
Chapter 23- Alkenes
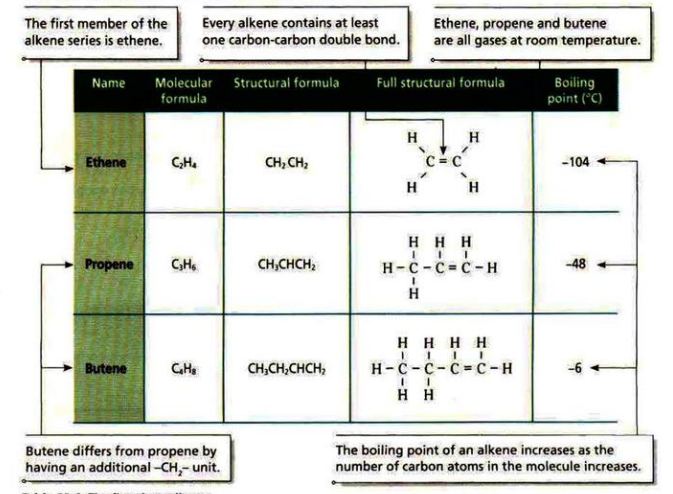
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with double bonds between two carbon atoms.
The general formula is C
nH2n
Isomers of alkenes can be formed by branching them or changing the position of the double bond.
Catalytic cracking is used to manufacture alkenes from alkanes. It can also be used to manufacture hydrogen.
An alkane can be broken in three ways using cracking: Making one alkane and one alkene, and one hydrogen, making two alkenes and hydrogen, making an alkane.
Alkenes can also be combusted.
ADDITION REACTIONS OF ALKENES
Alkenes undergo addition reactions, i.e. reactions where only one product is formed. Double bonds are broken into single bonds.
HYDROGENATION: In presence of the catalyst nickel and 200 degrees celsius temperature, alkenes react with hydrogen to form alkanes.
Used in manufacture of margarine from vegetable oil.
BROMINATION: when bromine is added to an alkene, it immediately decolourises as the double bonds are broken and bromine atoms join the alkene.
Used in the test for saturation as bromine water decolourises in unsaturated substances only.
HYDRATION: In the presence of phosphoric (V) acid, 300 degrees celsius temperature and 60 atm pressure, alkenes react with steam to form alcohols.
Chapter 23- Alkenes
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with double bonds between two carbon atoms.
The general formula is C
nH2n

Isomers of alkenes can be formed by branching them or changing the position of the double bond.
Catalytic cracking is used to manufacture alkenes from alkanes. It can also be used to manufacture hydrogen.
An alkane can be broken in three ways using cracking: Making one alkane and one alkene, and one hydrogen, making two alkenes and hydrogen, making an alkane.
Alkenes can also be combusted.
ADDITION REACTIONS OF ALKENES
Alkenes undergo addition reactions, i.e. reactions where only one product is formed. Double bonds are broken into single bonds.
HYDROGENATION: In presence of the catalyst nickel and 200 degrees celsius temperature, alkenes react with hydrogen to form alkanes.
Used in manufacture of margarine from vegetable oil.
BROMINATION: when bromine is added to an alkene, it immediately decolourises as the double bonds are broken and bromine atoms join the alkene.
Used in the test for saturation as bromine water decolourises in unsaturated substances only.
HYDRATION: In the presence of phosphoric (V) acid, 300 degrees celsius temperature and 60 atm pressure, alkenes react with steam to form alcohols.
 Knowt
Knowt
