Science Cells Info
Cells
The Beginning of Cells
What is a cell?
A cell is the basic structural unit of and organism
CELLS are the building blocks of all living things and the systems found in each organism (remember grade 5 Science). All living things, whether it is a paramecium (a single cell) or a human (trillions of cells) are made up of cells.
There are hundreds of different types of cells found in a human and each cell has its own role to play within the human body. The different cells look much different and have different roles within the human body.
When was the first cell discovered?
the first cell was discovered in 1665 using a microscope (that was first invented in 1609)
Types Of Cells
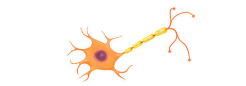
Nerve Cell |
|
Red Blood Cell |
|
Muscle Cell |
|
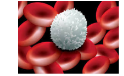
White Blood Cell |
|
Egg Cell (females only) |
|
Bone Cell |
|
Importance of Cells
What is an important reason for studying cells
To help prevent disease and illness such as cancer.
What things are harmful to cells?
Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun, x-rays, and microwaves.
How are cells involved in causing cancer?
Cells are involved in causing cancer because it is when abnormal harmful cells grow, dividing and they do not get destroyed.
What things can we do to keep our cells healthy?
We can have proper vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, fibre and amino acids. Aswel as a balaced and nutrient-rich died, paired with adequate hydration.
Humans, Plants, and Animals
Plants and Animals
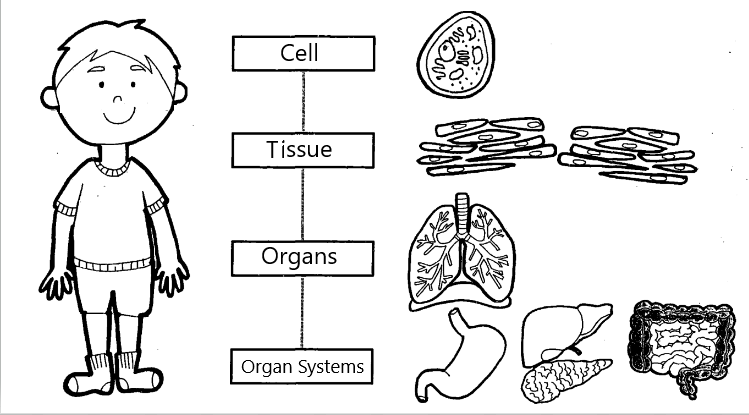
Plants and Animals have a very sophisticated level of organization that can be summarized as follows
A group of specialized cells form —> a tissue, a collection of tissue —> form an organ, many organs work together —> as a system.
Humans
The human body has 11 Systems that all work together to keep a human healthy. Name as many as you can.
The circulatory (cardiovascular) system
The lymphatic system
The respiratory system
The integumentary system
The endocrine system
The gastrointestinal (digestive) system
The urinary (excretory) system
The musculoskeletal system
The nervous system
The reproductive system
The immune system
How do you know if something is alive? List as many characteristics (traits) of something that is alive.
t is made of cells.
It can move.
It uses energy.
It grows and develops.
It can reproduce.
It responds to stimuli.
It adapts to surroundings.
What is biology?
the study of living organisms, divided into many specialized fields that cover their morphology, physiology, anatomy, behavior, origin, and distribution.
Define Organism.
An individual animal, plant, or single-celled life form
Diagram
Systems
Skeletal system
What is the skeletal system?
The skeletal system is made up of bones and cartilage. This system provides support for movement, attachment points for other tissues, and protection of other organs (for example, the spine protects the spinal cord)
Diagram
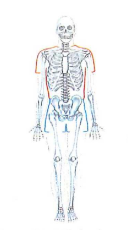
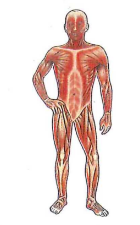
Muscular system
What is the muscular system?
The muscular system is made up of skeletal muscles, including tendons and ligaments (Figure 3.11). This system enables you to move from place to place. It also moves substances through your body. For example, swallowing food involves a series of muscle contractions to force food down the esophagus and into the stomach.
Diagram
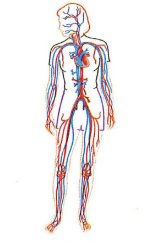
The circulatory (cardiovascular) system
What is the Circulatory System?
The circulatory system is made up of the heart (an organ), plus blood vessels and blood. Its main purpose is to deliver nutrients, move gases, and remove waste products.
Diagram
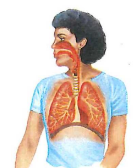
Respiratory system
What is the respiratory system?
The respiratory system is made up of the nose, trachea, and lungs. This system allows oxygen from the air to enter the body and waste carbon dioxide to exit the body. This process is called respiration.
Diagram
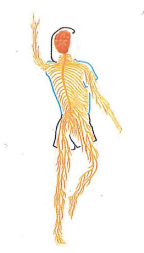
Nervous system
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that exist in every part of the body (Figure 3.14). This system sends and receives nerve messages throughout the body. It also controls behaviour, movement, and processes such as digestion and circulation.
Diagram
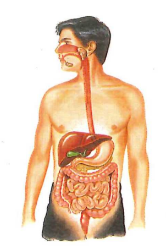
Digestive system
What is the digestive system?
The digestive system is made up of the mouth, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, and small and large intestines (Figure 3.15). This system breaks food down so that nutrients can be absorbed by the blood and transported to all cells. The colon also expels all solid waste from the body.
Diagram
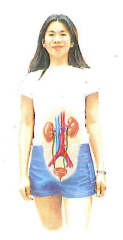
Excretory system
What is the excretory system
The excretory system is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. This system filters the blood and removes liquid waste and extra water from the body.
Diagram
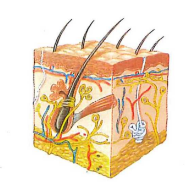
Integumentary system
What is the integumentary system?
The integumentary system is made up of skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands (Figure 3.17). The skin, hair, and nails cover and protect the body. Sweat glands are involved in maintaining normal body temperature.
Diagram
Endocrine system
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is made up of several glands that produce hormones. Hormones are chemicals that regulate every bodily function. Glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, and pancreas all produce hormones that carry messages to other parts of the body. In the brain, the hypothalamus acts, as the control center for the endocrine and nervous systems.
Lymphatic system
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is made up of lymph, lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymphoid tissue. This system protects the body. It is responsible for destroying and removing any invading organisms and abnormal cells.
Reproductive system
What is the reproductive system?
The reproductive system is made up of organs for producing offspring.
Science Cells Info
Cells
The Beginning of Cells
What is a cell?
A cell is the basic structural unit of and organism
CELLS are the building blocks of all living things and the systems found in each organism (remember grade 5 Science). All living things, whether it is a paramecium (a single cell) or a human (trillions of cells) are made up of cells.
There are hundreds of different types of cells found in a human and each cell has its own role to play within the human body. The different cells look much different and have different roles within the human body.
When was the first cell discovered?
the first cell was discovered in 1665 using a microscope (that was first invented in 1609)
Types Of Cells
Nerve Cell |
|
Red Blood Cell |
|
Muscle Cell |
|
White Blood Cell |
|
Egg Cell (females only) |
|
Bone Cell |
|
Importance of Cells
What is an important reason for studying cells
To help prevent disease and illness such as cancer.
What things are harmful to cells?
Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun, x-rays, and microwaves.
How are cells involved in causing cancer?
Cells are involved in causing cancer because it is when abnormal harmful cells grow, dividing and they do not get destroyed.
What things can we do to keep our cells healthy?
We can have proper vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, fibre and amino acids. Aswel as a balaced and nutrient-rich died, paired with adequate hydration.
Humans, Plants, and Animals
Plants and Animals
Plants and Animals have a very sophisticated level of organization that can be summarized as follows
A group of specialized cells form —> a tissue, a collection of tissue —> form an organ, many organs work together —> as a system.
Humans
The human body has 11 Systems that all work together to keep a human healthy. Name as many as you can.
The circulatory (cardiovascular) system
The lymphatic system
The respiratory system
The integumentary system
The endocrine system
The gastrointestinal (digestive) system
The urinary (excretory) system
The musculoskeletal system
The nervous system
The reproductive system
The immune system
How do you know if something is alive? List as many characteristics (traits) of something that is alive.
t is made of cells.
It can move.
It uses energy.
It grows and develops.
It can reproduce.
It responds to stimuli.
It adapts to surroundings.
What is biology?
the study of living organisms, divided into many specialized fields that cover their morphology, physiology, anatomy, behavior, origin, and distribution.
Define Organism.
An individual animal, plant, or single-celled life form
Diagram

Systems
Skeletal system
What is the skeletal system?
The skeletal system is made up of bones and cartilage. This system provides support for movement, attachment points for other tissues, and protection of other organs (for example, the spine protects the spinal cord)
Diagram

Muscular system
What is the muscular system?
The muscular system is made up of skeletal muscles, including tendons and ligaments (Figure 3.11). This system enables you to move from place to place. It also moves substances through your body. For example, swallowing food involves a series of muscle contractions to force food down the esophagus and into the stomach.
Diagram

The circulatory (cardiovascular) system
What is the Circulatory System?
The circulatory system is made up of the heart (an organ), plus blood vessels and blood. Its main purpose is to deliver nutrients, move gases, and remove waste products.
Diagram

Respiratory system
What is the respiratory system?
The respiratory system is made up of the nose, trachea, and lungs. This system allows oxygen from the air to enter the body and waste carbon dioxide to exit the body. This process is called respiration.
Diagram

Nervous system
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that exist in every part of the body (Figure 3.14). This system sends and receives nerve messages throughout the body. It also controls behaviour, movement, and processes such as digestion and circulation.
Diagram

Digestive system
What is the digestive system?
The digestive system is made up of the mouth, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, and small and large intestines (Figure 3.15). This system breaks food down so that nutrients can be absorbed by the blood and transported to all cells. The colon also expels all solid waste from the body.
Diagram

Excretory system
What is the excretory system
The excretory system is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. This system filters the blood and removes liquid waste and extra water from the body.
Diagram

Integumentary system
What is the integumentary system?
The integumentary system is made up of skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands (Figure 3.17). The skin, hair, and nails cover and protect the body. Sweat glands are involved in maintaining normal body temperature.
Diagram

Endocrine system
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is made up of several glands that produce hormones. Hormones are chemicals that regulate every bodily function. Glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, and pancreas all produce hormones that carry messages to other parts of the body. In the brain, the hypothalamus acts, as the control center for the endocrine and nervous systems.
Lymphatic system
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is made up of lymph, lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymphoid tissue. This system protects the body. It is responsible for destroying and removing any invading organisms and abnormal cells.
Reproductive system
What is the reproductive system?
The reproductive system is made up of organs for producing offspring.
 Knowt
Knowt