
Muscular System
4 Properties of Muscles
Excitability
Contractibility
Extensibility
Elasticity
Functions of the Muscular System
Maintaining posture
Spine(?)
Supporting soft tissue
Movement
Voluntary
involuntary
heart muscles
runnings
Guarding entrances and exits of the body
Opening mouth
‘Making a deposit
Generate heat and maintain body temp
shivering
Types of Muscle Tissue
Cardiac Muscle
Characteristics
Striated
Involuntary movement
Structure
Proteins for striations (sarcerations)
Thick = Actin
Thin = Myiacyn
Short, cylindrical-shaped, branched cells
They break off from each other.
Un-nucleated
Fibers are formed to create a network
Cells connect to each other at intercalated discs
Connects the cells together.
Location
Makes up walls of the wall
How do they work?
Contract quickly and rhythmically.
Visceral (smooth) Muscle
Characteristics
Involuntarily contracted
Non-striated
Structure
Flat, short, spindle-shaped cells
Uni-nucleated
Fibers are arranged to form sheets
Location
Lines internal organs, and vessels
How do they work?
Pull action = Peristalsis.
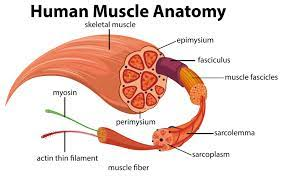
Skeletal Muscle
Characteristics
Striated
Voluntarily controlled
Attached to bones movement of fibrous tissue
Structure
Lond, cylindrical shaped cells
Multinucleated
Fibers are arranged to form bundles. Many bundles are in a Fascicle.
Location
Entire body
How do they work?
Contract quickly, but can’t stay contracted for long.
Muscle Movement
Origin
Start of muscle
Fixed
Insertion
End of the muscle
The part that actually moves
Prime Mover
Muscle that creates the action
Synergists
Help the movement happen
Antagonist
Muscle that opposes the action
Range of Motion
Abduction
Adduction
Flexion
Extension
Elevation
Depression
Rotation
Circumduction
Supination
Pronation
Dorsiflexion
Plantar Flexion
Muscular System
4 Properties of Muscles
Excitability
Contractibility
Extensibility
Elasticity
Functions of the Muscular System
Maintaining posture
Spine(?)
Supporting soft tissue
Movement
Voluntary
involuntary
heart muscles
runnings
Guarding entrances and exits of the body
Opening mouth
‘Making a deposit
Generate heat and maintain body temp
shivering
Types of Muscle Tissue
Cardiac Muscle
Characteristics
Striated
Involuntary movement
Structure
Proteins for striations (sarcerations)
Thick = Actin
Thin = Myiacyn
Short, cylindrical-shaped, branched cells
They break off from each other.
Un-nucleated
Fibers are formed to create a network
Cells connect to each other at intercalated discs
Connects the cells together.
Location
Makes up walls of the wall
How do they work?
Contract quickly and rhythmically.
Visceral (smooth) Muscle
Characteristics
Involuntarily contracted
Non-striated
Structure
Flat, short, spindle-shaped cells
Uni-nucleated
Fibers are arranged to form sheets
Location
Lines internal organs, and vessels
How do they work?
Pull action = Peristalsis.
Skeletal Muscle
Characteristics
Striated
Voluntarily controlled
Attached to bones movement of fibrous tissue
Structure
Lond, cylindrical shaped cells
Multinucleated
Fibers are arranged to form bundles. Many bundles are in a Fascicle.
Location
Entire body
How do they work?
Contract quickly, but can’t stay contracted for long.

Muscle Movement
Origin
Start of muscle
Fixed
Insertion
End of the muscle
The part that actually moves
Prime Mover
Muscle that creates the action
Synergists
Help the movement happen
Antagonist
Muscle that opposes the action

Range of Motion
Abduction
Adduction
Flexion
Extension
Elevation
Depression
Rotation
Circumduction
Supination
Pronation
Dorsiflexion
Plantar Flexion
 Knowt
Knowt