Chemistry- Unit 1
Unit 1.1
Household Product Safety(HHPS)
Types of frames used around the symbols are
Inverted Triangle- It means that the container is dangerous
Octagon- It means the product inside the container is dangerous
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS)
Pictograms | Name | The danger |
|---|---|---|
| Exploding Bomb | Explosives, Self- reactives, Organic Peroxides |
| Corrosion | Skin corrosion/burns, Eye damage, Corrosive to metals |
| Flame Over Circle | Oxidizing gases, liquids and solids |
| Gas Cylinder | Gases under pressure |
| Enviroment | Aquantic toxicity |
| Skull & Crossbones | Acute toxicity(fatal or toxic) |
| Exclamation Mark | Irritant(eye & skin), Skin sensitizer, Acute toxicity,Narcotic effects, Respiratory tract irritant, Hazardous to ozone layer(non-mandatory). |
| Health Hazard | Carcinogen, Mutagenicity, Reproductive toxicity, Respiratory sensitizer, Target organ toxicity, Aspiration toxicity. |
| Flame | Flamemables,Pyrophorics,Self-heating, Emits-flammable gas, Self reactives, Organic peroxides. |
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) identifies the specific chemical and physical hazards associated with the product.
Properties and Classification of Matter
Properties: describe the physical appearance and composition of a substance
Physical Properties include:
Boiling or condensation point
Melting or freezing point
Malleability(capable of being altered or controlled by outside forces or influences.)
Ductility(the ability of a material to be drawn or plastically deformed without fracture)
Color, state, and solubility
Crystal formation
Electrical conductivity and magnetism
Chemical Properties describe how reactive a substance is
Chemical properties include:
Ability to burn and flash point
Behavior in air
Reactions with water, acids, heat and litmus
Pure Substances and Mixtures
Pure substances- All substances that make up the substance are identical, so its chemical and physical are constant. (element of compound)
Element- Pure substance that cannot be broken down into an other substances
Compound- chemical combination of two or more elements in a specific ratio.
Mixtures- Combination of two or more pure substances
Hetereogenous Mixtures (different):
Mechanical Mixtures- different substances are visible
Suspentions- Where componets are in different states
Colloids- Suspended substances cannot be easily seperated
Homogenous mixture(same throughout):
Solutions- seperate compounds are not visible;one substance is dissolved in another.
Chemical Reactions
Two important features of a chemical reaction are:
New substances with new physical and chemical properties are formed
Energy flows into or out of the system during a reaction.
To indicate a chemical change 2 or more of the following should occur:
Heat or light is produced or absorbed
the starting material is used up, or a new substance is produced
There is a change in color
A percipitate( solid) or bubbles(gas) formed in the liquid
The change is difficult to reverse
New odour forms
Atomic Models
Greek Theory- Proposed that matter could be composed of small, indivisble particles
John Dalton (Billiard Ball Theory)-
He rediscovered the atomic concept of matter
States the law of multiple proportions
When 2 or more elements form a series of Compounds form a fixed mass that have interger ratios of each other
Ex. Methane:CH4, has a 1:4 ratio of carbon:hydrogen
To behave in this manner atoms need to be formed
JJ Thompson (Plum Pudding or Raising Bun Model)-
Most famous for discovering the electron
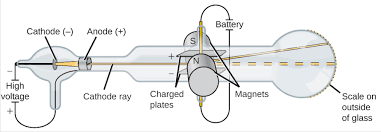
Thompson worked with a Cathode Ray Tubes(CRTs) .
Cathode ray tubes showed that all atoms contain tiny negatively charged subatomic particles or electrons.
Thomson proposed the plum pudding model of the atom, which had negatively-charged electrons embedded within a positively-charged "soup."
Rutherford (Planetary model)-
Rutherford fixed the problem in Thompson’s model
Rutherford designed an eperiment that helped fix the problem called the scattering experiment.
Alpha particles were expected to pass through the thin gold foil with little scattering.
Rutherford assumed that the alphas were interacting electrositcally with solid centers of the atom.
He discovered the nucleus with protons and neutrons.
Niels Bohr (Bohr Model)-
Bohr modified Rutherfors’s theory
He observed that electrons don’t orbit the nucleus but they exist with diffrent energy levels.
Schroedinger ( Electron Cloud or Quantum Mechanical Model)-
An elvolving model but currently thought of as a cloud of negative charges.
Chemistry- Unit 1
Unit 1.1
Household Product Safety(HHPS)
Types of frames used around the symbols are
Inverted Triangle- It means that the container is dangerous
Octagon- It means the product inside the container is dangerous
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS)
Pictograms | Name | The danger |
|---|---|---|
| Exploding Bomb | Explosives, Self- reactives, Organic Peroxides |
| Corrosion | Skin corrosion/burns, Eye damage, Corrosive to metals |
| Flame Over Circle | Oxidizing gases, liquids and solids |
| Gas Cylinder | Gases under pressure |
| Enviroment | Aquantic toxicity |
| Skull & Crossbones | Acute toxicity(fatal or toxic) |
| Exclamation Mark | Irritant(eye & skin), Skin sensitizer, Acute toxicity,Narcotic effects, Respiratory tract irritant, Hazardous to ozone layer(non-mandatory). |
| Health Hazard | Carcinogen, Mutagenicity, Reproductive toxicity, Respiratory sensitizer, Target organ toxicity, Aspiration toxicity. |
| Flame | Flamemables,Pyrophorics,Self-heating, Emits-flammable gas, Self reactives, Organic peroxides. |
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) identifies the specific chemical and physical hazards associated with the product.
Properties and Classification of Matter
Properties: describe the physical appearance and composition of a substance
Physical Properties include:
Boiling or condensation point
Melting or freezing point
Malleability(capable of being altered or controlled by outside forces or influences.)
Ductility(the ability of a material to be drawn or plastically deformed without fracture)
Color, state, and solubility
Crystal formation
Electrical conductivity and magnetism
Chemical Properties describe how reactive a substance is
Chemical properties include:
Ability to burn and flash point
Behavior in air
Reactions with water, acids, heat and litmus
Pure Substances and Mixtures
Pure substances- All substances that make up the substance are identical, so its chemical and physical are constant. (element of compound)
Element- Pure substance that cannot be broken down into an other substances
Compound- chemical combination of two or more elements in a specific ratio.
Mixtures- Combination of two or more pure substances
Hetereogenous Mixtures (different):
Mechanical Mixtures- different substances are visible
Suspentions- Where componets are in different states
Colloids- Suspended substances cannot be easily seperated
Homogenous mixture(same throughout):
Solutions- seperate compounds are not visible;one substance is dissolved in another.
Chemical Reactions
Two important features of a chemical reaction are:
New substances with new physical and chemical properties are formed
Energy flows into or out of the system during a reaction.
To indicate a chemical change 2 or more of the following should occur:
Heat or light is produced or absorbed
the starting material is used up, or a new substance is produced
There is a change in color
A percipitate( solid) or bubbles(gas) formed in the liquid
The change is difficult to reverse
New odour forms
Atomic Models
Greek Theory- Proposed that matter could be composed of small, indivisble particles
John Dalton (Billiard Ball Theory)-
He rediscovered the atomic concept of matter
States the law of multiple proportions
When 2 or more elements form a series of Compounds form a fixed mass that have interger ratios of each other
Ex. Methane:CH4, has a 1:4 ratio of carbon:hydrogen
To behave in this manner atoms need to be formed
JJ Thompson (Plum Pudding or Raising Bun Model)-
Most famous for discovering the electron
Thompson worked with a Cathode Ray Tubes(CRTs) .
Cathode ray tubes showed that all atoms contain tiny negatively charged subatomic particles or electrons.
Thomson proposed the plum pudding model of the atom, which had negatively-charged electrons embedded within a positively-charged "soup."

Rutherford (Planetary model)-
Rutherford fixed the problem in Thompson’s model
Rutherford designed an eperiment that helped fix the problem called the scattering experiment.
Alpha particles were expected to pass through the thin gold foil with little scattering.
Rutherford assumed that the alphas were interacting electrositcally with solid centers of the atom.
He discovered the nucleus with protons and neutrons.
Niels Bohr (Bohr Model)-
Bohr modified Rutherfors’s theory
He observed that electrons don’t orbit the nucleus but they exist with diffrent energy levels.
Schroedinger ( Electron Cloud or Quantum Mechanical Model)-
An elvolving model but currently thought of as a cloud of negative charges.
 Knowt
Knowt