Chapter 5: Algorithms and Programming Part 2
Programming
Programs can be developed for creative expression, to satisfy personal curiosity, to create new knowledge, or to solve problems (to help people, organizations, or society).
Advances in computing have generated and increased creativity in other fields.
Programs Can Be Flexible
When it was targeted to a smaller, local audience simply to satisfy Zuckerberg’s personal curiosity and enjoyment, Facebook was held to much different standards in its development.
When it was made for billions of people to use, changes had to be made to accommodate so many people and to target it toward a wide market of people that might use it—making it appealing to a wider audience.
Programming Design Steps
The first step in programming is planning and identifying programmer and user concerns that can affect the solution.
Consultation and communication with program users are important aspects of program development to solve problems.
When designing a large program, an iterative process helps with correctly coding.
Program Documentation
Program documentation is helpful in all stages of program development.
Documentation does not slow down run speed and is necessary when collaborating or programming alone.
Documentation is useful during initial program development and when modifications are made.
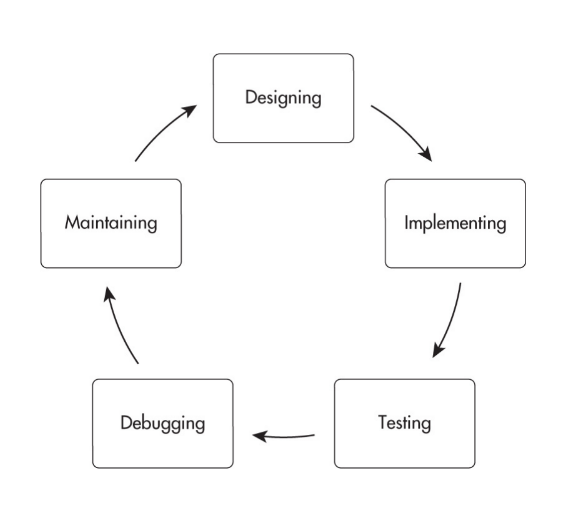
Flowcharts
A flowchart is a way to represent an algorithm visually.
LISTS
Lists are an organized and formatted way of storing and retrieving data.
Each element in a list can be accessed by its index.
Traversing a List
Traversing a list means that you are accessing all the elements of the list one by one.
Procedures
A procedure is a set of code that is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the procedure’s name.
In some languages, a procedure could be called a method or subroutine.
The purpose of the above procedure is to append all negative numbers in aList into bList.
Line 3 iterates through aList.
If the element in aList is less than 0, line 5 causes the element to be appended into bList.
A call to keepPositive(aList, bList) where aList[2, −5, −11, 6] and bList[ ] would result in bList containing the numbers [−5, −11].
Chapter 5: Algorithms and Programming Part 2
Programming
Programs can be developed for creative expression, to satisfy personal curiosity, to create new knowledge, or to solve problems (to help people, organizations, or society).
Advances in computing have generated and increased creativity in other fields.
Programs Can Be Flexible
When it was targeted to a smaller, local audience simply to satisfy Zuckerberg’s personal curiosity and enjoyment, Facebook was held to much different standards in its development.
When it was made for billions of people to use, changes had to be made to accommodate so many people and to target it toward a wide market of people that might use it—making it appealing to a wider audience.
Programming Design Steps
The first step in programming is planning and identifying programmer and user concerns that can affect the solution.
Consultation and communication with program users are important aspects of program development to solve problems.
When designing a large program, an iterative process helps with correctly coding.
Program Documentation
Program documentation is helpful in all stages of program development.
Documentation does not slow down run speed and is necessary when collaborating or programming alone.
Documentation is useful during initial program development and when modifications are made.
Flowcharts
A flowchart is a way to represent an algorithm visually.
LISTS
Lists are an organized and formatted way of storing and retrieving data.
Each element in a list can be accessed by its index.
Traversing a List
Traversing a list means that you are accessing all the elements of the list one by one.
Procedures
A procedure is a set of code that is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the procedure’s name.
In some languages, a procedure could be called a method or subroutine.
The purpose of the above procedure is to append all negative numbers in aList into bList.
Line 3 iterates through aList.
If the element in aList is less than 0, line 5 causes the element to be appended into bList.
A call to keepPositive(aList, bList) where aList[2, −5, −11, 6] and bList[ ] would result in bList containing the numbers [−5, −11].
 Knowt
Knowt