
Separation of Mixture
Mind Map: Separation of Mixtures Physically
Central Idea: Separation of Mixtures
Separating mixtures into their individual components using physical methods.
Main Branches:
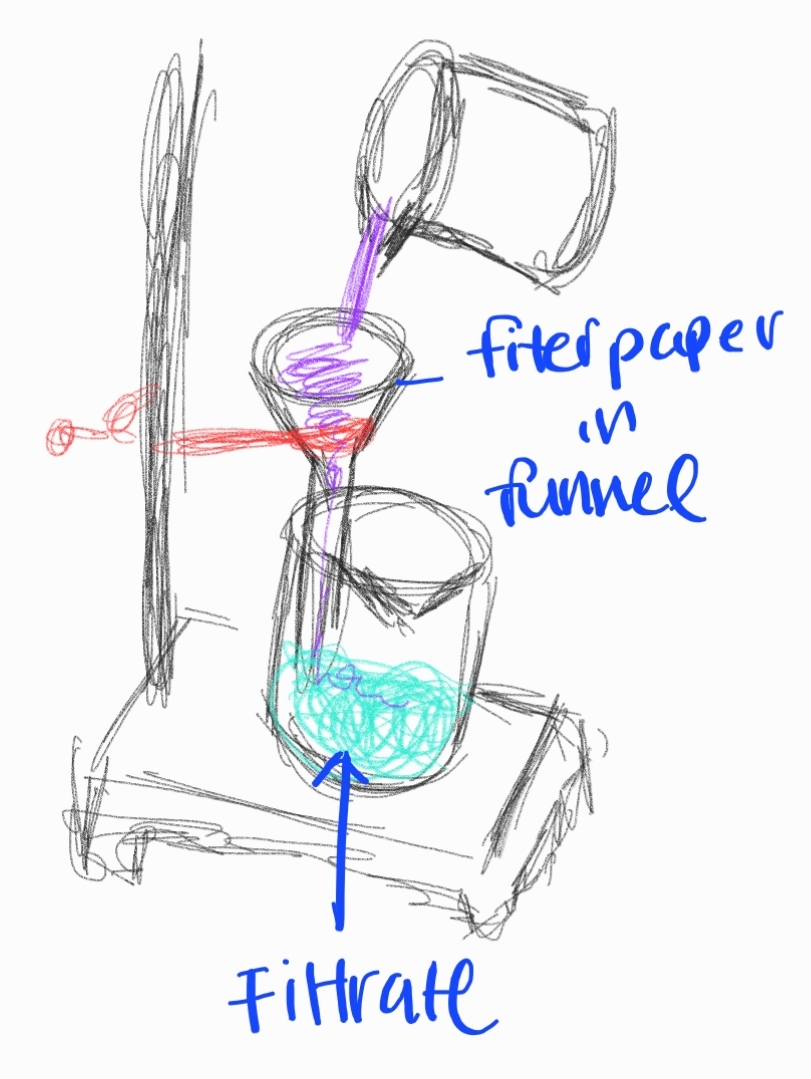
Filtration
Separating solid particles from a liquid or gas using a filter medium.
Sub-branches:
Gravity Filtration
Vacuum Filtration
Hot Filtration
Distillation
Separating a mixture of liquids based on their boiling points.
Sub-branches:
Simple Distillation
Fractional Distillation: used to separate petroleum into simpler mixtures of LIQUID hydrocarbons
process is dependent on the differences in the boiling points of the hydrocarbon fractions
Evaporation
Separating a mixture of a solid dissolved in a liquid by heating and vaporizing the liquid.
STRONG HEATING required → crucible used (usually made of porcelain)
Sub-branches:
Simple Evaporation
Crystallization: separate a dissolved solid from its solvent
concertation solution at HIGH temp and allow it to cool so the solute crystals of the solute form at the bottom of the vessel
can add a single “seed crystal” of solute into a solution to initiate crystallization
Magnetic Separation
Separating magnetic materials from non-magnetic materials using magnets.
Sub-branches:
Electromagnetic Separation
High-Gradient Magnetic Separation
Centrifugation
Separating components of a mixture based on their density using centrifugal force.
Sub-branches:
Sedimentation Centrifugation
Differential Centrifugation
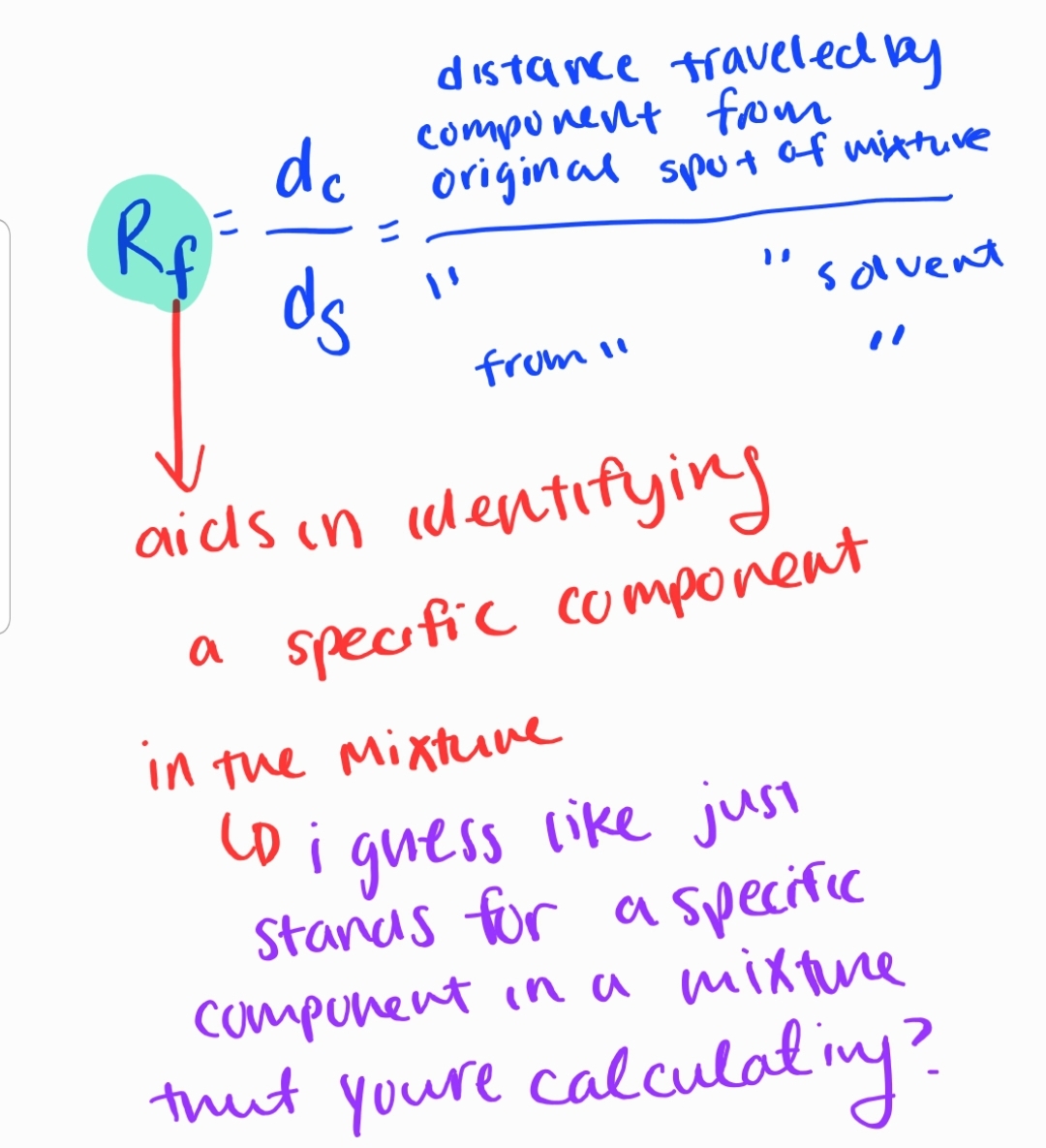
Chromatography: chroma= color graphein= to write
Separating mixtures based on the differential movement of components in a mobile phase.
Sub-branches:
Paper Chromatography
Thin-Layer Chromatography
Sieving
Separating particles of different sizes using a sieve or mesh.
Sub-branches:
Wet Sieving
Dry Sieving
Decantation
Separating a mixture of a liquid and solid by pouring off the liquid layer.
Sub-branches:
Gravity Decantation
Centrifugal Decantation
Sublimation
Separating a mixture of a solid and a volatile substance by heating the mixture, causing the solid to directly vaporize.
Sub-branches:
Reverse Sublimation
Freeze-Drying
Extraction
Separating a mixture by selectively dissolving one or more components into a solvent.
Sub-branches:
Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Solid-Liquid Extraction
Note: This mind map provides an overview of various physical methods for separating mix
Separation of Mixture
Mind Map: Separation of Mixtures Physically
Central Idea: Separation of Mixtures
Separating mixtures into their individual components using physical methods.
Main Branches:
Filtration
Separating solid particles from a liquid or gas using a filter medium.
Sub-branches:
Gravity Filtration
Vacuum Filtration
Hot Filtration

Distillation
Separating a mixture of liquids based on their boiling points.
Sub-branches:
Simple Distillation
Fractional Distillation: used to separate petroleum into simpler mixtures of LIQUID hydrocarbons
process is dependent on the differences in the boiling points of the hydrocarbon fractions
Evaporation
Separating a mixture of a solid dissolved in a liquid by heating and vaporizing the liquid.
STRONG HEATING required → crucible used (usually made of porcelain)
Sub-branches:
Simple Evaporation
Crystallization: separate a dissolved solid from its solvent
concertation solution at HIGH temp and allow it to cool so the solute crystals of the solute form at the bottom of the vessel
can add a single “seed crystal” of solute into a solution to initiate crystallization
Magnetic Separation
Separating magnetic materials from non-magnetic materials using magnets.
Sub-branches:
Electromagnetic Separation
High-Gradient Magnetic Separation
Centrifugation
Separating components of a mixture based on their density using centrifugal force.
Sub-branches:
Sedimentation Centrifugation
Differential Centrifugation
Chromatography: chroma= color graphein= to write
Separating mixtures based on the differential movement of components in a mobile phase.
Sub-branches:
Paper Chromatography
Thin-Layer Chromatography

Sieving
Separating particles of different sizes using a sieve or mesh.
Sub-branches:
Wet Sieving
Dry Sieving
Decantation
Separating a mixture of a liquid and solid by pouring off the liquid layer.
Sub-branches:
Gravity Decantation
Centrifugal Decantation
Sublimation
Separating a mixture of a solid and a volatile substance by heating the mixture, causing the solid to directly vaporize.
Sub-branches:
Reverse Sublimation
Freeze-Drying
Extraction
Separating a mixture by selectively dissolving one or more components into a solvent.
Sub-branches:
Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Solid-Liquid Extraction
Note: This mind map provides an overview of various physical methods for separating mix
 Knowt
Knowt