
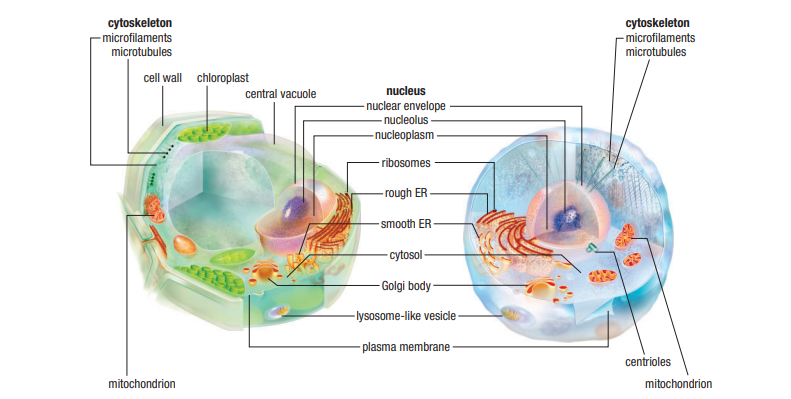
2.1: Cell Structure
Eukaryotic: membrane bound nucleus
Plant cells: cell wall, plastids, larger vacuole
Cytoskeleton: used for cell shape, internal structure, movement and cell division
Many cell are surrounded and supported by a complex extracellular matrix, able to interact with adjacent cells and environment via cell junctions.
Prokaryotes: no nuclear membrane, no mitochondria
Subunits of ribosomes are assembled from proteins and DNA in the nucleus
Name | Structure reference/ Analogy | Membrane? | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
Nucleus | Pearl in an oyster. | Y | Contains & protects almost all the DNA - separated from cytosol or metabolic processes that may damage it. Makes ribosome units. |
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Extension to nuclear envelope. Repeated, flat folds. | Y | Creates new polypeptide chains and sometimes enhances them into lipids or enzymes. |
Golgi body | Stack of pancakes. | Y | Vesicles fuse and empty here. Put finishing touches on chains like phosphates and sugars to make membrane proteins and then shipped of to plasma membrane or lysosomes. |
Transport/ Secretory vesicle | Marble-like structures. | Y | Transport within the cell or releases them from the cell. |
Mitochondrion | Looks like a kidney bean or a small, wrapped baby. | Y | Own DNA. Makes ATP. Basically an aerobic bacteria that got comfortable. |
Chloroplast | Two outer membranes with stroma inside. Stroma may look like stacks of coins. | Y | Contains enzymes, pigments and traces of DNA. Plastid. |
Lysosomes | Recycling centers: hold digestive enzymes. | Y | Vesicle containing powerful digestive enzymes. Carry disposals. |
Peroxisome | Recycling centers: Hold catlase | Y | Vesicle containing enzymes for digesting fatty or amino acids. |
Vacuole | Garbage bins. | Y | Vesicle that stores waste and aids in cellular metabolism and water balance. Maintains pressure. |
Ribosome | Folded ribbon. | N | Assemble polypeptide chains. |
Centriole | Two pills or logs lying on top of each other. | N | Makes tubules for cell division. |
Nuclear Membrane: Double membrane of 2 lipid bi-layers. Contains proteins that are receptors, transporters & spanners. Restricts access to DNA.
Nucleoplasm: vicious fluid similar to cytosol
Nucleolus: Dense, irregularly shaped region. Sub-units of ribosomes are assembled from proteins and RNA.
Chromatin: DNA & associated proteins in nucleus.
Endomembrane system: system of interacting organelles. Make lipids, enzymes & proteins for secretion/insertion into cell membrane. Destroys toxins. Recycles waste.
Nucleus: DNA → RNA → Nuclear pores → Cytosol
Rough ER: Cytosol => Polypeptide chains (by ribosomes)
Vesicles: bud from ER carrying chains to Golgi bodies, some go through interior of Rough ER
Smooth ER: The latter are packaged into Vesicles and sent off, some become enzymes. Rich in protein oriented cells.
Golgi body: Modified and sorted. New vesicles take them to plasma membrane or lysosomes.
Plastids: membrane-bound organelle that is involved in photosynthesis and storage in plants and algae
Chloroplast: double membrane, enzymes and pigments for photosynthesis - in stroma
Chromoplasts: stores pigments other than chlorophyll
Amyloplasts: stores starch
2.1: Cell Structure
Eukaryotic: membrane bound nucleus
Plant cells: cell wall, plastids, larger vacuole
Cytoskeleton: used for cell shape, internal structure, movement and cell division
Many cell are surrounded and supported by a complex extracellular matrix, able to interact with adjacent cells and environment via cell junctions.
Prokaryotes: no nuclear membrane, no mitochondria
Subunits of ribosomes are assembled from proteins and DNA in the nucleus
Name | Structure reference/ Analogy | Membrane? | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
Nucleus | Pearl in an oyster. | Y | Contains & protects almost all the DNA - separated from cytosol or metabolic processes that may damage it. Makes ribosome units. |
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Extension to nuclear envelope. Repeated, flat folds. | Y | Creates new polypeptide chains and sometimes enhances them into lipids or enzymes. |
Golgi body | Stack of pancakes. | Y | Vesicles fuse and empty here. Put finishing touches on chains like phosphates and sugars to make membrane proteins and then shipped of to plasma membrane or lysosomes. |
Transport/ Secretory vesicle | Marble-like structures. | Y | Transport within the cell or releases them from the cell. |
Mitochondrion | Looks like a kidney bean or a small, wrapped baby. | Y | Own DNA. Makes ATP. Basically an aerobic bacteria that got comfortable. |
Chloroplast | Two outer membranes with stroma inside. Stroma may look like stacks of coins. | Y | Contains enzymes, pigments and traces of DNA. Plastid. |
Lysosomes | Recycling centers: hold digestive enzymes. | Y | Vesicle containing powerful digestive enzymes. Carry disposals. |
Peroxisome | Recycling centers: Hold catlase | Y | Vesicle containing enzymes for digesting fatty or amino acids. |
Vacuole | Garbage bins. | Y | Vesicle that stores waste and aids in cellular metabolism and water balance. Maintains pressure. |
Ribosome | Folded ribbon. | N | Assemble polypeptide chains. |
Centriole | Two pills or logs lying on top of each other. | N | Makes tubules for cell division. |
Nuclear Membrane: Double membrane of 2 lipid bi-layers. Contains proteins that are receptors, transporters & spanners. Restricts access to DNA.
Nucleoplasm: vicious fluid similar to cytosol
Nucleolus: Dense, irregularly shaped region. Sub-units of ribosomes are assembled from proteins and RNA.
Chromatin: DNA & associated proteins in nucleus.
Endomembrane system: system of interacting organelles. Make lipids, enzymes & proteins for secretion/insertion into cell membrane. Destroys toxins. Recycles waste.
Nucleus: DNA → RNA → Nuclear pores → Cytosol
Rough ER: Cytosol => Polypeptide chains (by ribosomes)
Vesicles: bud from ER carrying chains to Golgi bodies, some go through interior of Rough ER
Smooth ER: The latter are packaged into Vesicles and sent off, some become enzymes. Rich in protein oriented cells.
Golgi body: Modified and sorted. New vesicles take them to plasma membrane or lysosomes.
Plastids: membrane-bound organelle that is involved in photosynthesis and storage in plants and algae
Chloroplast: double membrane, enzymes and pigments for photosynthesis - in stroma
Chromoplasts: stores pigments other than chlorophyll
Amyloplasts: stores starch

 Knowt
Knowt