
Cells
Cells
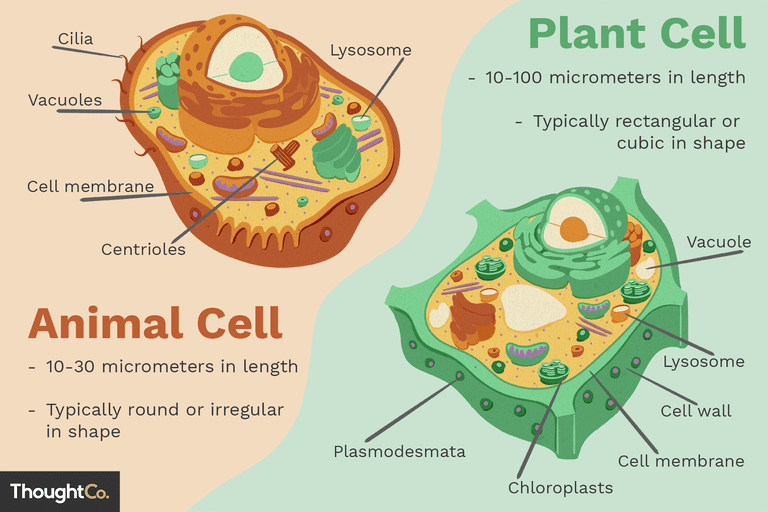
Cells are made up of many parts and are separated into 2 broad groups: animal cells, and plant cells. There are a few differences between the 2 types of cells, as they do not have all the same parts.
Cell Theory
Before cells were discovered, it was thought that life can from inorganic things. After the invention of microscopes, that theory was disproven and we now know that life comes from preexisting life. In the 1660s, a man named Robert Hooke discovered the first cells, and since then scientists have worked together to make the cell theory through their observations.
As of now, the cell theory states:
- All organisms are made up of cells
- Cells are the building blocks for all life
- Cells are born from preexisting cells
- Genetic information (DNA) is passed on during cell division
- Energy flows inside cells
- All cells have the same fundamental chemical composition
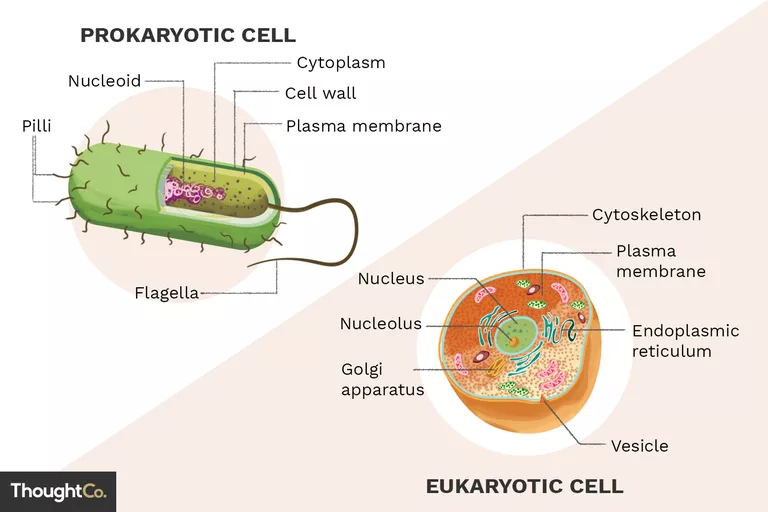
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells
The main difference between the 2 types of cells is that only Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled bacteria and Eukaryotic cells are in things like fungi, plants and animals.
Parts Of A Cell And Their Functions
The parts of a cell are called organelles. There are many different parts of a cell, each with its own function:
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, sometimes also called the plasma membrane is found in all types of cells. Its function is to transport materials coming in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable meaning it can only let some things in and keeps other things out/in.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is only found in plants, algae, fungi and certain types of bacteria (animal cells do not have a cell wall) The cell wall gives the cell a shape and also protects the cell. It also filters materials, like the cell membrane. They are typically made out of cellulose.
Nucleus
The nucleus is like the brain or control center of the cell. It controls all of the cell's activities, like growth and reproduction, and contains all of the cell's chromosomes. Chromosomes are strands of DNA. The nucleus has a nuclear envelope that encloses the nucleus and other organelles.
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is found inside the nucleus. Its function is to produce ribosomes and then transport them to the cytoplasm. The nucleolus is a circular and petite frame of a cell that contains protein and RNA. Its function is to synthesize ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and then integrate it with proteins to produce incomplete ribosomes (ribosomal subunits).
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope acts as a membrane similar to the cell membrane. The envelope has pores and spaces for RNA and proteins to pass through while the nuclear envelope keeps all of the chromatin and the nucleolus inside.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is inside the cell wall, so it's an organelle animal cells do not have. All other organelles in eukaryotic cells are found in the cytoplasm. It is the place holding together all other organelles inside the cell.
The cytoplasm (also called cytosol) is the liquid fluid that fills the actual cell. The cytoplasm has various molecules in its solution such as enzymes, sugars and amino acids all of which help the cell working. The cytoplasm also dissolves enzymes from its fluid to break down larger molecules and the results can then be used for the organelles of a cell. It is found everywhere inside a cell excluding the nucleus.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The ER is the transportation facility of a eukaryotic cell. It transports materials throughout the cell, folds proteins and It is made up of 2 more organelles: the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
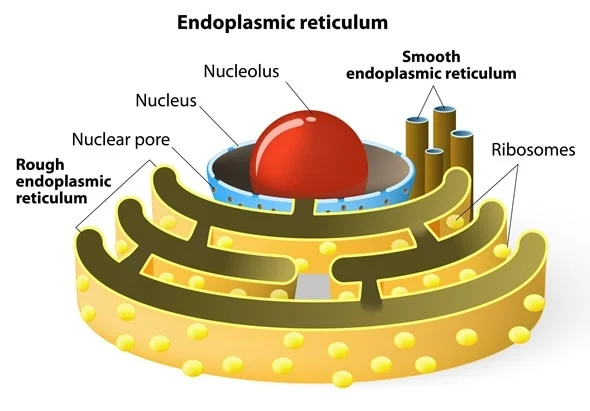
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The rough ER is called the rough ER because it has ribosomes on it which gives it a rough appearance. The function of the rough ER is protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is the process when proteins are being created with cells that use DNA, and RNA.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The function of the smooth ER is that it is a storage unit for lipids and proteins. Unlike the rough ER, the smooth ER does not have ribosomes on it, giving it a smooth appearance.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is "the powerhouse of the cell". The main function of the mitochondria is to produce and release energy throughout the cell. The mitochondria of a cell take nutrients and break them down, and then creates energy molecules for cells. This biochemical process of the cell is called cellular respiration. Mitochondria are the organelles that keep a cell filled with energy.
The organelle is made up of 2 membranes: The outer one is like this skin and covers the organelle. The inner membrane folds over many times and creates layered structures called cristae. The fluid contained in the mitochondria is called the matrix.
Golgi Complex/Apparatus
The function of the Golgi complex is to receive proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and are processed even more. Then the proteins are sorted and distributed to their final destinations.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes make protein inside a cell. Proteins are part of every cell and are part of almost every single function inside of a cell. Protein helps with many cell functions, for example repairing any sort of damage.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are a form of storage in a cell. They may store food or any nutrients a cell may need to live. They can also collect waste so the remainder of the cell is protected from contamination. The waste would ultimately be sent out of the cell. The vacuoles can also help plants store water. A plant only has one large vacuole.
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are only found in plant cells. Chloroplasts work to convert light from the sun into energy; this process is called photosynthesis. Most chloroplasts are oval-shaped, but they can be shapes such as stars, cups, and ribbons. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which is the reason why plants look green.
Cells
Cells
Cells are made up of many parts and are separated into 2 broad groups: animal cells, and plant cells. There are a few differences between the 2 types of cells, as they do not have all the same parts.

Cell Theory
Before cells were discovered, it was thought that life can from inorganic things. After the invention of microscopes, that theory was disproven and we now know that life comes from preexisting life. In the 1660s, a man named Robert Hooke discovered the first cells, and since then scientists have worked together to make the cell theory through their observations.
As of now, the cell theory states:
- All organisms are made up of cells
- Cells are the building blocks for all life
- Cells are born from preexisting cells
- Genetic information (DNA) is passed on during cell division
- Energy flows inside cells
- All cells have the same fundamental chemical composition
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells
The main difference between the 2 types of cells is that only Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled bacteria and Eukaryotic cells are in things like fungi, plants and animals.

Parts Of A Cell And Their Functions
The parts of a cell are called organelles. There are many different parts of a cell, each with its own function:
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, sometimes also called the plasma membrane is found in all types of cells. Its function is to transport materials coming in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable meaning it can only let some things in and keeps other things out/in.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is only found in plants, algae, fungi and certain types of bacteria (animal cells do not have a cell wall) The cell wall gives the cell a shape and also protects the cell. It also filters materials, like the cell membrane. They are typically made out of cellulose.
Nucleus
The nucleus is like the brain or control center of the cell. It controls all of the cell's activities, like growth and reproduction, and contains all of the cell's chromosomes. Chromosomes are strands of DNA. The nucleus has a nuclear envelope that encloses the nucleus and other organelles.
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is found inside the nucleus. Its function is to produce ribosomes and then transport them to the cytoplasm. The nucleolus is a circular and petite frame of a cell that contains protein and RNA. Its function is to synthesize ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and then integrate it with proteins to produce incomplete ribosomes (ribosomal subunits).
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope acts as a membrane similar to the cell membrane. The envelope has pores and spaces for RNA and proteins to pass through while the nuclear envelope keeps all of the chromatin and the nucleolus inside.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is inside the cell wall, so it's an organelle animal cells do not have. All other organelles in eukaryotic cells are found in the cytoplasm. It is the place holding together all other organelles inside the cell.
The cytoplasm (also called cytosol) is the liquid fluid that fills the actual cell. The cytoplasm has various molecules in its solution such as enzymes, sugars and amino acids all of which help the cell working. The cytoplasm also dissolves enzymes from its fluid to break down larger molecules and the results can then be used for the organelles of a cell. It is found everywhere inside a cell excluding the nucleus.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The ER is the transportation facility of a eukaryotic cell. It transports materials throughout the cell, folds proteins and It is made up of 2 more organelles: the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.

Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The rough ER is called the rough ER because it has ribosomes on it which gives it a rough appearance. The function of the rough ER is protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is the process when proteins are being created with cells that use DNA, and RNA.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The function of the smooth ER is that it is a storage unit for lipids and proteins. Unlike the rough ER, the smooth ER does not have ribosomes on it, giving it a smooth appearance.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is "the powerhouse of the cell". The main function of the mitochondria is to produce and release energy throughout the cell. The mitochondria of a cell take nutrients and break them down, and then creates energy molecules for cells. This biochemical process of the cell is called cellular respiration. Mitochondria are the organelles that keep a cell filled with energy.
The organelle is made up of 2 membranes: The outer one is like this skin and covers the organelle. The inner membrane folds over many times and creates layered structures called cristae. The fluid contained in the mitochondria is called the matrix.
Golgi Complex/Apparatus
The function of the Golgi complex is to receive proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and are processed even more. Then the proteins are sorted and distributed to their final destinations.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes make protein inside a cell. Proteins are part of every cell and are part of almost every single function inside of a cell. Protein helps with many cell functions, for example repairing any sort of damage.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are a form of storage in a cell. They may store food or any nutrients a cell may need to live. They can also collect waste so the remainder of the cell is protected from contamination. The waste would ultimately be sent out of the cell. The vacuoles can also help plants store water. A plant only has one large vacuole.
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are only found in plant cells. Chloroplasts work to convert light from the sun into energy; this process is called photosynthesis. Most chloroplasts are oval-shaped, but they can be shapes such as stars, cups, and ribbons. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which is the reason why plants look green.
 Knowt
Knowt
