israel’s supporters
Worldwide oil shortage + inflation
Camp David Accords: President Carter arranged a peace settlement b/t Egypt and Israel
Anti-American sentiment grew in Iran → Iranian militants seizing the U.S. Embassy there & holding 50+ staff members as hostages
Latin America
U.S. oppositions to communism often led Washington to support corrupt + ruthless dictators, esp. in Latin America
JFK set up the Peace Corps (technical aid to developing countries) & the Alliance of Progress (land reform + economic development in Latin America)
President Johnson judged neighbors based on their commitment against communism
Deployed troops to prevent Communist takeover in the Dominican Republic
Similar to “Big Stick” policy — preventing Communist gov’ts from coming to power in the W. hemisphere
Carter’s administration negotiated a new treaty for the Panama Canal — granting people of Panama to have control of the canal
Policies in Africa
Civil War broke out in the Congo after gaining freedom → U.S. helped UN stop the insurrection
Nixon admin. strengthened ties w/ White minority gov’ts & the CIA spent millions to prevent Black rebels from overthrowing control in Angola
U.S. decided to no longer back White minority gov’ts
Carter focused on human rights for foreign policy — appointed Andrew Young as U.S. ambassador for the UN
Championed the cause worldwide
Limits of a Superpower
By the 1970s the U.S. began to lose its competitive edge gained from WW2
8.8 The Vietnam War
Eisenhower’s Domino Theory
1954: France gave up Indochina (Laos, Cambodia, & Vietnam)
Vietnam was divided until a general election: North = communist; South = anti-Communist & led by Diem
Domino theory: if S. Vietnam fell under Communist control, so would other nations in SE Asia
SEATO: regional defense pact b/t 8 nations to defend one another in case of an attack within the region
Escalation of the Vietnam War in the 1960s
JFK adopted Eisenhower’s Domino Theory → continued U.S. military aid to S. Vietnam
Diem was unpopular → assassinated
Vietnam had 7 different governments in 1964
Tonkin Gulf Resolution: passed by Johnson + Congress & allowed LBJ to take ‘all necessary measures’ to protect U.S. interests in Vietnam
America’s War
Operation Rolling Thunder: authorized by Johnson - prolonged air attack against N. Vietnam
1965: Johnson used U.S. combat troops to fight
Credibility gap: Misinformation from military + civilian leaders & Johnson’s reluctance to discuss the scope + costs of the war
“Hawks”: supporters of the war - believed the war was an act of Soviet-backed communism against S. Vietnam
“Doves”: opponents of the war - viewed the conflict as a civil war b/t Vietnamese nationalists v. communists
Most opposition from college students, who would be drafted after graduation
Tet Offensive: Vietcong launched a surprise attack on every American base in S. Vietnam
U.S. inflicted heavier losses on Vietcong + recovered lost territory
Millions viewed this as a setback for Johnson’s Vietnam policy
Peace talks took place in 1968 → deadlocked over minor issues
Coming Apart at Home, 1968
Election was divided: Nixon, Hubert Humphrey (Dem), George Wallace (Ind.)
Nixon won majority of electoral votes, but popular vote was close
Richard Nixon’s Vietnam Policy
Vietnamization: reduce U.S. involvement in the war while avoiding the appearance of defeat
Gradually withdrew troops, but gave S. Vietnam money, weapons, & training
Nixon Doctrine: future Asian allies would get U.S. support w/o extensive ground forces
April 1970: U.S. forces invaded Cambodia to destroy Vietnamese Communist bases there
Kent State protest: 4 students died — U.S. Senate repealed Gulf of Tonkin resolution
My Lai massacre: U.S. troops killed women and children here in 1968
Pentagon Papers: secret gov’t study documenting mistakes + deceptions of policymakers in dealing with Vietnam
U.S. & N. Vietnam couldn’t reach a deal → Nixon ordered a massive bombing of N. Vietnam
Paris Accords: U.S. would withdraw the last of its troops in return for 500+ prisoners of war, cease-fire, and free elections in Vietnam
War Power Act: passed by Congress that required the president to report to Congress within 48 hours after taking military action + Congress had to approve military action that last more than 60 days
Defeat in SE Asia
Fail of Saigon (1975): Vietnam was reunified under the Communist gov’t → low point of American prestige overseas
Genocide in Cambodia: Cambodia fell to a Communist faction that killed millions to rid the country of Western influence
8.9 The Great Society
Johnson wanted to expand social reforms of the New Deal → “Great Society”
The War on Poverty
Brought to attention by “The Other America” book
Johnson created: the OEO w/ a billion dollar budget
Self-help programs for the poor: Head Start for preschoolers & Job Corps for vocational education
The Election of 1964
Democratic Congress + President → LBJ won re-election
Great Society Reforms

Congress increased funding for: mass transit, public housing, & crime prevention
Passed automotive industry regulations + Johnson created the Department of Transportation
Clean air + water laws enacted & federal parks + wilderness areas were expanded
Johnson jeopardized his domestic achievements by escalating the war in Vietnam
Changes in Immigration
1980s: Most immigrants from Latin America + Asia → escaping Communist takeovers
Immigration Act of 1965: opened the U.S. to immigration from all parts of the world
Rise of undocumented immigrants → employers were penalized for hiring illegal immigrants
8.10 The African American Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s
The Leadership of Dr. MLK Jr.
“Leader of the civil rights movement” → nonviolent protests against segregation
“Letter from Birmingham Jail” moved JFK to support a tougher civil rights bill
March on Washington (1963): 200k+ people joined this peaceful march to support jobs + the civil rights bill
“I Have a Dream” speech
Federal Civil Rights Acts of 1964 and 1965
Civil Rights Act (1964): made segregation illegal in all public facilities (e.g. hotels & restaurants)
Set up Equal Employment Opportunity Commission
24th amendment ratified → abolished poll taxes
March to Montgomery: met with beating & tear gas → televised pictures sent LBJ to send federal troops to protect King + other marchers
Voting Rights Act of 1965: ended literacy tests & federal registrars where Black people had been kept from voting since Reconstruction
Black Muslims and Malcolm X
Preached black nationalism, separatism, and self-improvement
Malcolm X criticized King as “Uncle Tom” & advocated self-defense against white people
Race Riots and Black Power
Malcolm X’s radicalism inspired groups like: Black Panthers, SNCC, & CORE
Race riots erupted in black neighborhoods of major cities w/ increasing casualties + destruction of property
Mid-1960s: civil rights spread to “de facto segregation” & discrimination caused by racist attitudes
King was assassinated in 1968 → nationwide rioting
Revealed anger + frustrations of Black people nationwide
8.11 The Civil Rights Movement Expands
The Women’s Movement
Due to: increased education + employment, civil rights movement, & sexual revolution
The Feminine Mystique (1963): a book encouraging middle-class women to seek fulfillment in professional careers in addition to being a wife/mother
Helped found the Nat’l Organization for Women (NOW)
Congress passed: Equal Pay Act (1963), Civil Rights Act (1964), & Title IX (1972- ended sex discrimination in schools)
Equal Rights Amendment: passed by Congress, but missed ratification by all 38 states
Latino Americans
Many were forced to take low-paying agricultural jobs → exploitation
Cesar Chavez led the United Farm Workers Association
Victories: bilingual education in schools & elections to public office
American Indian Movement
Eisenhower admin made an unsuccessful attempt at assimilation
AIM had militant actions (e.g. takeover of the abandoned Alcatraz Prison)
Indian Self-Determination Act 1975: gave reservations + tribal lands greater control over internal programs, education, and law enforcement
Gay Rights Movement
Police raid at Stonewall → riot & the gay rights movement
Mid-1970s: homosexuality was no longer classified a mental illness
1993: President Clinton settled for “don’t ask, don’t tell” for gays in the military
The Warren Court and Individual Rights
Earl Warren = chief justice of Supreme Court (1953-69)
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka (1954)
Gideon v. Wainwright = state courts must provide counsel for poor defendants (1963)
Miranda v. Arizona (1966) = police inform an arrest person of their right to remain silent
Baker v. Carr (1962): “one man, one vote” election districts needed to be redrawn for equal representation of all citizens
Yates v. USA (1957): 1st amendment protected radical & revolutionary speech, unless it was a clear danger
8.12 Youth Culture of the 1960s
1960s: Baby Boomer generation was going to college → university enrollments increased
Influenced by: civil rights movement & other groups demanding equality
Student Movement and the New Left
Students for a Democratic Society: university students that rebelled against authority
Called for university decisions to be made by a participatory democracy
Free Speech Movement (1964): took place at UC-Berkeley & demanded an end to university restrictions on students’ political activities
Students Against the Vietnam War
Grew w/ the escalation of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War & increase of young men into the draft
Student could usually claim a deferment, but faced draft after college
Draft-card burning, sit-ins, & protests
Chicago Convention: mix of peaceful & radical antiwar protestors damaged property & taunted police
Weather Underground: embraced violence & vandalism → riots, bombings, stealing weapons
Discredit idealism of New Left to many Americans
The Counterculture
Rebellious styles of dress, music, & drug use
Emergence of “hippies” & singers like Bob Dylan
Woodstock Music Festival: hundreds of thousands attended → represented this culture
Sexual Revolution: changed attitudes about casual sex & sexual themes in media
8.13 The Environment and Natural Resources from 1968-80
Origins of the Environmental Movement
Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring explained the negative side effects of insecticide in American agriculture
Barry Commoner found a cancer-causing substance in children’s teeth due to nuclear weapon tests
Public Awareness
Ohio’s Cuyahoga River burst into flames due to oil on the surface
Three Mile Island nuclear power plant accident
Earth Day (1970): reflected growing concerns over air + water pollution & destruction of the natural environment
The Apollo Crew took photos of Earth from space → “Earthrise” images for the environmental movement
The Environmental movement grew extensively by the late 1960s — many organizations (e.g. the Sierra Club) established operations in Washington D.C.
Government Environmental Protection
President Johnson signed almost 300 conservation + beautification bills
Wilderness Act: set aside some federal lands from commercial economic development to preserve their natural state
Environmental Protection Agency: created by Nixon; responsible for enforcing federal policies on various environmental issues (e.g. air + water pollution)
Clean Air Act (1970): regulated air emissions + authorized the EPA to regulate emissions of harmful air pollutants
Endangered Species Act: aimed to protect ecosystems that wildlife depend on
Congress reduced speed limits + many Americans bought more fuel-efficient cars from Japan
1970s were a high point of this movement
8.14 Society in Transition
1970s was marked by many losses → transition to a more conservative Republican government
The Nixon Presidency
Aimed to appeal to the conservative “silent majority” that was disaffected by: civil rights, liberal court rulings, counterculture, etc.
Asked federal courts in the South to delay integration plans & nominated 2 conservative judges to the Supreme Court
Helped Nixon win re-election + his foreign policy success in China + USSR
Watergate Scandal
June 1972: a group of men hired by Nixon’s reelection committee broke into the offices of the Democratic national headquarters — only part of a series of illegal activities
Nixon had ordered wire taps on gov’t employees + reporters to prevent news leaks
Nixon’s aides were called “plumbers” to discredit opponents
There wasn’t solid proof that Nixon ordered these activities, but there was proof of his attempt of an illegal cover up
Nixon chose to resign in Aug. 1974 → Ford became president
Gerald Ford in the White House (1974-77)
Granted Nixon a full & unconditional pardon
Democratic Congress investigated abuse in the executive branch (esp. the CIA)
An Outsider in the White House
The Iranian hostage crisis + economic crisis hurt Carter’s approval by Americans
“National malaise” speech: blamed U.S. problems on a “moral and spiritual crisis”
The Burger Court
Nixon appointed conservative Warren Burger to the Supreme Court
Made several decisions that upset conservatives
Roe v. Wade: protected abortion rights in a 7-2 vote
Conservative Resurgence
Protest movements, a slowing economy, & declining standard of living → many Americans had a conservative reaction to liberal policies
Moral Majority: campaigns to unseat liberal members of Congress
Business interests influenced federal + state gov’ts to lower taxes & weaken labor unions
“Think tanks” promoted free-market ideas
President Johnson implemented affirmative action to ensure minorities had equal access to education
Regents of the University of California v. Bakke ruled while race could be considered, racial quotas were unconstitutional
Conservatives intensified campaigns to end preferences on race + ethnicity
 Knowt
Knowt