
Developmental Psychology
Infancy and Childhood
Schema - frameworks that help us organize and interpret info
Ex. kid learns schema dog through picture books
Assimilation - interpreting new experiences in terms of existing schemas
Ex. kid might call any four-legged animal a dog
Accommodation - adjusting current schemas to incorporate new info
Ex. kid recognizes a cat is not the same as a dog
Stranger anxiety - common in infants starting at 8 months; traditional belief: infants would become attached to whoever provided their food
Secure vs. insecure attachment
Secure - Infants in their mother’s presence they play comfortably, happily exploring their new environment. When she leaves, they become distressed; when she returns, they seek contact with her.
Insecure - marked either by anxiety or avoidance of trusting relationships; infants are less likely to explore their surroundings; they may even cling to their mother. When she leaves, they either cry loudly and remain upset or seem indifferent to her departure and return
Critical period - early in life when exposure to certain stimuli and events leads to normal development
Imprinting - the process by which certain animals form strong attachments during an early-life critical period
Temperament - a person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
Basic trust - according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers
Self-concept - all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, “Who am I?”
Developmental Theories
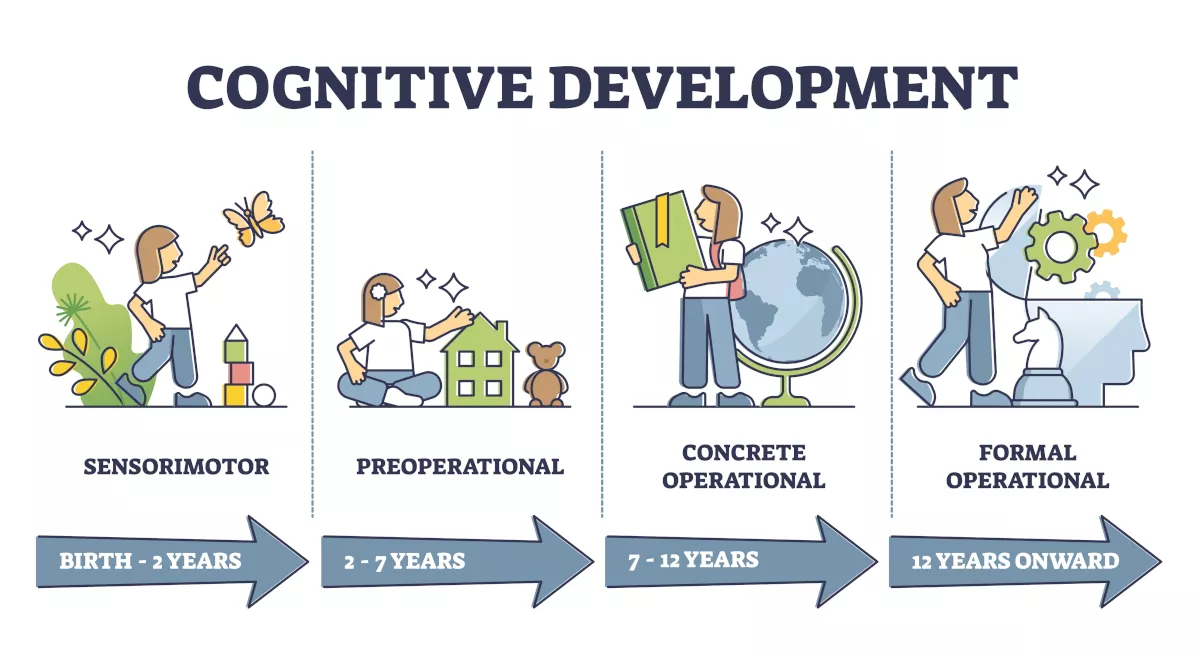
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development:
Sensorimotor - birth to 2 years; babies experience the world through senses and they learn that they can do things through movement
Object permanence - recognizing that something is still there even if they can’t see it doesn’t develop till ~8 months; lack concept of conservation
Pre-operational - 2-7 years; the child learns to use language but cannot comprehend conservation
Concrete operational - 7-12 years; kids can think logically about physical events and understand math transformations
Formal operational - 12+ years; develop abstract thinking; consider hypotheticals and estimate consequences
Harlow’s “wire and cloth mother” study
Psychologists Harry Harlow and Margaret Harlow raised monkeys with two artificial mothers—one a bare wire cylinder with a wooden head and an attached feeding bottle, the other a cylinder with no bottle but covered with foam rubber and wrapped with terry cloth. The Harlows’ discovery surprised many psychologists: The infants much-preferred contact with the comfortable cloth mother, even while feeding from the nourishing mother.
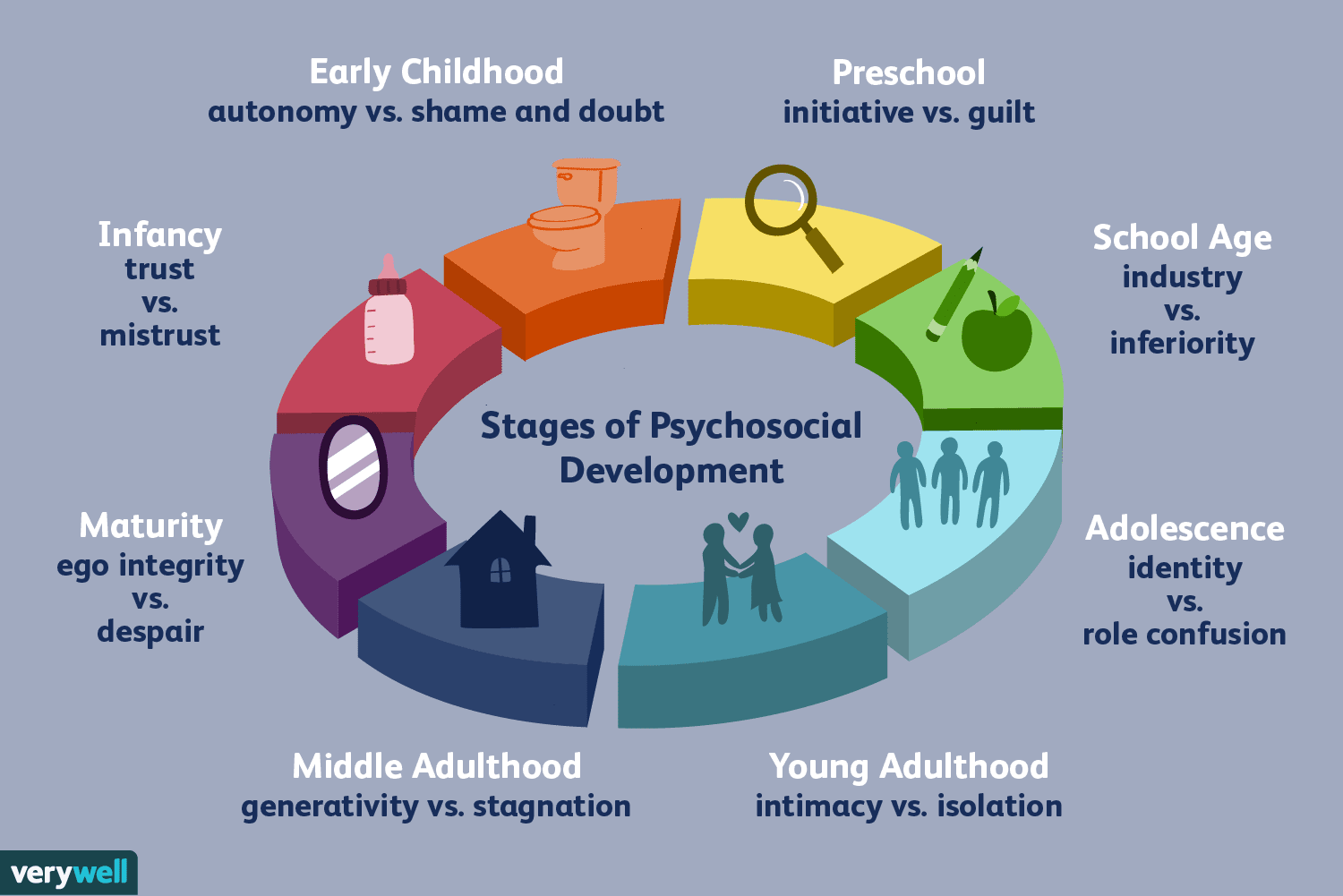
Erikson’s developmental theories (know each of the “conflicts”)
Trust vs mistrust - if needs are met they develop trust
Autonomy vs shame and doubt - toddlers will learn to do things for themselves or will doubt their own abilities
Initiative vs guilt - preschoolers learn to initiate tasks and carry out plans or to be guilty about efforts at independence
Competence vs inferiority - kids will learn to enjoy applying themselves to tasks or they will feel inferior
Identity vs role confusion - teens work at testing roles and then forming them into an identity or they become confused about who they are
Intimacy vs isolation - young adults form close relationships and develop a capacity for intimacy or they feel socially isolated
Generativity vs stagnation - middle-aged people develop a sense of contributing to the world or feel a lack of purpose
Integrity vs despair - as older adults reflect on life, they feel a sense of satisfaction and accomplishment or a sense of failure
Gender Development / Identity
Gender role - a set of expected behaviors for males or for females
Gender identity - our sense of being male or female
Social learning theory - the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
Gender typing - the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role
Transgender - an umbrella term describing people whose gender identity or expression differs from that associated with their birth sex
Identity - a consistent and comfortable sense of who we are
Social identity - part of our identity that comes from group membership
Primary vs. secondary sex characteristics
Primary - the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
Secondary - nonreproductive sexual traits, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
Sexual orientation - when during sexual attraction one feels to the opposite (heterosexual), same (homosexual), or both (bisexual) sexes
Parenting Styles
Authoritarian parents impose rules and expect obedience: “Don’t interrupt.” “Keep your room clean.” “Don’t stay out late or you’ll be grounded.” “Why? Because I said so.”
Permissive parents submit to their children’s desires. They make few demands and use little punishment.
Authoritative parents are both demanding and responsive. They exert control by setting rules and enforcing them, but they also explain the reasons for rules. And, especially with older children, they encourage open discussion when making the rules and allow exceptions.
Adulthood
Emerging adulthood - for some people in modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood
Menopause - the time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce declines
Social clock - a social standard that says there are certain expectations about when people should get married, have kids, retire, etc (most powerful when comparing yourself to others)
Developmental Disorders
Disorder | Impairments |
|---|---|
Asperger Syndrome | Communication differences, clashes in social interaction, repetitive behaviors, eye contact avoidance, preferring set routines, irritability, anxiety |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder | Paying attention, controlling impulsive behavior, or being overly active |
Autism Spectrum Disorder | Behavior, communication, social interactions, learning (delayed cognitive skills), abilities (often have a special skill), no physical differences |
Cerebral Palsy | Balance, coordination, stiff reflexes, vibrations in muscle tone, involuntary movement, speech, chewing and swallowing issues, development issues, over-sensitive nerves |
Childhood Disintegrative Disorder | Produce speech and communication, comprehend language, social skills, self-care skills, control over bowel and bladder, play skills, and motor skills (up to a certain point development is normal) |
Developmental Coordination Disorder | Delayed development of crawling, walking, self-feeding, and dressing |
Down Syndrome | Intellectual disability, attention span, verbal memory, expressive communication, behavior, digestive &immune & heart functions, hearing & vision, motor skill impairments |
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome | Nervous system problems, minor facial features, growth problems, difficulty socializing, difficulty controlling anger, and problems understanding other's motives |
Fragile X Syndrome | Intellectual disability, females have milder symptoms, delays in talking, prominent jaw and forehead, large ears, flat feet long face, and can also have memory/mood disorders |
Intellectual Disability | Getting dressed efficiently/independently, understanding concepts & social implications & results of their actions, poor muscle control (used to be called mental retardation) |
Klinefelter Syndrome | Infertility, gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue), decreased body hair & muscle mass, can be connected to learning and emotional difficulties (extra X chromosome in males) |
Rett Syndrome | Loss of speech, involuntary hand movements, mobility, muscle tone, seizures, scoliosis, breathing issues, sleep disturbances, and slowed growth of feet/hands/head |
Tourette’s Syndrome | Simple motor (blinking, jerking, shoulder shrugging), vocal (throat clearing, sniffing, barking, grunting), and complex motor tics (jumping, twisting, |
Trisomy X | Only affects women (extra x chromosome), 1 in every 1000 have it and only 10% of them know they have it; increase in risk of learning disabilities, slight correlation with low IQ |
Turner Syndrome | Height, regressed sexual development, altered features (webbed neck, low ears, broad chest), and health development |
Williams Syndrome |
Developmental Psychology
Infancy and Childhood
Schema - frameworks that help us organize and interpret info
Ex. kid learns schema dog through picture books
Assimilation - interpreting new experiences in terms of existing schemas
Ex. kid might call any four-legged animal a dog
Accommodation - adjusting current schemas to incorporate new info
Ex. kid recognizes a cat is not the same as a dog
Stranger anxiety - common in infants starting at 8 months; traditional belief: infants would become attached to whoever provided their food
Secure vs. insecure attachment
Secure - Infants in their mother’s presence they play comfortably, happily exploring their new environment. When she leaves, they become distressed; when she returns, they seek contact with her.
Insecure - marked either by anxiety or avoidance of trusting relationships; infants are less likely to explore their surroundings; they may even cling to their mother. When she leaves, they either cry loudly and remain upset or seem indifferent to her departure and return
Critical period - early in life when exposure to certain stimuli and events leads to normal development
Imprinting - the process by which certain animals form strong attachments during an early-life critical period
Temperament - a person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
Basic trust - according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers
Self-concept - all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, “Who am I?”
Developmental Theories
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development:
Sensorimotor - birth to 2 years; babies experience the world through senses and they learn that they can do things through movement
Object permanence - recognizing that something is still there even if they can’t see it doesn’t develop till ~8 months; lack concept of conservation
Pre-operational - 2-7 years; the child learns to use language but cannot comprehend conservation
Concrete operational - 7-12 years; kids can think logically about physical events and understand math transformations
Formal operational - 12+ years; develop abstract thinking; consider hypotheticals and estimate consequences

Harlow’s “wire and cloth mother” study
Psychologists Harry Harlow and Margaret Harlow raised monkeys with two artificial mothers—one a bare wire cylinder with a wooden head and an attached feeding bottle, the other a cylinder with no bottle but covered with foam rubber and wrapped with terry cloth. The Harlows’ discovery surprised many psychologists: The infants much-preferred contact with the comfortable cloth mother, even while feeding from the nourishing mother.
Erikson’s developmental theories (know each of the “conflicts”)
Trust vs mistrust - if needs are met they develop trust
Autonomy vs shame and doubt - toddlers will learn to do things for themselves or will doubt their own abilities
Initiative vs guilt - preschoolers learn to initiate tasks and carry out plans or to be guilty about efforts at independence
Competence vs inferiority - kids will learn to enjoy applying themselves to tasks or they will feel inferior
Identity vs role confusion - teens work at testing roles and then forming them into an identity or they become confused about who they are
Intimacy vs isolation - young adults form close relationships and develop a capacity for intimacy or they feel socially isolated
Generativity vs stagnation - middle-aged people develop a sense of contributing to the world or feel a lack of purpose
Integrity vs despair - as older adults reflect on life, they feel a sense of satisfaction and accomplishment or a sense of failure

Gender Development / Identity
Gender role - a set of expected behaviors for males or for females
Gender identity - our sense of being male or female
Social learning theory - the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
Gender typing - the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role
Transgender - an umbrella term describing people whose gender identity or expression differs from that associated with their birth sex
Identity - a consistent and comfortable sense of who we are
Social identity - part of our identity that comes from group membership
Primary vs. secondary sex characteristics
Primary - the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
Secondary - nonreproductive sexual traits, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
Sexual orientation - when during sexual attraction one feels to the opposite (heterosexual), same (homosexual), or both (bisexual) sexes
Parenting Styles
Authoritarian parents impose rules and expect obedience: “Don’t interrupt.” “Keep your room clean.” “Don’t stay out late or you’ll be grounded.” “Why? Because I said so.”
Permissive parents submit to their children’s desires. They make few demands and use little punishment.
Authoritative parents are both demanding and responsive. They exert control by setting rules and enforcing them, but they also explain the reasons for rules. And, especially with older children, they encourage open discussion when making the rules and allow exceptions.
Adulthood
Emerging adulthood - for some people in modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood
Menopause - the time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce declines
Social clock - a social standard that says there are certain expectations about when people should get married, have kids, retire, etc (most powerful when comparing yourself to others)
Developmental Disorders
Disorder | Impairments |
|---|---|
Asperger Syndrome | Communication differences, clashes in social interaction, repetitive behaviors, eye contact avoidance, preferring set routines, irritability, anxiety |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder | Paying attention, controlling impulsive behavior, or being overly active |
Autism Spectrum Disorder | Behavior, communication, social interactions, learning (delayed cognitive skills), abilities (often have a special skill), no physical differences |
Cerebral Palsy | Balance, coordination, stiff reflexes, vibrations in muscle tone, involuntary movement, speech, chewing and swallowing issues, development issues, over-sensitive nerves |
Childhood Disintegrative Disorder | Produce speech and communication, comprehend language, social skills, self-care skills, control over bowel and bladder, play skills, and motor skills (up to a certain point development is normal) |
Developmental Coordination Disorder | Delayed development of crawling, walking, self-feeding, and dressing |
Down Syndrome | Intellectual disability, attention span, verbal memory, expressive communication, behavior, digestive &immune & heart functions, hearing & vision, motor skill impairments |
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome | Nervous system problems, minor facial features, growth problems, difficulty socializing, difficulty controlling anger, and problems understanding other's motives |
Fragile X Syndrome | Intellectual disability, females have milder symptoms, delays in talking, prominent jaw and forehead, large ears, flat feet long face, and can also have memory/mood disorders |
Intellectual Disability | Getting dressed efficiently/independently, understanding concepts & social implications & results of their actions, poor muscle control (used to be called mental retardation) |
Klinefelter Syndrome | Infertility, gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue), decreased body hair & muscle mass, can be connected to learning and emotional difficulties (extra X chromosome in males) |
Rett Syndrome | Loss of speech, involuntary hand movements, mobility, muscle tone, seizures, scoliosis, breathing issues, sleep disturbances, and slowed growth of feet/hands/head |
Tourette’s Syndrome | Simple motor (blinking, jerking, shoulder shrugging), vocal (throat clearing, sniffing, barking, grunting), and complex motor tics (jumping, twisting, |
Trisomy X | Only affects women (extra x chromosome), 1 in every 1000 have it and only 10% of them know they have it; increase in risk of learning disabilities, slight correlation with low IQ |
Turner Syndrome | Height, regressed sexual development, altered features (webbed neck, low ears, broad chest), and health development |
Williams Syndrome |
 Knowt
Knowt
