
Glaciation
The Ice Ages
An Ice Age is when large parts of several continents were covered by ice sheets.
The last Ice Age was 1,000,000 to 10,000 years ago.
Snow and Ice accumulated until it was compacted together.
This formed masses of ice called glaciers.
These glaciers formed in upland areas and moved downslope
Some glaciers joined together to form ice sheets.
What causes an Ice Age?
Three things happen altogether:
The Earths orbit of the sun changes from elliptical to circular shape.
The angle of Earths axis changes- poles tilted further from the sun.
The Earth wobbles on its axis-If it wobbles away from the sun, it gets colder.
Glacial erosion
Processes of glacial erosion
Plucking
Friction between the base of a glacier and the ground.
Ice melts at the base
When it stops, it refreezes.
Plucks up pieces of rock.
Abrasion
Plucked rocks scratch and scrape the ground.
Scratch marks are known as striations.
Features of Glacial Erosion
Landforms are generally found in upland areas.
Cirques
Aretes
Pyramidal Peaks
U-Shaped Valleys
Ribbon Lakes
Hanging Valleys
Fjord
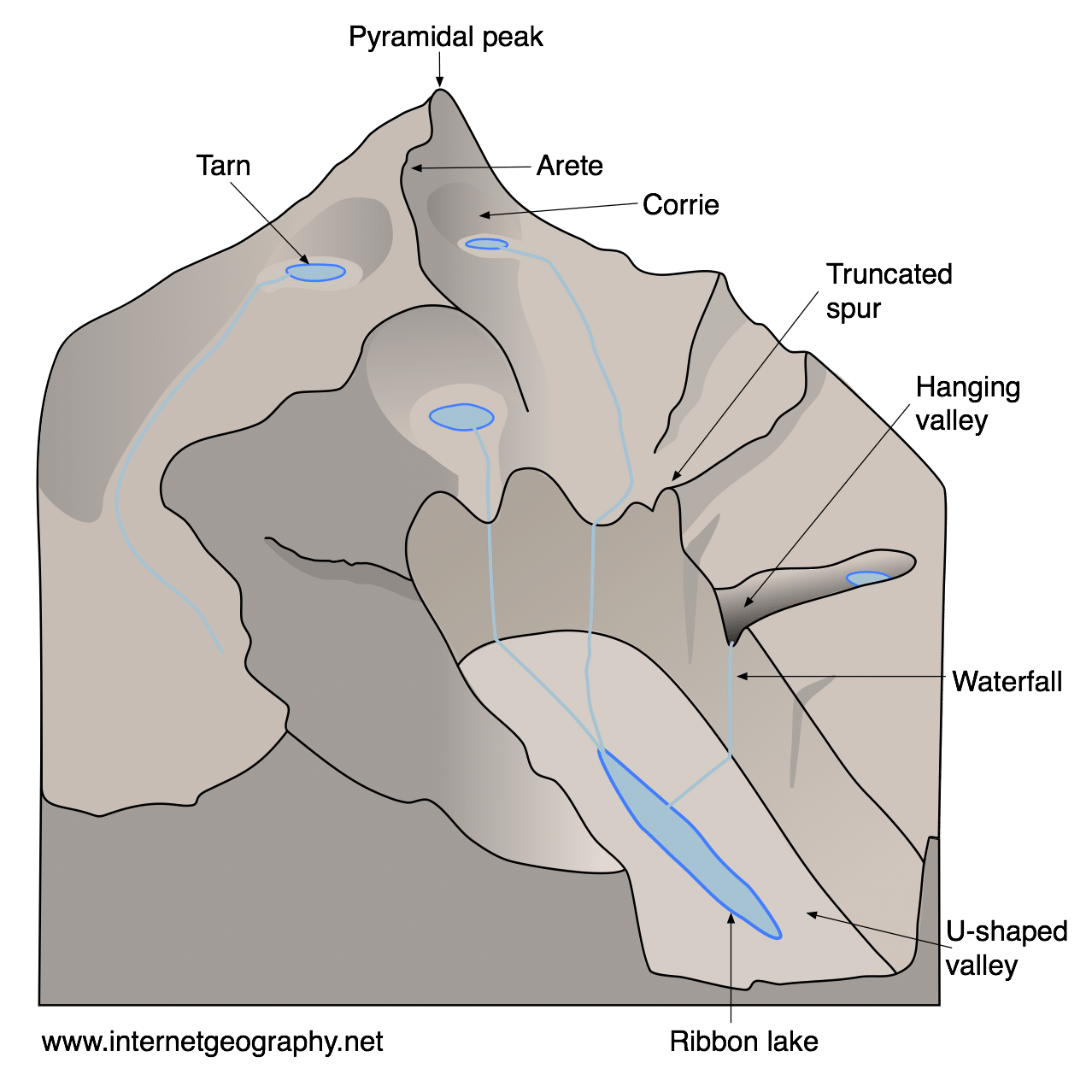
Glaciated valley/U-Shaped Valley: a V-Shaped Valley straightened and flattened by the movement of a large glacier.
Cirque/Corrie: A large hollow on the side of a mountain. It has three steep sides and is the birthplace of a glacier.
Tarn: A small lake inside a Cirque.
Pyramidal Peak: Steep-Sided pyramid-shaped mountain that was eroded on all sides by a cirque.
Arete: A narrow, steep-sided ridge usually between two cirques.
Paternoster lakes: When a long, narrow lake occupies the floor of a glaciated valley, it is called a ribbon lake. When multiple ribbon lakes are linked, they are called Paternoster lakes.
Truncated spur: Originally an interlocking spur that was eroded, having its ‘head’ cut off as the glacier moves.
Hanging Valley: A small tributary valley that hangs above the main glaciated valley.
A cirque/Corrie
A cirque is a basin-shaped hollow in mountains. They have three steep sides and often contain a lake. They are the birthplace of a glacier. Snow accumulates in a hollow in the side of a mountain. It compresses to form ice. The ice moves and plucks rocks from the side of the mountain. This makes the hollow even deeper through the process of abrasion. The hollow overflows and the ice moves downhill. Often, ice melts inside them and forms a lake called a tarn.
E.g. the Devil’s Punchbowl, Co. Kerry.
Glacial deposition
Features of glacial deposition
Drumlins (meltwater)
Eskers
Boulder Clay Plains (meltwater)
Erratics
Moraines
Outwash plains
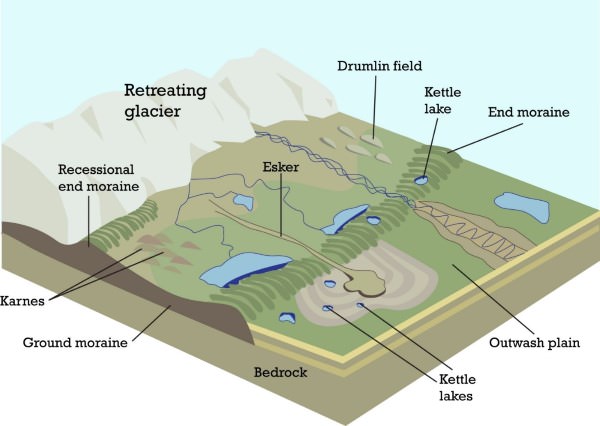
A drumlin
A drumlin is an oval-shaped hill made of boulder clay.
They form when meltwater deposits a large amount of boulder clay from under the glacier.
The glacier moves forward, smoothening and rounding the mound of clay, to form a drumlin
E.g. Clew Bay, Co. Mayo.
Erratics
Erratics are large boulders that were transported from their original location by a glacier and then deposited in an area where the rock type is different.
E.g. there are boulders of granite in the Burren, Co. Clare, where the local rock type is limestone. The nearest source of granite is north county Galway, which tells us the ice sheet that passed over the Burren came from the North.
Impacts of glaciation
Benefits of glaciation
Agriculture- boulder clay/ fertile soil/ The Golden Vale.
Tourism- Beautiful landscapes/ Glendalough/ The Burren.
Hydroelectricity- Glacial lakes/ Turlough Hill.
Roads- Natural routeways/ Gap of Dunloe.
Industry- Sand and gravel from eskers in construction industry/ water supply from glacial lakes.
Negative impacts of glaciation
Poor agricultural land in upland areas. Glaciers removed soil cover/ unsuitable for agriculture. Sheep farming and forestry may be only options.
Poor drainage- Glacial deposits, such as drumlins, can cause bogs to develop in some areas.
Flooding- glacier and ice caps in the Artic and Antartic are melting/ sea levels are rising.
Glaciation
The Ice Ages
An Ice Age is when large parts of several continents were covered by ice sheets.
The last Ice Age was 1,000,000 to 10,000 years ago.
Snow and Ice accumulated until it was compacted together.
This formed masses of ice called glaciers.
These glaciers formed in upland areas and moved downslope
Some glaciers joined together to form ice sheets.
What causes an Ice Age?
Three things happen altogether:
The Earths orbit of the sun changes from elliptical to circular shape.
The angle of Earths axis changes- poles tilted further from the sun.
The Earth wobbles on its axis-If it wobbles away from the sun, it gets colder.
Glacial erosion
Processes of glacial erosion
Plucking
Friction between the base of a glacier and the ground.
Ice melts at the base
When it stops, it refreezes.
Plucks up pieces of rock.
Abrasion
Plucked rocks scratch and scrape the ground.
Scratch marks are known as striations.
Features of Glacial Erosion
Landforms are generally found in upland areas.
Cirques
Aretes
Pyramidal Peaks
U-Shaped Valleys
Ribbon Lakes
Hanging Valleys
Fjord

Glaciated valley/U-Shaped Valley: a V-Shaped Valley straightened and flattened by the movement of a large glacier.
Cirque/Corrie: A large hollow on the side of a mountain. It has three steep sides and is the birthplace of a glacier.
Tarn: A small lake inside a Cirque.
Pyramidal Peak: Steep-Sided pyramid-shaped mountain that was eroded on all sides by a cirque.
Arete: A narrow, steep-sided ridge usually between two cirques.
Paternoster lakes: When a long, narrow lake occupies the floor of a glaciated valley, it is called a ribbon lake. When multiple ribbon lakes are linked, they are called Paternoster lakes.
Truncated spur: Originally an interlocking spur that was eroded, having its ‘head’ cut off as the glacier moves.
Hanging Valley: A small tributary valley that hangs above the main glaciated valley.
A cirque/Corrie
A cirque is a basin-shaped hollow in mountains. They have three steep sides and often contain a lake. They are the birthplace of a glacier. Snow accumulates in a hollow in the side of a mountain. It compresses to form ice. The ice moves and plucks rocks from the side of the mountain. This makes the hollow even deeper through the process of abrasion. The hollow overflows and the ice moves downhill. Often, ice melts inside them and forms a lake called a tarn.
E.g. the Devil’s Punchbowl, Co. Kerry.
Glacial deposition
Features of glacial deposition
Drumlins (meltwater)
Eskers
Boulder Clay Plains (meltwater)
Erratics
Moraines
Outwash plains

A drumlin
A drumlin is an oval-shaped hill made of boulder clay.
They form when meltwater deposits a large amount of boulder clay from under the glacier.
The glacier moves forward, smoothening and rounding the mound of clay, to form a drumlin
E.g. Clew Bay, Co. Mayo.
Erratics
Erratics are large boulders that were transported from their original location by a glacier and then deposited in an area where the rock type is different.
E.g. there are boulders of granite in the Burren, Co. Clare, where the local rock type is limestone. The nearest source of granite is north county Galway, which tells us the ice sheet that passed over the Burren came from the North.
Impacts of glaciation
Benefits of glaciation
Agriculture- boulder clay/ fertile soil/ The Golden Vale.
Tourism- Beautiful landscapes/ Glendalough/ The Burren.
Hydroelectricity- Glacial lakes/ Turlough Hill.
Roads- Natural routeways/ Gap of Dunloe.
Industry- Sand and gravel from eskers in construction industry/ water supply from glacial lakes.
Negative impacts of glaciation
Poor agricultural land in upland areas. Glaciers removed soil cover/ unsuitable for agriculture. Sheep farming and forestry may be only options.
Poor drainage- Glacial deposits, such as drumlins, can cause bogs to develop in some areas.
Flooding- glacier and ice caps in the Artic and Antartic are melting/ sea levels are rising.
 Knowt
Knowt