
Chapter 16 - Organizational culture
What is organizational culture?
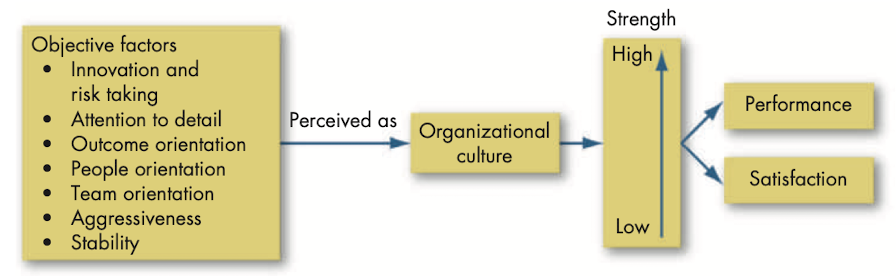
Organizational culture: system of shared meaning held by members that distinguishes the organization from other organizations.
Characteristics
Innovation and risk taking: degree to which employees are encouraged to be innovative and take risks.
Attention to detail: degree to which employees are expected to exhibit precision, analysis and attention to detail.
Outcome orientation: degree to which management focuses on results or outcomes rather than on the techniques and processes used to achieve those outcomes.
People orientation: degree to which management decisions take into consideration the effect of outcomes on people within the organization.
Team orientation: degree to which work activities are organized around teams rather than individuals.
Aggressiveness: degree to which people are aggressive and competitive rather than easy going.
Stability: degree to which organizational activities emphasize maintaining the status quo in contrast to growth.
Dominant culture: culture that expresses the core values that are shared by a majority of the organization's members.
Subcultures: mini-cultures within an organization, typically defined by department designations and geographical separation.
Core values: primary or dominant values that are accepted throughout the organization.
Strong culture: culture in which the core values are intensely held and widely shared.
What do cultures do?
Functions of culture
Boundary-defining role → it creates distinctions between one organization and others.
Conveying a sense of identity for organization members.
Facilitating the generation of commitment to something larger than one’s individual self interest
Enhancing the stability of the social system
Serving as a sense-making and control mechanism that guides and shapes the attitudes and behavior of employees.
Culture creates climate
Organizational climate: shared perceptions organizational members have about their organization and work environment.
Ethical work climate (EWC): shared concept of right and wrong behavior in the workplace that reflects the true values of the organization and shapes the ethical decision making of its members.
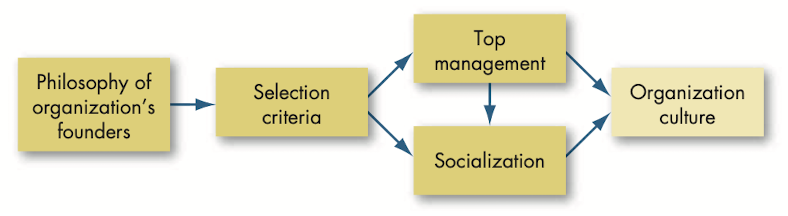
Institutionalization: condition that occurs when an organization takes on a life of its own, apart from any of its members, and acquires immortality.
Creating and sustaining culture
Socialization: process that adapts employees to the organization’s culture.
Pre-arrival stage: period of learning in the socialization process that occurs before a new employee joins the organization.
Encounter stage: stage in the socialization process in which a new employee sees what the organization is really like and confronts the possibility that expectations and reality may diverge.
Metamorphosis stage: stage in the socialization process in a which a new employee changes and adjusts to the job, work group and organization.
How employees learn culture
Stories
Rituals: repetitive sequences of activities that express and reinforce the key values of the organization, which goals are most important, which people are important and which are expendable.
Symbols
Material symbols: what conveys to employees who is important, the degree of egalitarianism top management desires and the kinds of behavior that are appropriate.
Language
Creating a positive organizational culture
Positive organizational culture: culture that emphasizes building on employee strengths, rewards more than punishes and emphasizes individual vitality and growth.
Spirituality and organizational culture
Workplace spirituality: recognition that people have an inner life that nourishes and is nourished by meaningful work that takes place in the context of community.
Chapter 16 - Organizational culture
What is organizational culture?
Organizational culture: system of shared meaning held by members that distinguishes the organization from other organizations.
Characteristics
Innovation and risk taking: degree to which employees are encouraged to be innovative and take risks.
Attention to detail: degree to which employees are expected to exhibit precision, analysis and attention to detail.
Outcome orientation: degree to which management focuses on results or outcomes rather than on the techniques and processes used to achieve those outcomes.
People orientation: degree to which management decisions take into consideration the effect of outcomes on people within the organization.
Team orientation: degree to which work activities are organized around teams rather than individuals.
Aggressiveness: degree to which people are aggressive and competitive rather than easy going.
Stability: degree to which organizational activities emphasize maintaining the status quo in contrast to growth.
Dominant culture: culture that expresses the core values that are shared by a majority of the organization's members.
Subcultures: mini-cultures within an organization, typically defined by department designations and geographical separation.
Core values: primary or dominant values that are accepted throughout the organization.
Strong culture: culture in which the core values are intensely held and widely shared.
What do cultures do?
Functions of culture
Boundary-defining role → it creates distinctions between one organization and others.
Conveying a sense of identity for organization members.
Facilitating the generation of commitment to something larger than one’s individual self interest
Enhancing the stability of the social system
Serving as a sense-making and control mechanism that guides and shapes the attitudes and behavior of employees.
Culture creates climate
Organizational climate: shared perceptions organizational members have about their organization and work environment.
Ethical work climate (EWC): shared concept of right and wrong behavior in the workplace that reflects the true values of the organization and shapes the ethical decision making of its members.
Institutionalization: condition that occurs when an organization takes on a life of its own, apart from any of its members, and acquires immortality.
Creating and sustaining culture
Socialization: process that adapts employees to the organization’s culture.
Pre-arrival stage: period of learning in the socialization process that occurs before a new employee joins the organization.
Encounter stage: stage in the socialization process in which a new employee sees what the organization is really like and confronts the possibility that expectations and reality may diverge.
Metamorphosis stage: stage in the socialization process in a which a new employee changes and adjusts to the job, work group and organization.

How employees learn culture
Stories
Rituals: repetitive sequences of activities that express and reinforce the key values of the organization, which goals are most important, which people are important and which are expendable.
Symbols
Material symbols: what conveys to employees who is important, the degree of egalitarianism top management desires and the kinds of behavior that are appropriate.
Language
Creating a positive organizational culture
Positive organizational culture: culture that emphasizes building on employee strengths, rewards more than punishes and emphasizes individual vitality and growth.
Spirituality and organizational culture
Workplace spirituality: recognition that people have an inner life that nourishes and is nourished by meaningful work that takes place in the context of community.

 Knowt
Knowt
