
Hyper/Hypo and Isotonic Solutions
The tonicity of a solution is the concentration of solutes. Typically, when you discuss tonicity, you are referring to the solution the cell is in, not the cell itself. The aqueous environment surrounding a cell can be hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic.
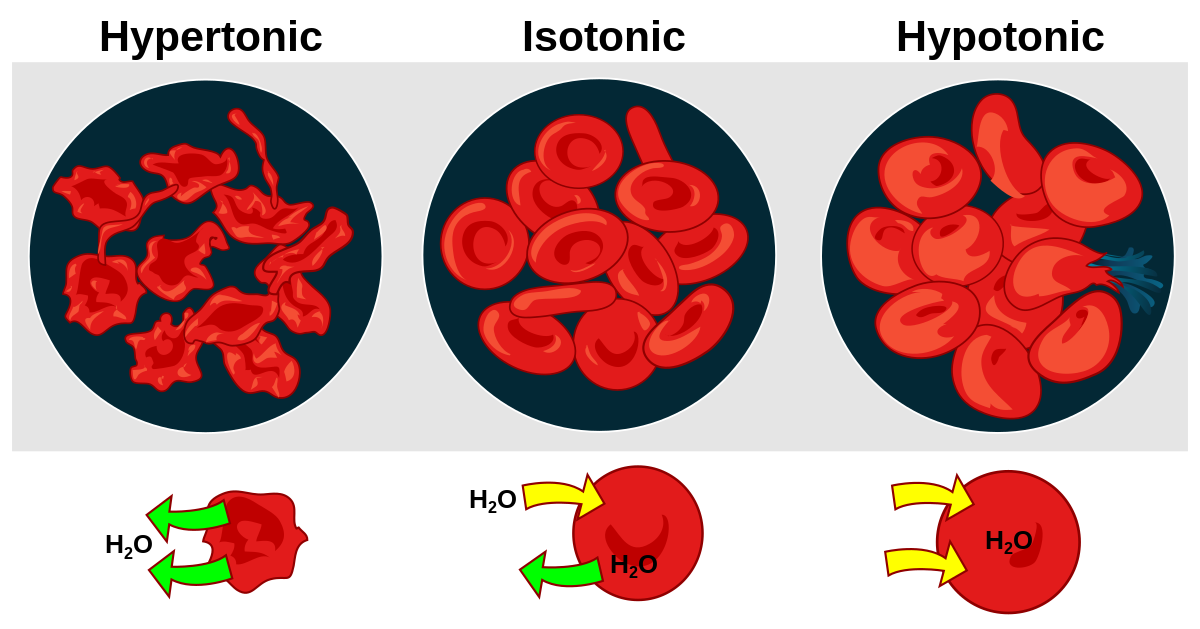
Hypertonic
The root hyper means “above” or “beyond”, so a hypertonic solution is one that has a higher solute concentration than the cell. Because the solution outside the cell is so concentrated, the liquid inside the cell will move out of the cell, trying to reach equilibrium. This can cause the cell to shrivel.
For example, let’s pretend that we have a cell that has a 2% NaCl concentration within and it is in an environment that has a 4% NaCl concentration. Because the environment has more solutes, the liquid within the cell will move out of the cell, trying to reach equilibrium.
Because environments need to be in equilibrium, and the movement of water in and out of cells (osmosis) is passive transport, this tendency towards equilibrium happens automatically.
Hypotonic
The root hypo means “below” or “under”, so a hypotonic solution is one that has a lower solute concentration than the cell. Because the solution outside the cell has so few solutes, the liquid in the environment will move into the cell, trying to reach equilibrium. This can cause the cell to burst (lyse).
For example, let’s pretend that we have the same cell in our previous example with 2% NaCl solutes. However, this time, the cell is in distilled water, which is 100% water, with no solutes. Because the environment has fewer solutes than the cell, the liquid outside the cell will rush into the cell, trying to reach equilibrium.
This is good for plants because it allows the cell to establish turgor pressure, which is when the plant cell is rigid and full of water. When plant cells are full of water, they can stand upright. When plant cells do not have enough water the vacuole shrinks and take away the pressure on the cell wall. This is why they wilt.
However, animal cells do not have cell walls. This means that they do not have anything to protect them from bursting if they are placed in a hypotonic solution. This is one reason why the water we drink does not go directly into our bloodstream. If it did, it could cause our cells to burst. It is also why you can drink too much water too quickly.
Isotonic
The root iso means “same”, so an isotonic solution is one that has the same solute concentration as found within the cell. Because the solution outside the cell has the same concentration of solutes as the cell, the water in the environment will move into the cell and the liquid in the cell will move out of the cell because equilibrium has been established. This is the ideal environment for an animal cell.
If you’ve ever been hospitalized, you may have had an IV to keep you hydrated. Typically, IV saline solution is about 0.9% NaCl, which is isotonic. You wouldn’t want this to be entirely fresh water, because it is injected straight into your bloodstream. If you wear contacts, you might also put your contacts in saline solution at night. This solution is isotonic as well, so when you put your contacts back in your eyes, they do not have fresh water on them.
All cells are in aqueous solutions, which means their environments are hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic. The ideal environment for animal cells is an isotonic solution because the cells will neither burst nor shrink. The ideal environment for plant cells is a hypotonic solution because water will rush into the cell, keeping the plant from wilting.
 Edited: 05 October 2022
Edited: 05 October 2022
Hyper/Hypo and Isotonic Solutions
The tonicity of a solution is the concentration of solutes. Typically, when you discuss tonicity, you are referring to the solution the cell is in, not the cell itself. The aqueous environment surrounding a cell can be hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic.
Hypertonic
The root hyper means “above” or “beyond”, so a hypertonic solution is one that has a higher solute concentration than the cell. Because the solution outside the cell is so concentrated, the liquid inside the cell will move out of the cell, trying to reach equilibrium. This can cause the cell to shrivel.
For example, let’s pretend that we have a cell that has a 2% NaCl concentration within and it is in an environment that has a 4% NaCl concentration. Because the environment has more solutes, the liquid within the cell will move out of the cell, trying to reach equilibrium.
Because environments need to be in equilibrium, and the movement of water in and out of cells (osmosis) is passive transport, this tendency towards equilibrium happens automatically.
Hypotonic
The root hypo means “below” or “under”, so a hypotonic solution is one that has a lower solute concentration than the cell. Because the solution outside the cell has so few solutes, the liquid in the environment will move into the cell, trying to reach equilibrium. This can cause the cell to burst (lyse).
For example, let’s pretend that we have the same cell in our previous example with 2% NaCl solutes. However, this time, the cell is in distilled water, which is 100% water, with no solutes. Because the environment has fewer solutes than the cell, the liquid outside the cell will rush into the cell, trying to reach equilibrium.
This is good for plants because it allows the cell to establish turgor pressure, which is when the plant cell is rigid and full of water. When plant cells are full of water, they can stand upright. When plant cells do not have enough water the vacuole shrinks and take away the pressure on the cell wall. This is why they wilt.
However, animal cells do not have cell walls. This means that they do not have anything to protect them from bursting if they are placed in a hypotonic solution. This is one reason why the water we drink does not go directly into our bloodstream. If it did, it could cause our cells to burst. It is also why you can drink too much water too quickly.
Isotonic
The root iso means “same”, so an isotonic solution is one that has the same solute concentration as found within the cell. Because the solution outside the cell has the same concentration of solutes as the cell, the water in the environment will move into the cell and the liquid in the cell will move out of the cell because equilibrium has been established. This is the ideal environment for an animal cell.
If you’ve ever been hospitalized, you may have had an IV to keep you hydrated. Typically, IV saline solution is about 0.9% NaCl, which is isotonic. You wouldn’t want this to be entirely fresh water, because it is injected straight into your bloodstream. If you wear contacts, you might also put your contacts in saline solution at night. This solution is isotonic as well, so when you put your contacts back in your eyes, they do not have fresh water on them.
All cells are in aqueous solutions, which means their environments are hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic. The ideal environment for animal cells is an isotonic solution because the cells will neither burst nor shrink. The ideal environment for plant cells is a hypotonic solution because water will rush into the cell, keeping the plant from wilting.
 Edited: 05 October 2022
Edited: 05 October 2022
 Knowt
Knowt
