Nutrition
MCAT
Biology
Fundamentals of Nutrition
Factors affecting Nutrition
Macronutrients
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
University/Undergrad
Nutrition fundamentals: basic units of food, energy, metabolism, and real-life references.
Fundamental nutrients
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Water
Vitamins
Minerals
How is energy converted in digesting nutrients?
from Chemical to Cellular energy (through metabolism)
Why can Water be considered a macronutrient?
The body needs a large amount of it. But it does not carry calories.
Some sources of Carbohydrates:
grains
milk
fruits
starchy veggies (compare w/ non-starchy veggies)
Structural categories of Carbohydrates:
simple carbohydrates (AKA: simple sugars/monosaccharides)
complex carbohydrates (AKA: complex sugars/polysaccharides)
What are simple carbohydrates?
Consist of one or two basic units.
Are quickly absorbed by the body and
Provide immediate energy.
What are complex carbohydrates?
Long chains of simple sugars (compare w/ monosaccharides in polysaccharides).
Can be branched/unbranched.
Metabolic process of complex carbohydrates:
(Guide: from digestion to utilization)
Complex sugars → Simple sugars (glucose) → Transported to cells → Use for energy production or Build Macromolecules.
Macronutrients definition:
nutrients needed in large amounts (think macro-)
Classes of Macronutrients:
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Water
(Hint: all are larger groups of nutrients)
Image of Macronutrients
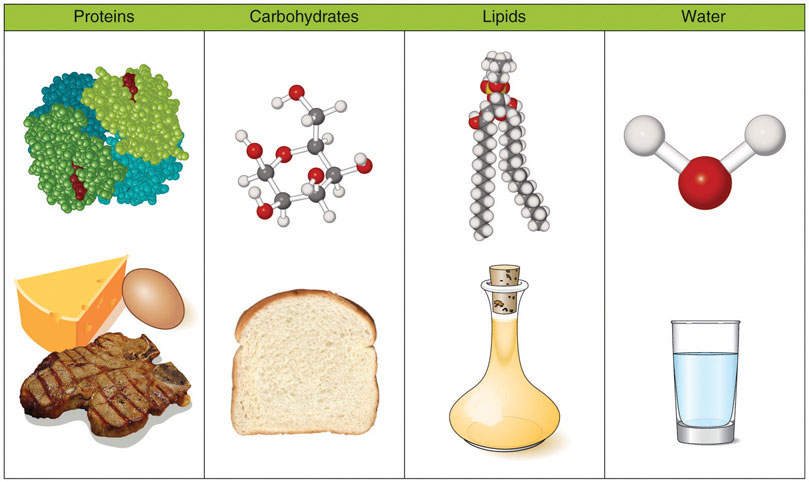
Calorie definition:
a unit of food energy
Factors affecting nutrition:
taste, texture, and appearance
allergies
green food/sustainability choices
development
sex
ethnicity, culture, and religions
beliefs about food
personal preferences
lifestyle
economics
medications and therapy
health (chronic conditions)
alcohol consumption
false advertisement
psychological factors
What are common forms of vegetarianism?
Lacto-ovo vegetarian (most common)
Lacto-vegetarian
Ovo-vegetarian
Vegan
Lacto-ovo vegetarian diet:
includes animal foods, eggs, and dairy.
Lacto-vegetarian diet:
includes dairy, no eggs.
Ovo-vegetarian diet:
include eggs, no dairy.
Vegan diet:
no dairy, eggs, animal foods or by-product.
How do taste, texture, and appearance affect nutrition?
Dislikes in certain foods and avoidance.
How does Development affect nutrition?
Picky eaters have limited development.
How does Sex affect nutrition?
Men consume more calories > women.
Male bodies burn more calories and have a larger size.
How does lifestyle affect nutrition?
Changing diets to achieve goals.
How does Economics affect nutrition?
Low SES = unhealthy food.
How do Medications and Therapy affect nutrition?
Corticosteroids can increase weight.
Intense therapies like chemotherapy can lead to loss of appetite.
How do Psychological Factors affect nutrition?
Severe stress and depression lead to Anorexia and weight loss.
How does Alcohol Consumption affect nutrition?
Increased -OH = decreased appetite.
Why can’t Fiber be digested by the human small intestine?
There are no enzymes in the small intestine to digest the cellulose/cell wall (compare w/ herbivores’ appendix).
How is Fiber broken down in the human body?
By bacteria in the large intestine (esp. colon).
Amount of energy from one gram of Carbohydrates:
4 kcal per 1g of carbohydrates.
How do carbohydrates help the body operate on the organ level?
Supply energy for the heart, kidneys, the nervous system.
Done because of stored glucose.
How is Glucose stored in human bodies?
As glycogen.
What is Glycogen?
Mention its structure, storage form, and purpose of use.
multi-branched polysaccharide of glucose.
main storage form of glucose (in humans)
stored for future and urgent uses.
When and How is Glycogen used in the human body?
broken down when glucose levels decline.
Forms and uses of glycogen is storage in humans:
(Hint: Three forms of energy reserves)
creatine phosphate (very short-term storage)
glycogen phosphate (short-term storage)
triglycerides in adipose tissues (long-term storage)
How are storage molecules of Carbohydrates also called in plants vs. animals?
Plants: starch.
Animals: glycogen.
Define Lipids:
Hydrophobic molecules.
Insoluble in water
Solvents Lipids can dissolve in:
chloroform
ether
benzene
Key functions of Lipids:
energy storage
structural integrity of cellular membranes
insulation and protection for organs
(in adipose tissues)
cell signaling
vitamin absorption
temperature regulation (in homeostasis)
3 Main Types of Lipids:
triglycerides (triacylglycerols)
phospholipids
sterols (steroids)
Some sources of Lipids:
butter
oils
meats
dairy products
nuts
seeds
many processed foods
Amount of energy from one gram of Lipids:
9 kcal per 1g of lipids.
(compare w/ carbohydrates)
Malnutrition: (Definition and Subgroups)
Definition: Lack of necessary or appropriate food.
Subgroups: Undernutrition and Overnutrition.
Overnutrition: (Definition and Outcomes)
Definition: Caloric intake is higher than normal.
Outcomes: Resulting in accumulated adipose tissue → obesity.
Undernutrition: (Definition and Outcomes)
Definition: Intake of nutrients insufficient to meet daily energy requirements.
Outcomes: weight loss, weakness, delayed wound healing, increased infection risk, impaired pulmonary function, prolonged length of hospitalization.
Proteins definition:
Macromolecules
Have chains of subunits: amino acids.
Composition of Proteins:
carbon
oxygen
hydrogen
nitrogen
Composition of Lipids:
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
Composition of Carbohydrates:
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
Sources of proteins:
meats
dairy products
sea food
plant-based foods
soy
What are proteins also referred to as?
(Hint: based on its importance and Greek terminology)
Workhouses of life.
Amount of energy from one gram of Proteins:
4 kcal per 1g of proteins.
(compare w/ carbohydrates)
Key functions of proteins:
Structural integrity of bones, muscles, and skin
Conduct most chemical reactions in the body
Estimated number of protein types in the body:
>100,000 different proteins
How does DNA create proteins?
(Guide: use cooking as an analogy.)
DNA = a cookbook with different recipes.
Transcription = copying a recipe.
Translation = cooking by using the recipe.
Key functions of Water:
chemical reactions in the body
transportation of materials (in and out of body)
cushioning organs and cells
lubricating joints
body temperature regulation
Micronutrients definition:
nutrients supplied to the body in smaller amounts.
Micronutrients composition:
16 essential minerals
13 essental vitamins
Key functions of Micronutrients:
Not main sources of energy.
But assist in chemical reactions.
What form do micronutrients take to assist in chemical reactions?
cofactors
coenzymes (i.e., components of enzymes)
electrolytes
What are cofactors?
(Guide: properties and functions)
can be either inorganic (e.g., metal ions) or organic.
non-protein compounds binding to enzymes.
What are coenzymes?
(Guide: properties and functions)
organic molecules.
act as carriers → transfer chemical groups between enzymes.
What are enzymes?
biocatalysts
catalyze chemical reactions in the body
e.g., producing energy, digesting nutrients, building macromolecules.
What are macro minerals?
Minerals needed in large amounts by adults; >100mg/day.
What are trace minerals?
Minerals needed in small amounts; from 0.2mg → 15mg/day.
Functions of macro minerals Sodium and Potassium:
fluid balance
nerve transmission
muscle contraction
Functions of macro mineral Chlorine:
fluid balance
stomach acid production
Functions of macro mineral Calcium:
bone and teeth health maintenance
nerve transmission
muscle contraction
blood clotting
Functions of macro mineral Phosphorus:
bone and teeth health maintenance
acid-base balance
Functions of macro mineral Magnesium:
protein production
nerve transmission
muscle contraction
Functions of macro mineral Sulfur:
protein production
Functions of trace mineral Iron:
carrying oxygen
assisting in energy production
Functions of trace mineral Selenium:
Antioxidant
Functions of trace mineral Zinc:
protein and DNA production
wound healing
growth
immune function
Functions of trace mineral Iodine:
Thyroid hormone production
growth
metabolism
Functions of trace mineral Copper:
coenzyme
iron metabolism
Functions of trace mineral Manganese:
coenzyme
Functions of trace mineral Fluroide:
bone and teeth health maintenance
tooth decay prevention
Functions of trace mineral Chromium:
assisting insulin in glucose metabolism
Functions of trace mineral Molybdenum:
coenzyme
Which macro minerals are responsible for Fluid balance?
sodium
chloride
potassium
Which macro minerals are responsible for Nerve transmission and Muscle contraction?
sodium
potassium
calcium
magnesium
Which macro minerals are responsible for Bone and teeth health maintenance?
calcium
phosphorus
Which macro mineral is responsible for Blood clotting?
calcium
Which macro mineral is responsible for protein production?
magnesium
sulfur
Which trace mineral is responsible for carrying oxygen and energy production?
iron
Which trace minerals are responsible for growth?
zinc
iodine
Which trace mineral is responsible for:
Thyroid hormone production
Growth
Metabolism?
iodine
Which trace minerals are coenzymes?
copper
manganese
molybdenum
Which trace minerals are responsible for Metabolism?
iodine
copper (iron metabolism)
chromium (glucose metabolism)
Which trace mineral is an Antioxidant?
selenium
Which trace mineral is responsible for:
Bone and teeth health maintenance
tooth decay and prevention
fluoride
Categories of vitamins:
(Guide: based on solubility)
water-soluble
fat-soluble
What are water-soluble vitamins?
vitamin C
all B vitamins
What are all vitamin B’s?
thiamin (B1)
riboflavin (B2)
niacin (B3)
pantothenic acid (B5)
pyridoxine (B6)
biotin (B7)
folate (B9)
cobalamin (B12)
What vitamins are coenzymes?
vitamin B’s
What vitamins are responsible for energy metabolism assistance?
thiamin (B1)
riboflavin (B2)
niacin (B3)
pantothenic acid (B5)
Which vitamin is responsible for amino acid synthesis assistance?
pyridoxine (B6)
Which vitamin is responsible for amino and fatty acids metabolism?
biotin (B7)
Which vitamin is essential for growth?
folate (B9)
Which vitamin is responsible for red blood cell synthesis?
cobalamin (B12)