NUCLEIC ACIDS
It is discovered in 1869 by Swiss physician Friedrich Miescher
Carries the blueprints for proteins, control the life of a cell, determine the inherited traits, and store and express genetic information.
The sugar used to form nucleotides divides nucleic acids into two classes, which are the DNA and the RNA
DNA and RNA, are made of nucleotides containing a pentose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base. DNA is responsible for encoding information that cells use to create proteins, while RNA has multiple forms that carry out various functions within cells, such as facilitating protein synthesis
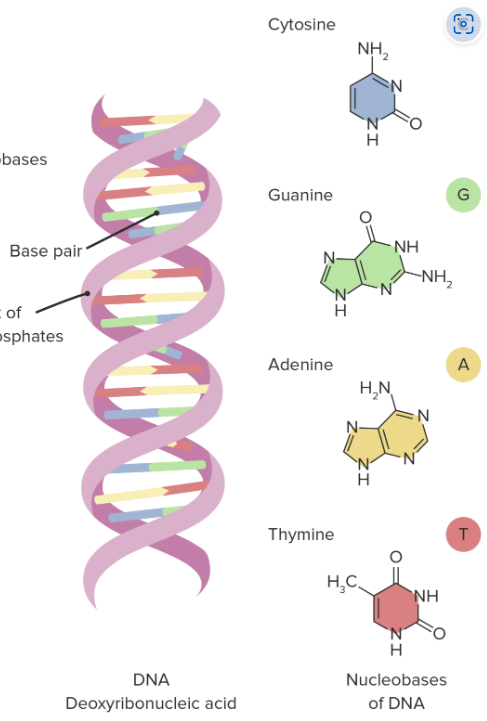
DNA: The Double Helix
DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid
● DNA is the instruction manual for life and is essential for normal development and survival in humans.
● DNA is found in chromosomes in the nucleus, as well as in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
● Genes within the DNA carry instructions for making polypeptide chains and determining the order of amino acids.
● DNA's sole function is to carry genetic information, which is encoded in the nucleotide sequence. The double helix structure of DNA is formed by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs with A: T and G: C pairs being the most stable. The chains are complementary and antiparallel.
RNA: The Mediator of Translation
RNA - Ribonucleic Acid
RNA is a polynucleotide that translates the DNA language into the language of protein biosynthesis.
RNA contains four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
It serves as a short short-lived- lived messenger (messenger RNA) and carrier (transfer RNA) of amino acids to the ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm.
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
While translation is the assembly of amino acids forming the polypeptide chain.
|
|
|---|
NUCLEIC ACIDS
It is discovered in 1869 by Swiss physician Friedrich Miescher
Carries the blueprints for proteins, control the life of a cell, determine the inherited traits, and store and express genetic information.
The sugar used to form nucleotides divides nucleic acids into two classes, which are the DNA and the RNA
DNA and RNA, are made of nucleotides containing a pentose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base. DNA is responsible for encoding information that cells use to create proteins, while RNA has multiple forms that carry out various functions within cells, such as facilitating protein synthesis
DNA: The Double Helix
DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid
● DNA is the instruction manual for life and is essential for normal development and survival in humans.
● DNA is found in chromosomes in the nucleus, as well as in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
● Genes within the DNA carry instructions for making polypeptide chains and determining the order of amino acids.
● DNA's sole function is to carry genetic information, which is encoded in the nucleotide sequence. The double helix structure of DNA is formed by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs with A: T and G: C pairs being the most stable. The chains are complementary and antiparallel.
RNA: The Mediator of Translation
RNA - Ribonucleic Acid
RNA is a polynucleotide that translates the DNA language into the language of protein biosynthesis.
RNA contains four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
It serves as a short short-lived- lived messenger (messenger RNA) and carrier (transfer RNA) of amino acids to the ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm.
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
While translation is the assembly of amino acids forming the polypeptide chain.
|
|
|---|
 Knowt
Knowt