
Ch 22 - Economic inequality and poverty
Equity: fairness in opportunities given to people despite their differences
Equality: disparities in incomes and wealth given to people
Inequality is inevitable since it influences productivity
Inequality is not determined by the level of national income
Result of national policies and industries that do not cater for economic growth → fair and inclusive
The failing of these policies causes economic growth not to generate higher income and better opportunities
Types of inequality:
Inequality in outcomes: inequalities in income and wealth
Inequalities of opportunities: when a person isn't earning as much, meaning they cant afford to buy assets
Raising levels of inequality in income, wealth, and opportunity reflect a lack of equity
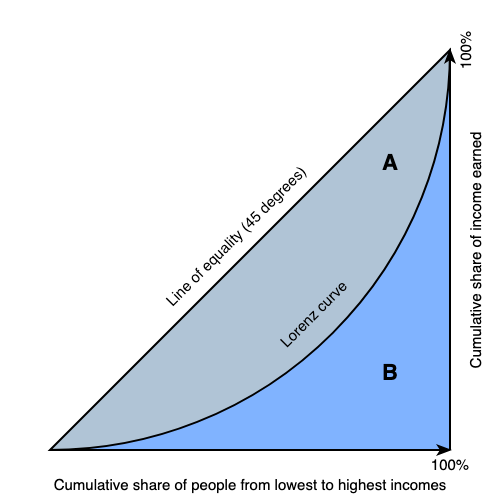
How to measure inequality using a Lorenz curve:
Used to compare two or more countries in terms of economic distribution
Compare change in income distribution for a single country over time
A lorenz curve is constructed using cumulative share of income
Difference between income inequality and wealth inequality:
Wealth: also known as net worth, value of all a person’s total assets minus total liabilities. This includes large assets such as real estate, stocks, and so on.
Income: all the money people can earn from wages and every source of earning.
liabilities: all the debt a personal owes. This is deducted from wealth as it does not contribute to their amount of money.
PPP, purchasing power parity: means that it will buy approximately the same amount of goods and services in any country
Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): people who are in extreme poverty and lack the three dimensions: education, healthy, and standard of living. These methods of identifying poverty are called indicators.
Absolute poverty: occurs when a person’s income isn’t enough to sustain their basic needs of survival
Relative poverty: is a comparative measure based on the living standards in a country
Means that a person is poor relative to the other in a country
Causes of inequality and poverty:
inequality of opportunities
discrimination
difference in human capital
different levels of ownership
globalisation and tech progress
market oriented, supply side policies
government tax and benefits policies
unequal status and power
Consequences of inequality and poverty:
Harms economic growth
Decreased quantity of living standards and social stability
Role of taxation in reducing poverty and income inequality:
Taxes can be composed to reduce consumption on producers, goods and services that create negative externalities
Direct taxes may be raised or lowered to change the level of AD in the economy to achieve macroeconomic goals. Households pay direct tax in the form of income taxes
Businesses pay taxes on their profits, known as corporate taxes
How are taxes calculated:
Percentage of tax = Tax paid / total income * 100
Indirect taxes are regressive, meaning that they take a larger share of income from lower income people than from higher income
Indirect taxes care an important source of revenue for governments, and can be used to discourage the consumption of goods that create negative externalities. since they are regressive, they worsen income inequality
An income tax structure is progressive if it taxes a larger percentage of a larger income and a smaller percentage of a smaller income. Most direct tax structures are progressive.
Progressive income tax structure which makes the distribution of income more equal will offset to some extent by the country’s indirect taxes
Gives the government the funds to finance its necessary expenditures and allows for distributive policies
Transfer payments: governments use tax revenues to redistribute income and provide different types of assistance to groups in the economy to improve their living standards and opportunities
Their assistance represents income that is transferred
Policies which promote equal opportunities through investments in human capital:
Governments need to apply policies which ensure equal opportunities for people of all income tax. This can be done using targeted government subsidies, transfers, and programs supporting lower income households.
Increase opportunities available to those who may have been denied opportunities for their race, gender, age..
Minimum wage: minimum amount of remuneration that an employer can legally pay a worker
Can be an element of a policy to overcome poverty and reduce inequality
Increasing minimum wage helps:
Higher wages encourage people to join the labour market and reduce unemployment
Increased consumption by low wage workers
Higher paying jobs help them expand their skills
Reduction of inequality and poverty
Ch 22 - Economic inequality and poverty
Equity: fairness in opportunities given to people despite their differences
Equality: disparities in incomes and wealth given to people
Inequality is inevitable since it influences productivity
Inequality is not determined by the level of national income
Result of national policies and industries that do not cater for economic growth → fair and inclusive
The failing of these policies causes economic growth not to generate higher income and better opportunities
Types of inequality:
Inequality in outcomes: inequalities in income and wealth
Inequalities of opportunities: when a person isn't earning as much, meaning they cant afford to buy assets
Raising levels of inequality in income, wealth, and opportunity reflect a lack of equity
How to measure inequality using a Lorenz curve:
Used to compare two or more countries in terms of economic distribution
Compare change in income distribution for a single country over time
A lorenz curve is constructed using cumulative share of income

Difference between income inequality and wealth inequality:
Wealth: also known as net worth, value of all a person’s total assets minus total liabilities. This includes large assets such as real estate, stocks, and so on.
Income: all the money people can earn from wages and every source of earning.
liabilities: all the debt a personal owes. This is deducted from wealth as it does not contribute to their amount of money.
PPP, purchasing power parity: means that it will buy approximately the same amount of goods and services in any country
Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): people who are in extreme poverty and lack the three dimensions: education, healthy, and standard of living. These methods of identifying poverty are called indicators.
Absolute poverty: occurs when a person’s income isn’t enough to sustain their basic needs of survival
Relative poverty: is a comparative measure based on the living standards in a country
Means that a person is poor relative to the other in a country
Causes of inequality and poverty:
inequality of opportunities
discrimination
difference in human capital
different levels of ownership
globalisation and tech progress
market oriented, supply side policies
government tax and benefits policies
unequal status and power
Consequences of inequality and poverty:
Harms economic growth
Decreased quantity of living standards and social stability
Role of taxation in reducing poverty and income inequality:
Taxes can be composed to reduce consumption on producers, goods and services that create negative externalities
Direct taxes may be raised or lowered to change the level of AD in the economy to achieve macroeconomic goals. Households pay direct tax in the form of income taxes
Businesses pay taxes on their profits, known as corporate taxes
How are taxes calculated:
Percentage of tax = Tax paid / total income * 100
Indirect taxes are regressive, meaning that they take a larger share of income from lower income people than from higher income
Indirect taxes care an important source of revenue for governments, and can be used to discourage the consumption of goods that create negative externalities. since they are regressive, they worsen income inequality
An income tax structure is progressive if it taxes a larger percentage of a larger income and a smaller percentage of a smaller income. Most direct tax structures are progressive.
Progressive income tax structure which makes the distribution of income more equal will offset to some extent by the country’s indirect taxes
Gives the government the funds to finance its necessary expenditures and allows for distributive policies
Transfer payments: governments use tax revenues to redistribute income and provide different types of assistance to groups in the economy to improve their living standards and opportunities
Their assistance represents income that is transferred
Policies which promote equal opportunities through investments in human capital:
Governments need to apply policies which ensure equal opportunities for people of all income tax. This can be done using targeted government subsidies, transfers, and programs supporting lower income households.
Increase opportunities available to those who may have been denied opportunities for their race, gender, age..
Minimum wage: minimum amount of remuneration that an employer can legally pay a worker
Can be an element of a policy to overcome poverty and reduce inequality
Increasing minimum wage helps:
Higher wages encourage people to join the labour market and reduce unemployment
Increased consumption by low wage workers
Higher paying jobs help them expand their skills
Reduction of inequality and poverty
 Knowt
Knowt
