
Cell and Its Chemistry (brief explanation)
The Modern Cell Theory:
All organisms are composed of one or more cells
Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms
Cells arise only by division of previously existing cell
This cell theory is proposed by German scientists named Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
CELL REQUIREMENTS:
Plasma Membrane
Encloses the cell and controls what goes in and out
Plasma membrane has a double layer of phospholipid molecules.
A phospholipid molecule is made up of glycerol which is a phosphate group and two chains of fatty acid.
Fats
Protein molecules are also found embedded in phospholipids.
The membrane is composed of both protein and phospholipid molecules.
Function:
Serves as the boundary between the outside environment and the inside of the cell.
Gives form and shape to the cells.
Connects one cell to two or more adjacent cells.
Cell membrane is also responsible for…
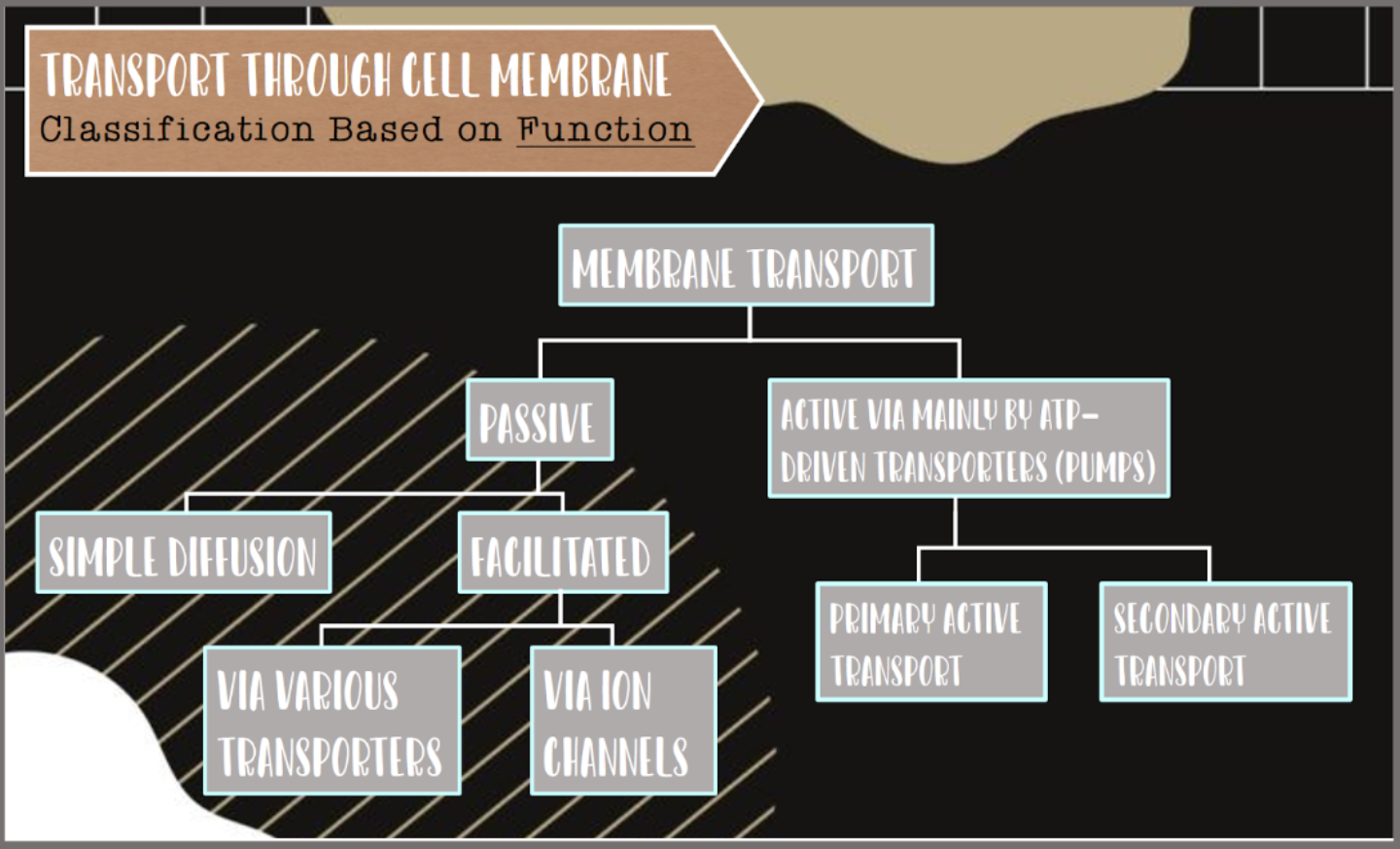
OSMOSISIt is the spontaneous movement of solvent molecules through a semi permeable (selective of what goes in and out) membrane.
The region of the higher solute concentration tends to equalize the lower solute concentration.
Is an essential process by means of which nutrients are delivered to the cells.
DiffusionIt is the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
TransportersIt lets nutrients enter the cell and by – products to leave the cell.
Sugar to glucose to energy
EndocytosisIt is the process in which cells absorb molecules by engulfing them.
The cell creates a small deformation inward called invagination.
Phagocytosis
Cell eating
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking
ExocytosisIt removes undigested residue of a substance brought in by endocytosis.
It also secretes substances such as hormones and enzymes.
Pathway
Protoplasm
Fills between cell membrane and the nucleus (this contain sugar, organelles, proteins, & amino acids)
These are the plasma or mass of jelly like materials inside the cell.
A protoplasm can change into a semisolid gel to semiliquid solution.
protoplasm: proto = first
plasm = substance
is divided in two forms :
liquid
Jelly Protoplasm is composed of: 20% Carbon 10% Hydrogen 62% Oxygen 3% nitrogen 5% other elements.
Genetic Material
All over characteristics of an organism which we refer to as DNA or “blueprint of life”
Gene is different from DNA. It is a portion of DNA pertaining to single characteristic.
Cell and Its Chemistry (brief explanation)
The Modern Cell Theory:
All organisms are composed of one or more cells
Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms
Cells arise only by division of previously existing cell
This cell theory is proposed by German scientists named Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
CELL REQUIREMENTS:
Plasma Membrane
Encloses the cell and controls what goes in and out
Plasma membrane has a double layer of phospholipid molecules.
A phospholipid molecule is made up of glycerol which is a phosphate group and two chains of fatty acid.
Fats
Protein molecules are also found embedded in phospholipids.
The membrane is composed of both protein and phospholipid molecules.
Function:
Serves as the boundary between the outside environment and the inside of the cell.
Gives form and shape to the cells.
Connects one cell to two or more adjacent cells.
Cell membrane is also responsible for…
OSMOSISIt is the spontaneous movement of solvent molecules through a semi permeable (selective of what goes in and out) membrane.
The region of the higher solute concentration tends to equalize the lower solute concentration.
Is an essential process by means of which nutrients are delivered to the cells.
DiffusionIt is the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
TransportersIt lets nutrients enter the cell and by – products to leave the cell.
Sugar to glucose to energy

EndocytosisIt is the process in which cells absorb molecules by engulfing them.
The cell creates a small deformation inward called invagination.
Phagocytosis
Cell eating
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking
ExocytosisIt removes undigested residue of a substance brought in by endocytosis.
It also secretes substances such as hormones and enzymes.
Pathway
Protoplasm
Fills between cell membrane and the nucleus (this contain sugar, organelles, proteins, & amino acids)
These are the plasma or mass of jelly like materials inside the cell.
A protoplasm can change into a semisolid gel to semiliquid solution.
protoplasm: proto = first
plasm = substance
is divided in two forms :
liquid
Jelly Protoplasm is composed of: 20% Carbon 10% Hydrogen 62% Oxygen 3% nitrogen 5% other elements.
Genetic Material
All over characteristics of an organism which we refer to as DNA or “blueprint of life”
Gene is different from DNA. It is a portion of DNA pertaining to single characteristic.
 Knowt
Knowt
