
Chapter 20- The Atmosphere and Environment
COMPOSITION
Air is a mixture of gases. The composition of sample of clean air is as follows:
Nitrogen: 78%, Oxygen: 20%, Carbon dioxide: 0.03%, Water vapour: 5%, Noble gases: 1% (with argon being the most).
Air is separated into its constituent elements by fractional distillation of liquified air.
It is first cooled to a very low temperature, and then gradually warmed. At different boiling points, different gases distil over, and separate.
AIR POLLUTION
The condition in which air contains a high concentration of certain chemicals that may harm living things or damage non-living things.
The substances that cause pollution are called air pollutants. Some pollutants and their effects are given below:
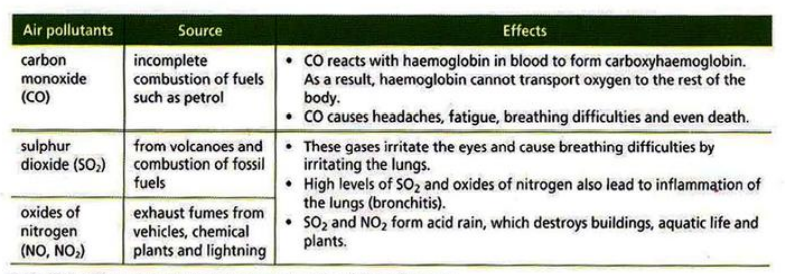
Acid rain is formed when toxic gases mix with water vapour in the atmosphere forming acid. The acid then rains with the rainwater.
Since the pH of the rainwater is not neutral, it causes harmful effects.
It reacts with marbles or carbonates on buildings, corroding them. It also reduces pH of water bodies and soil, harming aquatic and plant life.
The ozone layer is also depleted by chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons which exposes the earth to the UV radiation from the sun.
Air pollution is mainly reduced by switching to renewable resources for power generation, ctalytc converters (redox reactions that convert harmful gases to non-toxic ones) and flu gas desulfurization (removal of sulfur from its compounds).
The depletion in ozone may cause the disruption on weather patterns and the rise in temperature worldwide which is called global warming.
Global warming has adverse effects such as desertification, melting of glaciers and increase in natural disasters, and rapid evaporation increasing the greenhouse effect.
THE CARBON CYCLE
 STEPS FOR PURIFICATION OF WATER
STEPS FOR PURIFICATION OF WATER
Filteration is done to remove floating debris and solid clumps.
Water is screened.
Ammonium sulfate is added to the water to clump particles that settle at the bottom of the water. Water is then poured over.
Chlorine is added to the water to kill bacteria.
Fluorine is added to the water to prevent tooth decay.
Charcoal is added to remove bad odour.
Chapter 20- The Atmosphere and Environment
COMPOSITION
Air is a mixture of gases. The composition of sample of clean air is as follows:
Nitrogen: 78%, Oxygen: 20%, Carbon dioxide: 0.03%, Water vapour: 5%, Noble gases: 1% (with argon being the most).
Air is separated into its constituent elements by fractional distillation of liquified air.
It is first cooled to a very low temperature, and then gradually warmed. At different boiling points, different gases distil over, and separate.
AIR POLLUTION
The condition in which air contains a high concentration of certain chemicals that may harm living things or damage non-living things.
The substances that cause pollution are called air pollutants. Some pollutants and their effects are given below:

Acid rain is formed when toxic gases mix with water vapour in the atmosphere forming acid. The acid then rains with the rainwater.
Since the pH of the rainwater is not neutral, it causes harmful effects.
It reacts with marbles or carbonates on buildings, corroding them. It also reduces pH of water bodies and soil, harming aquatic and plant life.
The ozone layer is also depleted by chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons which exposes the earth to the UV radiation from the sun.
Air pollution is mainly reduced by switching to renewable resources for power generation, ctalytc converters (redox reactions that convert harmful gases to non-toxic ones) and flu gas desulfurization (removal of sulfur from its compounds).
The depletion in ozone may cause the disruption on weather patterns and the rise in temperature worldwide which is called global warming.
Global warming has adverse effects such as desertification, melting of glaciers and increase in natural disasters, and rapid evaporation increasing the greenhouse effect.
THE CARBON CYCLE
 STEPS FOR PURIFICATION OF WATER
STEPS FOR PURIFICATION OF WATER
Filteration is done to remove floating debris and solid clumps.
Water is screened.
Ammonium sulfate is added to the water to clump particles that settle at the bottom of the water. Water is then poured over.
Chlorine is added to the water to kill bacteria.
Fluorine is added to the water to prevent tooth decay.
Charcoal is added to remove bad odour.
 Knowt
Knowt
