
Chapter 5- Atomic Structure
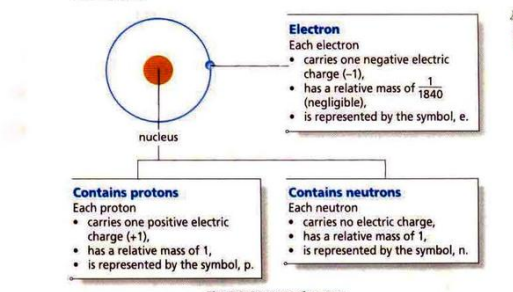
Atoms have three sub-atomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of an element.
Protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus while electrons orbit around the nucleus in electron shells.
Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons are neutral. Since an atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, it is neutral (no charge).
Atoms lose or gain electrons to become either positive ions (cations) or negative ions (anions).
Protons and neutrons have a significant mass in an atom while electrons have an almost negligible mass.
A proton number is the number of protons (and therefore electrons) in an atom. This is usually the smaller number.
Mass number is the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Number of neutrons can be determined by subtracting the proton number from the neutron number.
ISOTOPES
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of electrons and protons but different number of neutrons. Therefore, they have the same chemical but different physical properties and uses.
USES: Radioisotopes are used in radioactivity experiments.
ARRANGING ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
The first electron shell holds two electrons, while the second and third shells hold eight electrons each.
Each shell is filled before moving on to the next.
The way electrons are arranged in an atom determines the electronic structure or electronic configuration of an atom.
The outer most electrons are called valence electrons, and give the element its chemical properties.
Chapter 5- Atomic Structure
Atoms have three sub-atomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of an element.
Protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus while electrons orbit around the nucleus in electron shells.
Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons are neutral. Since an atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, it is neutral (no charge).

Atoms lose or gain electrons to become either positive ions (cations) or negative ions (anions).
Protons and neutrons have a significant mass in an atom while electrons have an almost negligible mass.
A proton number is the number of protons (and therefore electrons) in an atom. This is usually the smaller number.
Mass number is the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Number of neutrons can be determined by subtracting the proton number from the neutron number.
ISOTOPES
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of electrons and protons but different number of neutrons. Therefore, they have the same chemical but different physical properties and uses.
USES: Radioisotopes are used in radioactivity experiments.
ARRANGING ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
The first electron shell holds two electrons, while the second and third shells hold eight electrons each.
Each shell is filled before moving on to the next.
The way electrons are arranged in an atom determines the electronic structure or electronic configuration of an atom.
The outer most electrons are called valence electrons, and give the element its chemical properties.
 Knowt
Knowt
