
AP Environmental Science 9.4-9.5: Greenhouse Gases and Global Climate Change
Main Questions:
Is it proven?
What are potential consequences?
What can be done?
How Does This Relate to the Carbon Cycle?
Sources of Increased Atmospheric CO2
Burning Fossil Fuels
Deforestation
Carbon Balance: increased atmospheric CO2 less than expected based only on input
about 49% remains in atmosphere
about 29% uptake by oceans
carbon balance: about 22% unaccounted for
Consequences of Increased Greenhouse Gases
Human activity and natural processes lead to…
Increased atmospheric greenhouse gases, which leads to…
An increase in average global temperature, which causes…
Changes in climate, which can lead to…
Droughts
Increased rainfall and storms
Rising sea levels
Loss of biodiversity
Climate Changes During the Past 900,000 Years
Past cimate based on study of Antartic glaciers
Cycles of Ice Ages lasting about 100,000 years
Interglacial Periods lasting 10,000 to 12,500 years
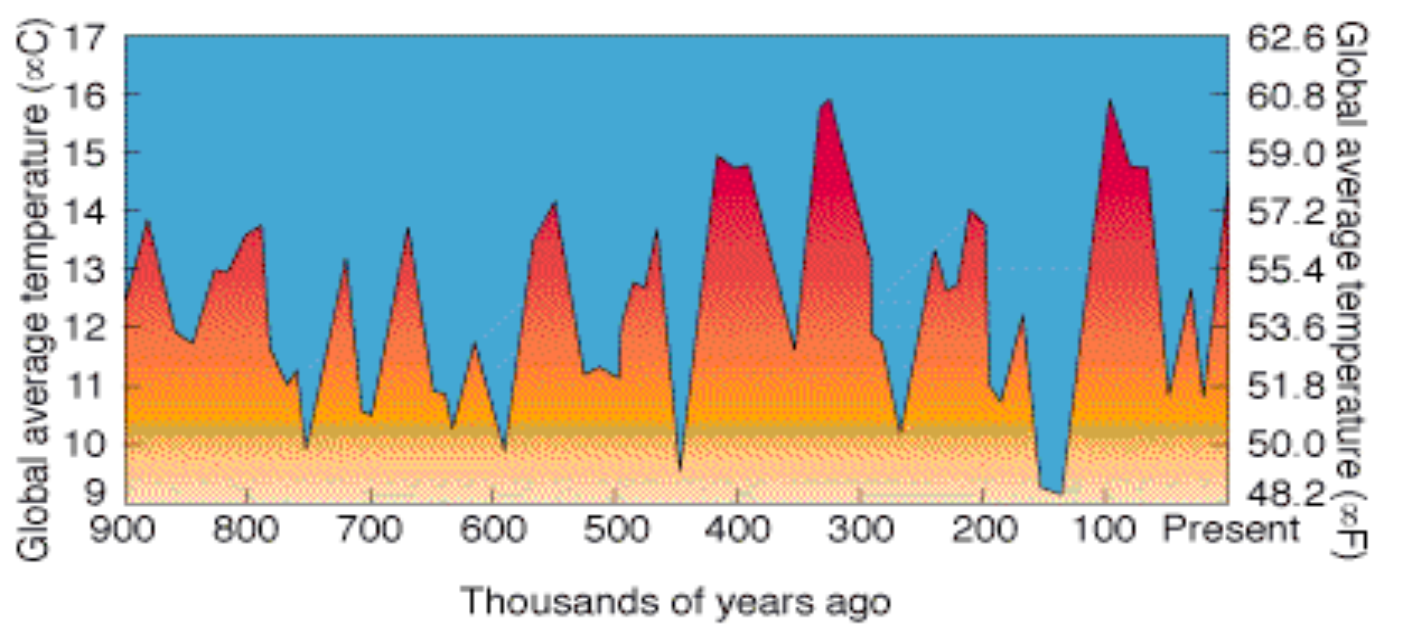
Climate During the Past 160,000 Years
End of last Ice Age about 10,000 yr BP
Now in warm interglacial period
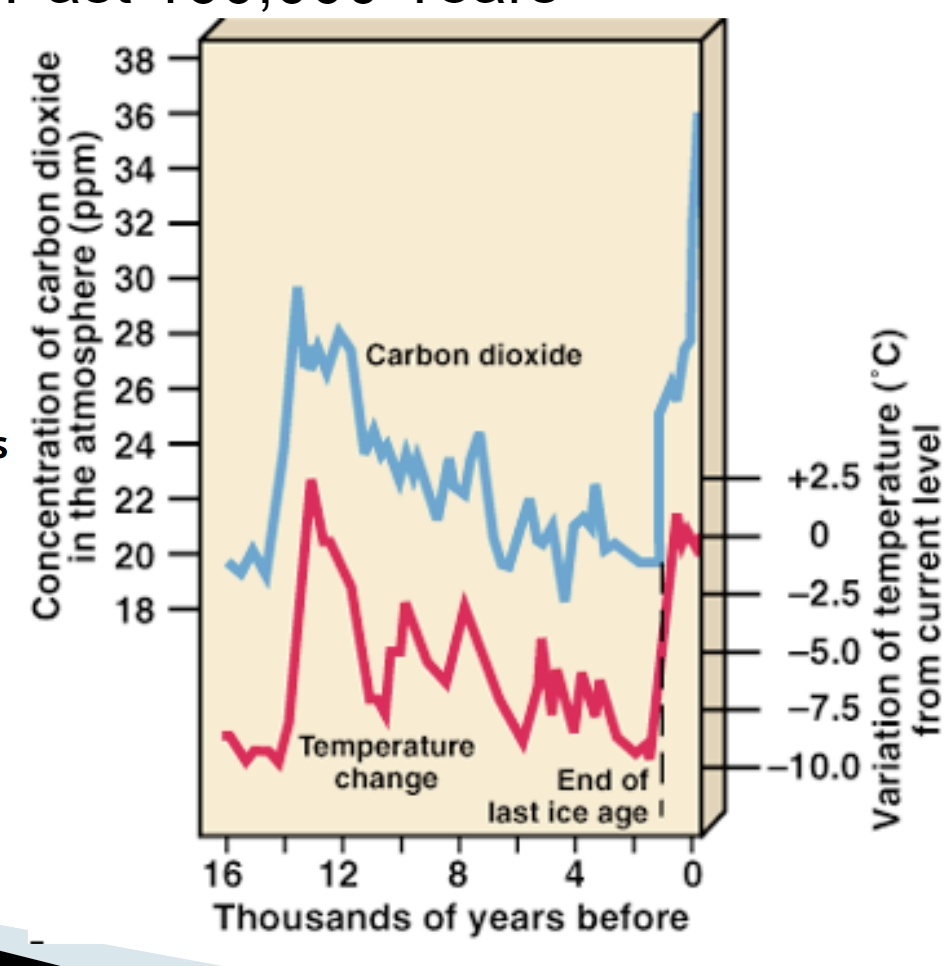
Based on ice core data, analysis of trapped gas
Correlation between CO2 and mean temperature
What is the Scientific Consensus?
Mean global temperature rose about 0.6º C (1º F) in past 100 years
Increase is real, not explained by natural variation in solar radiation
Warming greater at poles than equator, greater at night, mostly troposphere
Future Scenarios
General Circulation Models (GCMs) are used to predict future climates
Projected warming of 1 to 3.5 º C between 1990 & 2100
Likely scenario: doubling of CO2 (from 280 ppm to 560 ppm) before 2100 leading to warming of 2ºC
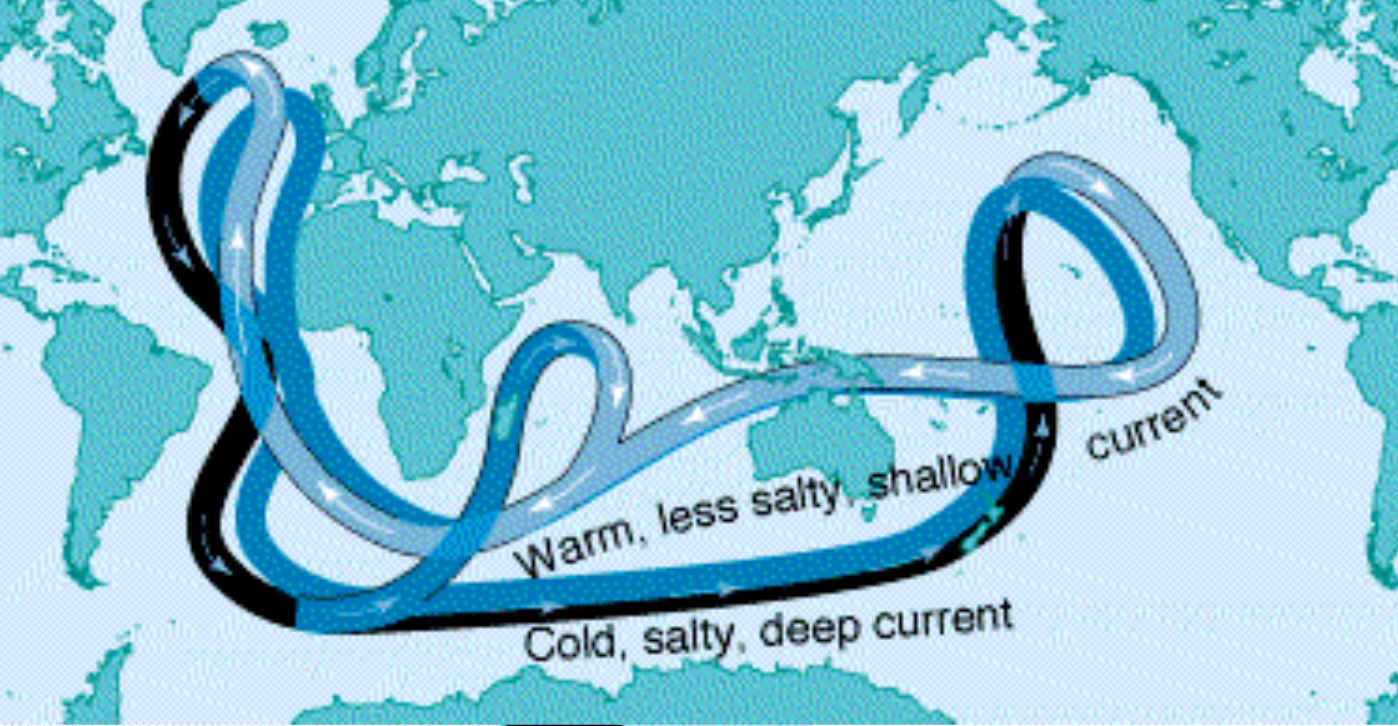
Role of the Oceans
Storage of CO2 in deep water
Warming could decrease ability of ocean to serve as “sink” for carbon
Ecological Implications
Shift of habitat to higher latitudes
Shift of habitat to higher elevations
Potential large loss of biodiversity
Solutions to Global Warming
Prevention
Cut fossil fuel use (especially coal) in half
Improve energy efficiency
Shift to renewable energy resources
Reduce deforestation
Use sustainable agriculture
Slow population growth
Clean Energy Use
Cleanup
Remove CO2 from vehicular and smokestack emissions
Plant and tend to trees
Actions
Waste less water
Develop crops that need less water
Move hazardous materials storage tanks away from coast
Prohibit new construction or remodeling on low-lying coastal areas
Stockpile 1-5 year supply of key foods
Expand existing wildlife reserves toward the poles
Connect wildlife reserves with corridors
International Agreements
Kyoto Agreement (1997)
38 developed countries must cut greenhouse gas emissions to 5.2% below 1990 levels between 2008-2012
Developing countries exempted
Allow emissions trading, in which countries can sell its excess reductions to others
Countries can also plant trees to meet goal
Impact on U.S.: Economic Incentives/Regulatory Changes
Reduce energy use by 18%
Reduce electricity use by 30%
Cut SO2 emissions by 50%
Cut NO2 emissions by 25%
Cut CO2 emissions by 14% below 1990 levels
Twice the amount specified in the Kyoto Treaty
AP Environmental Science 9.4-9.5: Greenhouse Gases and Global Climate Change
Main Questions:
Is it proven?
What are potential consequences?
What can be done?
How Does This Relate to the Carbon Cycle?
Sources of Increased Atmospheric CO2
Burning Fossil Fuels
Deforestation
Carbon Balance: increased atmospheric CO2 less than expected based only on input
about 49% remains in atmosphere
about 29% uptake by oceans
carbon balance: about 22% unaccounted for
Consequences of Increased Greenhouse Gases
Human activity and natural processes lead to…
Increased atmospheric greenhouse gases, which leads to…
An increase in average global temperature, which causes…
Changes in climate, which can lead to…
Droughts
Increased rainfall and storms
Rising sea levels
Loss of biodiversity
Climate Changes During the Past 900,000 Years
Past cimate based on study of Antartic glaciers
Cycles of Ice Ages lasting about 100,000 years
Interglacial Periods lasting 10,000 to 12,500 years

Climate During the Past 160,000 Years
End of last Ice Age about 10,000 yr BP
Now in warm interglacial period
Based on ice core data, analysis of trapped gas
Correlation between CO2 and mean temperature

What is the Scientific Consensus?
Mean global temperature rose about 0.6º C (1º F) in past 100 years
Increase is real, not explained by natural variation in solar radiation
Warming greater at poles than equator, greater at night, mostly troposphere
Future Scenarios
General Circulation Models (GCMs) are used to predict future climates
Projected warming of 1 to 3.5 º C between 1990 & 2100
Likely scenario: doubling of CO2 (from 280 ppm to 560 ppm) before 2100 leading to warming of 2ºC
Role of the Oceans
Storage of CO2 in deep water
Warming could decrease ability of ocean to serve as “sink” for carbon

Ecological Implications
Shift of habitat to higher latitudes
Shift of habitat to higher elevations
Potential large loss of biodiversity
Solutions to Global Warming
Prevention
Cut fossil fuel use (especially coal) in half
Improve energy efficiency
Shift to renewable energy resources
Reduce deforestation
Use sustainable agriculture
Slow population growth
Clean Energy Use
Cleanup
Remove CO2 from vehicular and smokestack emissions
Plant and tend to trees
Actions
Waste less water
Develop crops that need less water
Move hazardous materials storage tanks away from coast
Prohibit new construction or remodeling on low-lying coastal areas
Stockpile 1-5 year supply of key foods
Expand existing wildlife reserves toward the poles
Connect wildlife reserves with corridors
International Agreements
Kyoto Agreement (1997)
38 developed countries must cut greenhouse gas emissions to 5.2% below 1990 levels between 2008-2012
Developing countries exempted
Allow emissions trading, in which countries can sell its excess reductions to others
Countries can also plant trees to meet goal
Impact on U.S.: Economic Incentives/Regulatory Changes
Reduce energy use by 18%
Reduce electricity use by 30%
Cut SO2 emissions by 50%
Cut NO2 emissions by 25%
Cut CO2 emissions by 14% below 1990 levels
Twice the amount specified in the Kyoto Treaty
 Knowt
Knowt
