Chapter 11
Describing Concentration
Solute: The substance that dissolves
Solvent: The major component of the solution
Concentration: The amount of solute present in a solution
Dilute
Concentrated
Saturated
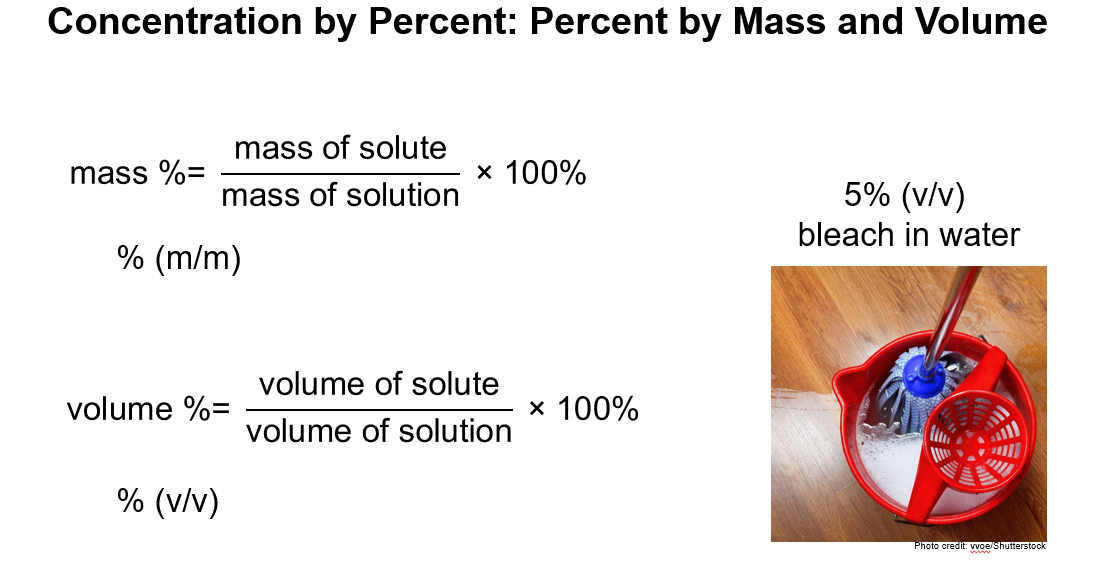
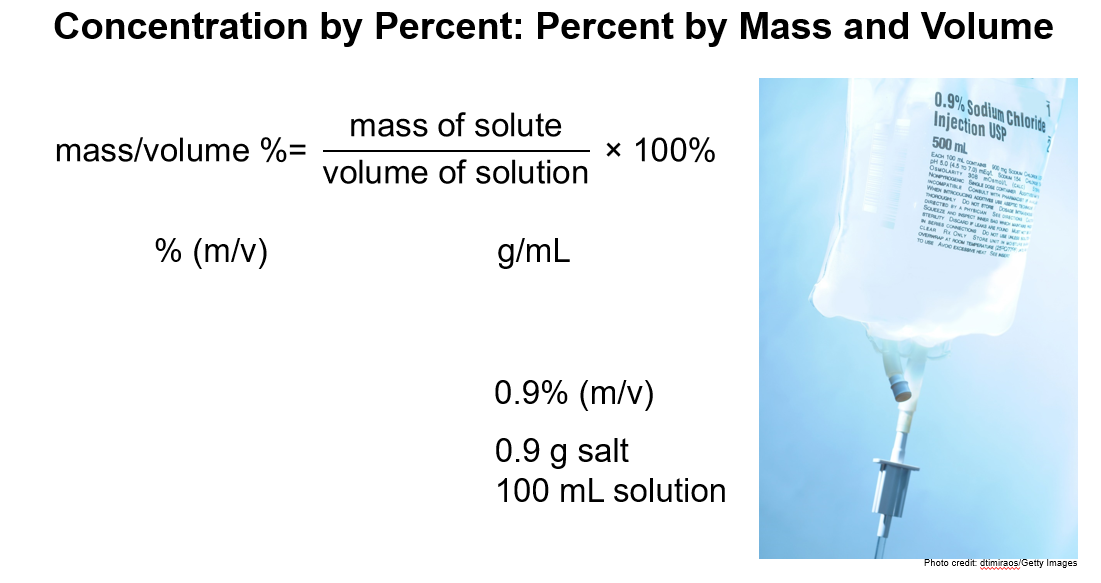
1. Percent
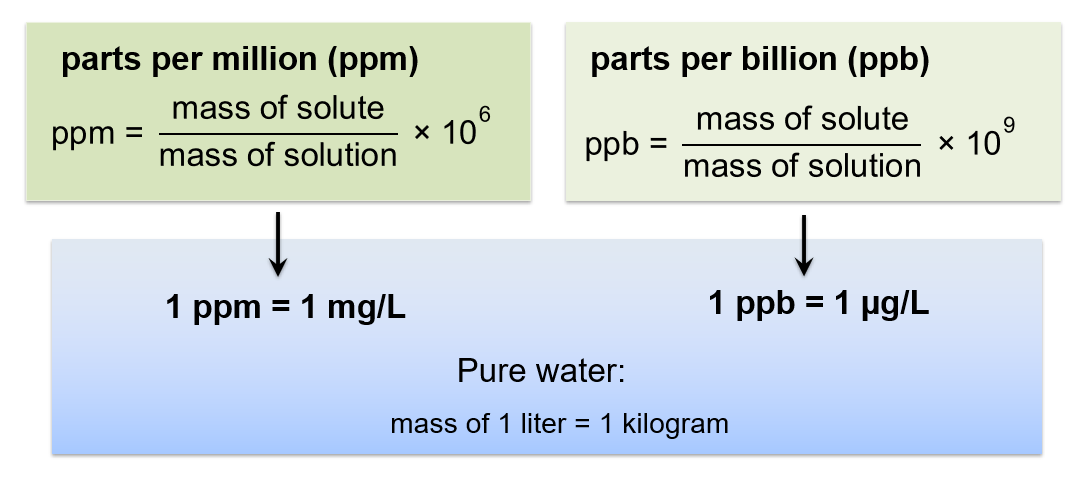
Very Dilute Solutions: ppm and ppb
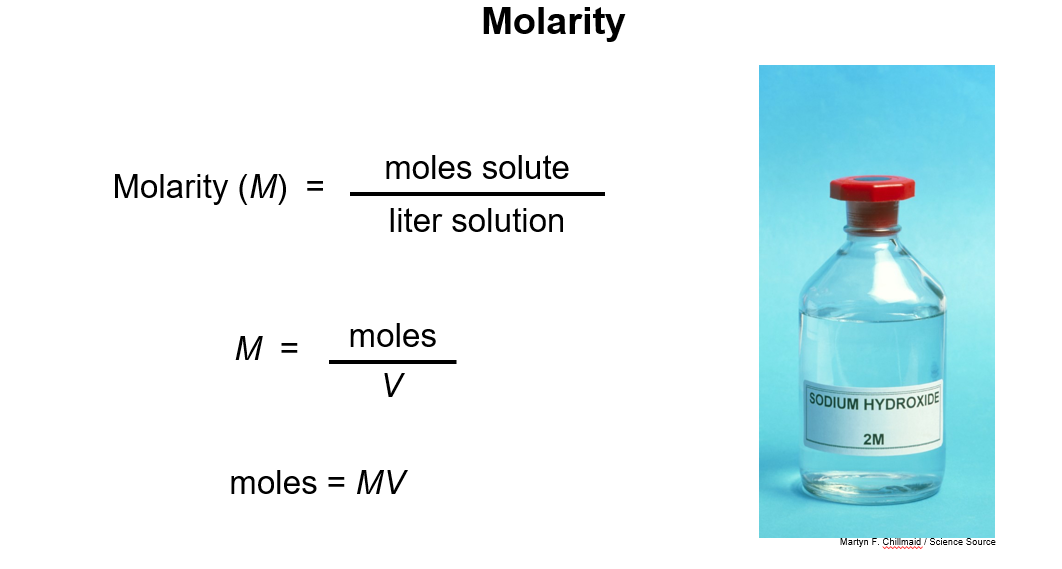
3. Molarity
Preparing Solutions for Known Molarity


Electrolyte Solutions
Ionic compounds dissociate in water
Electrolyte solutions contain dissolved ions
Molecular equation: shows ions together as compounds
Ionic equation: Shows dissociated ions as separate species
Reactions in Solutions
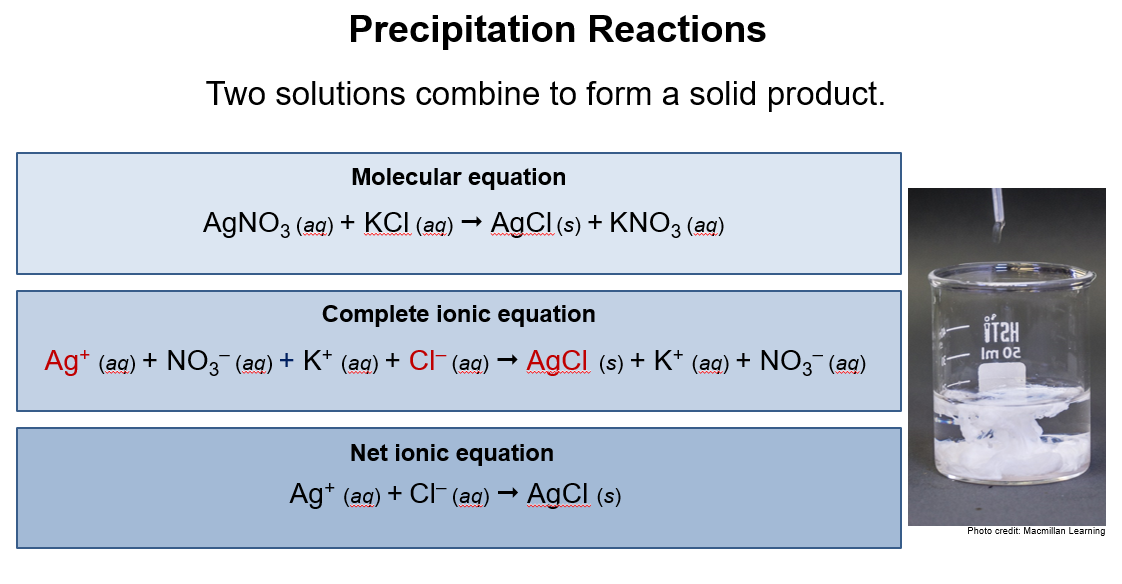
1. Precipitation
Two solutions combine to form a solid product
2. Acid - Base Neutralization Reaction
Acids and bases combine to form water and a salt
3. Metal Displacement Reactions
An ion of one metal reacts with the elemental form of another metal
Solution Stichometry
Gravimetric Analysis
Uses the mass of a precipitate to determine the concentration of a reactant
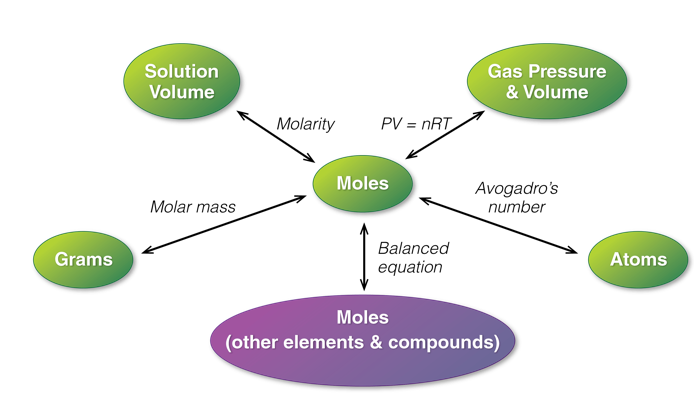
Advanced Stoichiometry Problems Map
Chapter 11
Describing Concentration
Solute: The substance that dissolves
Solvent: The major component of the solution
Concentration: The amount of solute present in a solution
Dilute
Concentrated
Saturated
1. Percent


Very Dilute Solutions: ppm and ppb

3. Molarity

Preparing Solutions for Known Molarity


Electrolyte Solutions
Ionic compounds dissociate in water
Electrolyte solutions contain dissolved ions
Molecular equation: shows ions together as compounds
Ionic equation: Shows dissociated ions as separate species
Reactions in Solutions
1. Precipitation
Two solutions combine to form a solid product
2. Acid - Base Neutralization Reaction
Acids and bases combine to form water and a salt
3. Metal Displacement Reactions
An ion of one metal reacts with the elemental form of another metal
Solution Stichometry
Gravimetric Analysis
Uses the mass of a precipitate to determine the concentration of a reactant
Advanced Stoichiometry Problems Map

 Knowt
Knowt