
Chapter 11 Service and Industry Topics
Deindustrialization
Define
Deindustrialization is when companies move industrial jobs to other regions

Example
Great Lakes
The manufacturing belt in the Great Lakes region turned to the rust belt as secondary industrial activity was moved to the Sunbelt and Northwest
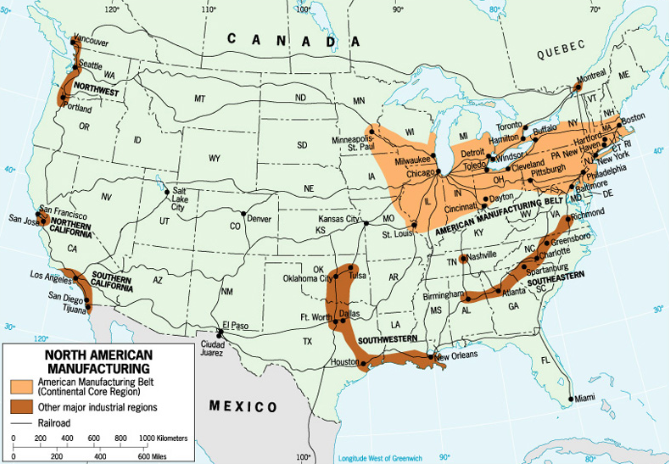
Deindustrialization in the Great Lakes regions happened because of
cheaper labor in the South (less skilled workers or less strong unions)
looser labor and environmental regulations in the South
decreased global demand for goods (Marshall Plan - as other places industrialized, U.S. factories shut down because they weren’t needed)
Europe, SE Asia, E Asia, Japan, China, Singapore, Taiwan, S. Korea
more machines in the G.L. region leading to less need for workers
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HfASWPpeZLE
Youngstown
Deindustrialization also occurred in Youngstown, Ohio
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IKuGNt1w0tA
After the steel mill closed in the 1970s, it turned into a brownfield
abandoned homes
80% pop decrease
lost 40,000 jobs
1/4 of Idora neighborhood vacant
137 homes there demolished
8.8% unemployment
$30k homes
In turn, Youngstown redeveloped
rebuilt as a college town
switch to tertiary activity
attract tech startup
400 new jobs
3D printing
Effects
The deindustrialized region switches to tertiary economic activities, works through unemployment, and may see brownfields
However, new industrial belts are created
Brownfields are sites of abandoned factories and vacant resident homes
old, torn down, vacant, residents lose jobs and move, environmental concerns, new people move in → crime

Locational Criteria
388-394 in textbook
Site features
Land
Labor
Capital
Situation features
In relation to other places
Variable costs
Energy
Transportation
Resources
Friction of distance: increased distance = increased time and costs
Industrialization’s heath was in Great Britain because of locational criteria
rivers, port city, ocean access, coal, highways
regional/global trade, colony resources
high wages incentivized the switch to machines
Weber’s Least Cost Theory
Costs
Transportation - the lowest possible cost of:
raw materials to the factory
finished products to the market
Labor
high labor reduces profits, so a factory might do better with cheap labor
Agglomeration
shared talents, services, and facilities
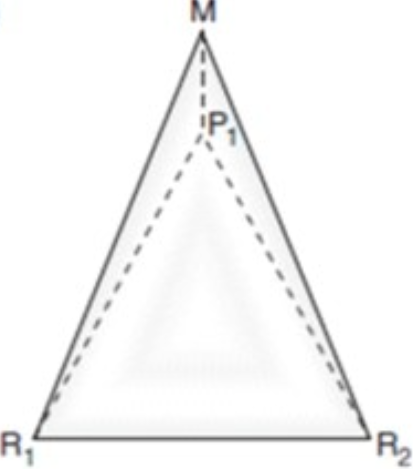
Bulk Gaining
The finished product weighs more than resources (beer, computers)
Because the resources are lighter, they are cheaper to transport and the finished product will be more expensive to transport
The factory will be closer to the market than the resources so the heavy finished products don’t have to travel far
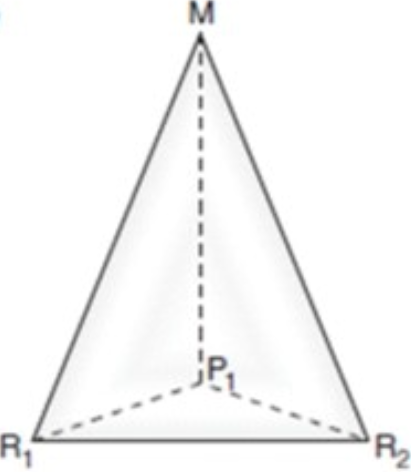
Bulk Reducing
The finished product weighs less than resources (copper, paper)
Because the finished products are lighter, they are cheaper to transport and the resources will be more expensive to transport
The factory will be closer to the resources than the market so the heavy resources don’t have to travel far
Economic Sectors
Primary
Getting raw materials
Growing chickens, planting trees, fishing, lumber, coal mining
Secondary
Processing raw materials into finished products
Manufacturing, construction, processing
Tertiary
Activities or services that move, sell, or trade products
Retain and wholesale trade, bank teller, carpet cleaners, fast food workers, teachers, urban planners, hairdressers
Producer- services performed for corporations
Finance, insurance, real estate, legal, accounting
Consumer- services performed for individuals
Entertainment, tourism, restaurants, education, health care
Geography based on market access rather than energy
Quaternary
Information creation and transfer (a subset of tertiary)
information, research, management investment analysts, university reseachesers
Quinary
Highest level of decision-making (a subset of tertiary)
legislative, presidential cabinet, high-level government work
Tourism
Tourism- travel taken for recreation rather than business.
Most important tertiary activity
World’s largest private industry in jobs and total value generated.
10 % world’s GDP
Half of world’s poorest 50 countries, leading service export sector.
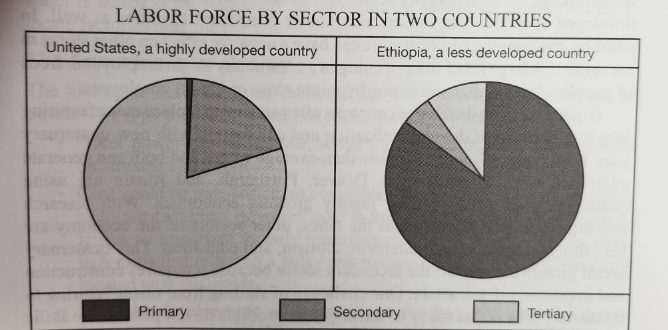
Labor Force
Other Resources
Chapter 11 Vocab
https://knowt.io/flashcards/057d1997-e7fc-4572-8d17-261f4d72dec6
Previously Released FRQs
2019 Set 2 Question 1 - Deindustrialization
Prompt Page 2
https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/media/pdf/ap19-frq-human-geography-set-2.pdf
Rubric Pages 2-3
https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/media/pdf/ap19-sg-human-geography-set-2_1.pdf
2016 Question 1 - Development and Economic Sectors
Prompt Page 2
https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap16_frq_human_geography.pdf
Rubric Pages 2-3
https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap16_human_geography_sg.pdf
2013 Question 1 - Agglomeration
Prompt Page 2
https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/apcentral/ap13_frq_human_geography.pdf
Rubric Pages 2-3
Chapter 11 Service and Industry Topics
Deindustrialization
Define
Deindustrialization is when companies move industrial jobs to other regions

Example
Great Lakes
The manufacturing belt in the Great Lakes region turned to the rust belt as secondary industrial activity was moved to the Sunbelt and Northwest

Deindustrialization in the Great Lakes regions happened because of
cheaper labor in the South (less skilled workers or less strong unions)
looser labor and environmental regulations in the South
decreased global demand for goods (Marshall Plan - as other places industrialized, U.S. factories shut down because they weren’t needed)
Europe, SE Asia, E Asia, Japan, China, Singapore, Taiwan, S. Korea
more machines in the G.L. region leading to less need for workers
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HfASWPpeZLE
Youngstown
Deindustrialization also occurred in Youngstown, Ohio
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IKuGNt1w0tA
After the steel mill closed in the 1970s, it turned into a brownfield
abandoned homes
80% pop decrease
lost 40,000 jobs
1/4 of Idora neighborhood vacant
137 homes there demolished
8.8% unemployment
$30k homes
In turn, Youngstown redeveloped
rebuilt as a college town
switch to tertiary activity
attract tech startup
400 new jobs
3D printing
Effects
The deindustrialized region switches to tertiary economic activities, works through unemployment, and may see brownfields
However, new industrial belts are created
Brownfields are sites of abandoned factories and vacant resident homes
old, torn down, vacant, residents lose jobs and move, environmental concerns, new people move in → crime

Locational Criteria
388-394 in textbook
Site features
Land
Labor
Capital
Situation features
In relation to other places
Variable costs
Energy
Transportation
Resources
Friction of distance: increased distance = increased time and costs
Industrialization’s heath was in Great Britain because of locational criteria
rivers, port city, ocean access, coal, highways
regional/global trade, colony resources
high wages incentivized the switch to machines
Weber’s Least Cost Theory
Costs
Transportation - the lowest possible cost of:
raw materials to the factory
finished products to the market
Labor
high labor reduces profits, so a factory might do better with cheap labor
Agglomeration
shared talents, services, and facilities
Bulk Gaining
The finished product weighs more than resources (beer, computers)
Because the resources are lighter, they are cheaper to transport and the finished product will be more expensive to transport
The factory will be closer to the market than the resources so the heavy finished products don’t have to travel far

Bulk Reducing
The finished product weighs less than resources (copper, paper)
Because the finished products are lighter, they are cheaper to transport and the resources will be more expensive to transport
The factory will be closer to the resources than the market so the heavy resources don’t have to travel far

Economic Sectors
Primary
Getting raw materials
Growing chickens, planting trees, fishing, lumber, coal mining
Secondary
Processing raw materials into finished products
Manufacturing, construction, processing
Tertiary
Activities or services that move, sell, or trade products
Retain and wholesale trade, bank teller, carpet cleaners, fast food workers, teachers, urban planners, hairdressers
Producer- services performed for corporations
Finance, insurance, real estate, legal, accounting
Consumer- services performed for individuals
Entertainment, tourism, restaurants, education, health care
Geography based on market access rather than energy
Quaternary
Information creation and transfer (a subset of tertiary)
information, research, management investment analysts, university reseachesers
Quinary
Highest level of decision-making (a subset of tertiary)
legislative, presidential cabinet, high-level government work
Tourism
Tourism- travel taken for recreation rather than business.
Most important tertiary activity
World’s largest private industry in jobs and total value generated.
10 % world’s GDP
Half of world’s poorest 50 countries, leading service export sector.
Labor Force

Other Resources
Chapter 11 Vocab
https://knowt.io/flashcards/057d1997-e7fc-4572-8d17-261f4d72dec6
Previously Released FRQs
2019 Set 2 Question 1 - Deindustrialization
Prompt Page 2
https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/media/pdf/ap19-frq-human-geography-set-2.pdf
Rubric Pages 2-3
https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/media/pdf/ap19-sg-human-geography-set-2_1.pdf
2016 Question 1 - Development and Economic Sectors
Prompt Page 2
https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap16_frq_human_geography.pdf
Rubric Pages 2-3
https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap16_human_geography_sg.pdf
2013 Question 1 - Agglomeration
Prompt Page 2
https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/apcentral/ap13_frq_human_geography.pdf
Rubric Pages 2-3
 Knowt
Knowt