Chapter 8 Political Geography Topics
Centripetal and Centrifugal
A centripetal force unifies while a centrifugal force divides
elongated (Chile) - centrifugal
fragmented (US) - centrifugal
Prorupted; large projecting extension (India) - centrifugal
Compact (Poland) - centripetal
Perforated; a state in another state (Lesotha) - centrifugal
Landlocked (Chad) - centrifugal
Enclave; perforated (Vatican City) - centrifugal
Exclave; Portion of a country is separated by alien territory (Campione d’Italia) - centrifugal
Having a federal government is centripetal because otherwise, it could be hard to govern every place, especially if a place is far away. It is also centrifugal because giving regional power creates the danger of devolution and succession
Neocolonialism is centrifugal because it creates reliance between the colonizing and colonized country
The environment of an area can be centrifugal. The Sahel region is ungoverned, has ethnic conflicts, and has poverty. This makes it easy for terrorists to attack
Shatterbelts are centrifugal and put stress from fighting countries onto neighboring states
Centripetal- unifying features (flag, song, pledge of allegiance) strong identity based on culture
Centrifugal- deep religious differences, language differences, internal boundary conflicts
Territoriality
Territoriality - creating ownership over defined space (bedroom, country, personal space)
Brings emotional response
Persian Gulf War 1990s
Iraq invade Kuwait
Kuwait was historically part of Iraq
WWII Germany Invasions
conquered much of Europe in WWII
Lost land from the Treaty of Versailles
Wanted to claim it back
Territoriality creates a sense of control, and sovereignty, over a place. States may demonstrate this territoriality through features (walls, borders, flags, laws, religion)
invades
Devolution and Balkanization
Balkanization- A process when centrifugal forces break apart a state into smaller pieces along ethnic/cultural lines
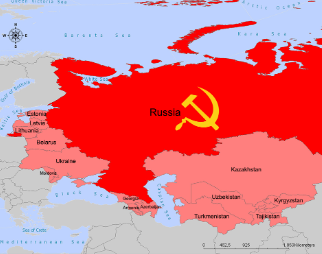
Soviet Union (political)
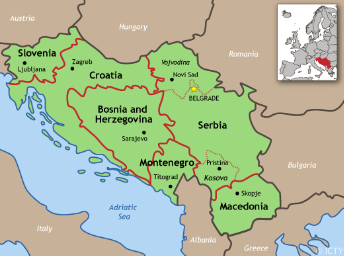
former Yugoslavia (ethnic/cultural)
Devolution- transfer of power from central gov’t to regional gov’t within a state
Hong Kong -
originally British colony handed off to China
put up wall
Hong Kong wants ind.
China wants to erase the border
own rights and autonomy until 2047
Gotton less eco. powerful, so Chine tolerates less
speak Cantonese not mandarin
identify as HK
umbrella mvmt → fight back
Impacts:
Formation of new states
Examples: Czechoslovakia forms- Czech. Rep., Slovakia,
Former Yugoslavia creates- Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Croatia, etc…
Increased pwr. to regions- Centrifugal and Centripetal
Examples: N. Ireland and Scotland in the UK
Political instability
Civil War- Sudan and South Sudan
Protests- Hong Kong and China
Regional separation- Centrifugal and Centripetal
Geography/Islands- Corsica (France), Sardinia (Italy), and N. Ireland
Migration
Yugoslavia
Economic instability
Russian Ruble collapses
Catalonia in Spain- Centrifugal and Centripetal
Yugoslavia, N. Ireland, Catalonia, Canada
Yugoslavia
Multiple nations in one state
conflict from different cultures and languages
split up into republics
Croatia and Serbia shatterbelt
N Ireland
cultural/ethnic border
Catholic Irish Nationalists
Unionist Protestant British
administer borders
deploy troops → prevent extremism
vehicle screenings
watch towers
tarif
shows devolution
own borders - some ind.
dual citizenship - mixed identity
able to vote to rejoin
Catalonia
holding polls
own language, culture, literature
new constitution → autonomy in regions
pay a lot of taxes but get little in return
Canada
Quebec mostly French
speak french
Centrifugal forces are present in Quebec, whereas the free-trade agreement between the United States, Canada, and Mexico challenges the Canadian government’s independence on a national level
Both examples challenge sovereignty at the national level because the Canadian government is not able to exercise complete control in either circumstance: an independent Quebec would arise as a result of devolutionary forces as Canada would lose all control over the region. Canada must work together with Mexico and the United States as a part of a free-trade agreement that is intended to benefit all countries involved
UNCLOS: EEZ
UNCLOS - Code of maritime law
territorial seas - sovereignty in 12 nautical miles
contiguous zone - limited sovereignty in 24 nm
Exclusive Economic Zone - resource extraction in 200 nm
High Seas - beyond 200 nm
UNCLOS authorizes 12nm and 200nm of territorial waters and EEZ as maximums. Since there isn’t a clear-cut boundary, there could be disagreements over how to interpret the boundaries. Also, when bodies of water are between countries, there could be tension because it has to be split evenly among them
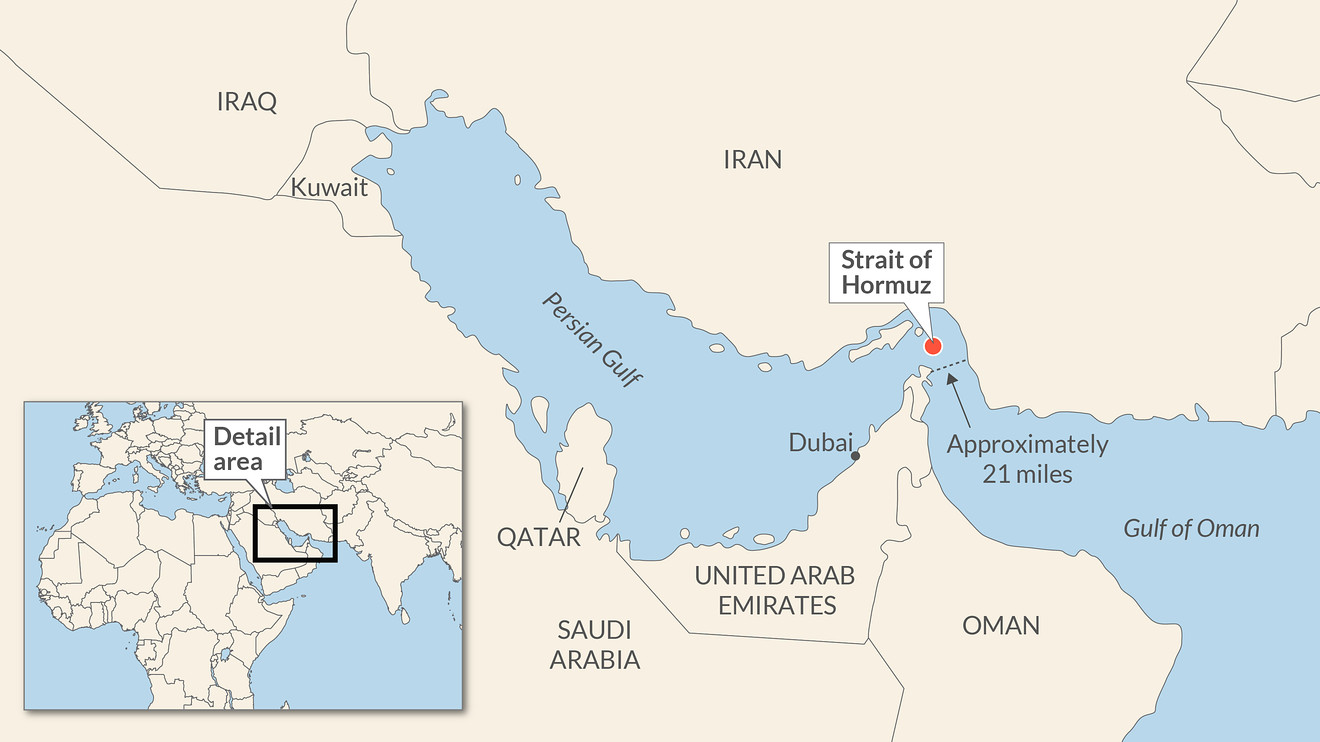
Strait of Hormuz
Chokepoint
Connects ME and world economy (oil)
Lots of oil → high traffic → conflict
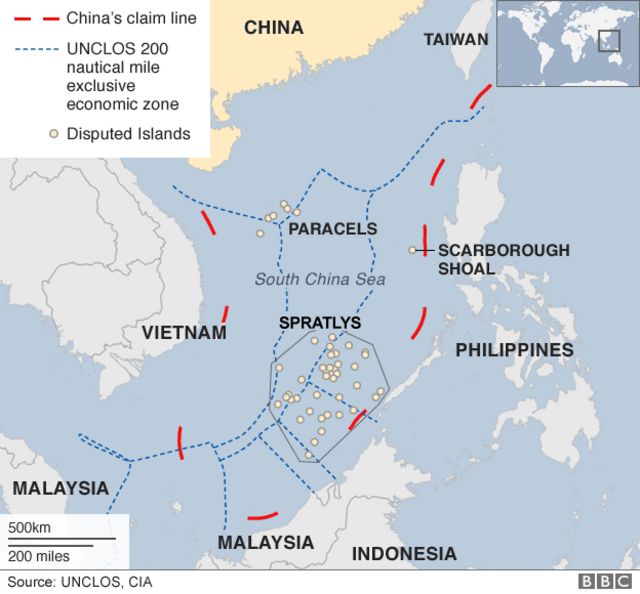
South China Sea
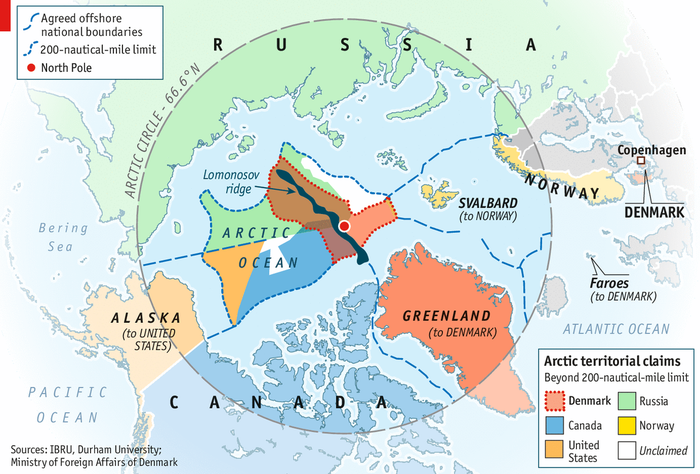
The Arctic
South China Sea, Arctic
South China Sea
The South China Sea has many resources (fisheries, gas, oil), is in the “backyard“ of the U.S., and provides trade to E Asia. Multiple countries have claims to this region and show conflict and territoriality
China has a historical claim because of naval expeditions (9 dash line), but the EEZ of different countries overlap
Airstrips, air defense zones, and building bases are all ways countries show their influence. China is ignoring other claims
Reusing my work from my concept paragraph lol
The political concept seen is that boundaries can cause conflict between states and that the Law of the Sea limits a state’s use of surrounding water. Found on page 299, the Law of the Sea states that within 12 nm from shore, a state has complete sovereignty over the waters. There is partial sovereignty within 24 nm, and within 200 nm there is the EEZ which is purely for economy and resources. However, China, Taiwan, and Japan all have strong territoriality over the Senkaku/Diaoyu islands. According to page 273, China has a historical claim to the islands. Found on page 273, Figure 8-6 shows that because China sent out expeditions in the East China Sea, they have a claim to the islands. However, page 273, it also explains how Japan has a claim to the islands because when Japan had control in 1895, China had not yet stated sovereignty over the islands. The sense of territoriality leads to conflict. As explained on page 273, China and Japan both have air defense zones to establish their claim over the other country’s claim. The meme illustrates this concept by showing how Japan thinks they should have control over the islands and then is shocked by China stepping in
Arctic
Territory in the Arctic is valuable because it provides ocean access, shipping routes, and resources (oil + natural gas), so northern countries such as Canada, Greenland/Denmark, Russia, USA, Norway, and Iceland have all claimed territory there
Problems with border
continental shelf
new claims
fight over resources
fight to exert power/influence
Russia has strong territoriality over the Arctic
Funding Coal Mining
actually losses money, but gives Russia a claim over the Arctic
roots to claim resources
Continental Shelf claim
flag under N Pole
visually ties Russia to the Arctic
Tourist spectacle
Barensburg tourists
visually ties Russia to the Arctic
Military coasts
Renovate outposts
military exercises
Supranational Organization
Supranational - alliances of multiple states/countries
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
European Union (EU)
United Nations (UN)
They take away some sovereignty because all members have to abide by the regulations of the supranational organization
→ Less control over tariffs, currency, borders, engaging in war
However, they unite for a political, economic, military, or environmental goal that is hard to achieve independently
→ Having more allies, protection, helping the environment, selling more goods
European Union
Benefits
Freedom of movement
citizens can live/work in any EU country
trading goods over borders
Common currency (Euro)
Centripetal to the EU as a whole
Drawbacks
membership dues
can’t control who passes the border
Can’t choose the currency (Euro)
lose pol./eco. sovereignty
centrifugal to individual states - lose national identity
Schengen Area - “meh“ borders, no border officers, stroll from countries
Eurozone - creates free trade and common currency
Other Resources -
8.1 and 8.2 Quizlet
https://quizlet.com/358492121/hug-chapter-8-key-issues-1-2-flash-cards/
8.3 and 8.4 Quizlet
https://quizlet.com/363422270/hug-chapter-8-key-issues-3-and-4-flash-cards/
Key Terms
https://knowt.io/flashcards/57e62b6b-e439-433f-bfb2-c61864fff61b
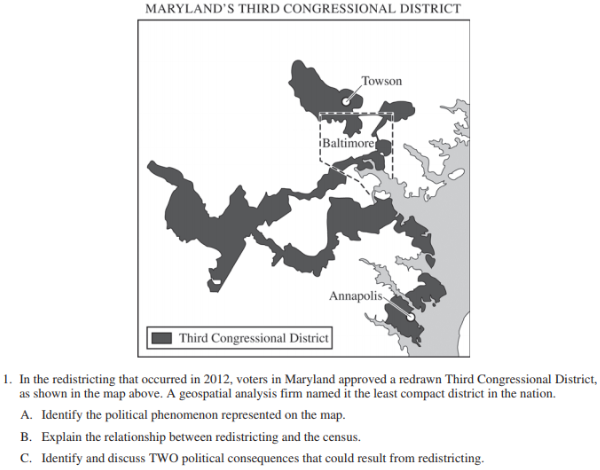
2017 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 6 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/ap/pdf/ap17-sg-human-geo.pdf
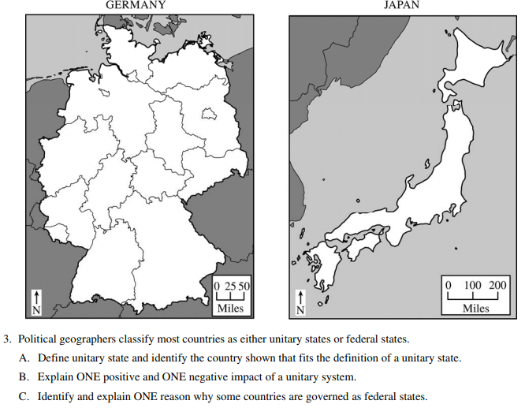
2015 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 2 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap15_human_geography_sg.pdf
2014 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 5 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap14_human_geography_scoring_guidelines.pdf

2010 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 3 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/apc/ap10_human_geo_scoring_guidelines.pdf

2005 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 2 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/apc/_ap05_sg_human_geogra_46637.pdf

Chapter 8 Political Geography Topics
Centripetal and Centrifugal
A centripetal force unifies while a centrifugal force divides
elongated (Chile) - centrifugal
fragmented (US) - centrifugal
Prorupted; large projecting extension (India) - centrifugal
Compact (Poland) - centripetal
Perforated; a state in another state (Lesotha) - centrifugal
Landlocked (Chad) - centrifugal
Enclave; perforated (Vatican City) - centrifugal
Exclave; Portion of a country is separated by alien territory (Campione d’Italia) - centrifugal
Having a federal government is centripetal because otherwise, it could be hard to govern every place, especially if a place is far away. It is also centrifugal because giving regional power creates the danger of devolution and succession
Neocolonialism is centrifugal because it creates reliance between the colonizing and colonized country
The environment of an area can be centrifugal. The Sahel region is ungoverned, has ethnic conflicts, and has poverty. This makes it easy for terrorists to attack
Shatterbelts are centrifugal and put stress from fighting countries onto neighboring states
Centripetal- unifying features (flag, song, pledge of allegiance) strong identity based on culture
Centrifugal- deep religious differences, language differences, internal boundary conflicts
Territoriality
Territoriality - creating ownership over defined space (bedroom, country, personal space)
Brings emotional response
Persian Gulf War 1990s
Iraq invade Kuwait
Kuwait was historically part of Iraq
WWII Germany Invasions
conquered much of Europe in WWII
Lost land from the Treaty of Versailles
Wanted to claim it back
Territoriality creates a sense of control, and sovereignty, over a place. States may demonstrate this territoriality through features (walls, borders, flags, laws, religion)
invades
Devolution and Balkanization
Balkanization- A process when centrifugal forces break apart a state into smaller pieces along ethnic/cultural lines
Soviet Union (political)

former Yugoslavia (ethnic/cultural)

Devolution- transfer of power from central gov’t to regional gov’t within a state
Hong Kong -
originally British colony handed off to China
put up wall
Hong Kong wants ind.
China wants to erase the border
own rights and autonomy until 2047
Gotton less eco. powerful, so Chine tolerates less
speak Cantonese not mandarin
identify as HK
umbrella mvmt → fight back
Impacts:
Formation of new states
Examples: Czechoslovakia forms- Czech. Rep., Slovakia,
Former Yugoslavia creates- Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Croatia, etc…
Increased pwr. to regions- Centrifugal and Centripetal
Examples: N. Ireland and Scotland in the UK
Political instability
Civil War- Sudan and South Sudan
Protests- Hong Kong and China
Regional separation- Centrifugal and Centripetal
Geography/Islands- Corsica (France), Sardinia (Italy), and N. Ireland
Migration
Yugoslavia
Economic instability
Russian Ruble collapses
Catalonia in Spain- Centrifugal and Centripetal
Yugoslavia, N. Ireland, Catalonia, Canada
Yugoslavia
Multiple nations in one state
conflict from different cultures and languages
split up into republics
Croatia and Serbia shatterbelt
N Ireland
cultural/ethnic border
Catholic Irish Nationalists
Unionist Protestant British
administer borders
deploy troops → prevent extremism
vehicle screenings
watch towers
tarif
shows devolution
own borders - some ind.
dual citizenship - mixed identity
able to vote to rejoin
Catalonia
holding polls
own language, culture, literature
new constitution → autonomy in regions
pay a lot of taxes but get little in return
Canada
Quebec mostly French
speak french
Centrifugal forces are present in Quebec, whereas the free-trade agreement between the United States, Canada, and Mexico challenges the Canadian government’s independence on a national level
Both examples challenge sovereignty at the national level because the Canadian government is not able to exercise complete control in either circumstance: an independent Quebec would arise as a result of devolutionary forces as Canada would lose all control over the region. Canada must work together with Mexico and the United States as a part of a free-trade agreement that is intended to benefit all countries involved
UNCLOS: EEZ
UNCLOS - Code of maritime law
territorial seas - sovereignty in 12 nautical miles
contiguous zone - limited sovereignty in 24 nm
Exclusive Economic Zone - resource extraction in 200 nm
High Seas - beyond 200 nm
UNCLOS authorizes 12nm and 200nm of territorial waters and EEZ as maximums. Since there isn’t a clear-cut boundary, there could be disagreements over how to interpret the boundaries. Also, when bodies of water are between countries, there could be tension because it has to be split evenly among them
Strait of Hormuz
Chokepoint
Connects ME and world economy (oil)
Lots of oil → high traffic → conflict

South China Sea
The Arctic
South China Sea, Arctic
South China Sea
The South China Sea has many resources (fisheries, gas, oil), is in the “backyard“ of the U.S., and provides trade to E Asia. Multiple countries have claims to this region and show conflict and territoriality
China has a historical claim because of naval expeditions (9 dash line), but the EEZ of different countries overlap
Airstrips, air defense zones, and building bases are all ways countries show their influence. China is ignoring other claims
Reusing my work from my concept paragraph lol
The political concept seen is that boundaries can cause conflict between states and that the Law of the Sea limits a state’s use of surrounding water. Found on page 299, the Law of the Sea states that within 12 nm from shore, a state has complete sovereignty over the waters. There is partial sovereignty within 24 nm, and within 200 nm there is the EEZ which is purely for economy and resources. However, China, Taiwan, and Japan all have strong territoriality over the Senkaku/Diaoyu islands. According to page 273, China has a historical claim to the islands. Found on page 273, Figure 8-6 shows that because China sent out expeditions in the East China Sea, they have a claim to the islands. However, page 273, it also explains how Japan has a claim to the islands because when Japan had control in 1895, China had not yet stated sovereignty over the islands. The sense of territoriality leads to conflict. As explained on page 273, China and Japan both have air defense zones to establish their claim over the other country’s claim. The meme illustrates this concept by showing how Japan thinks they should have control over the islands and then is shocked by China stepping in
Arctic
Territory in the Arctic is valuable because it provides ocean access, shipping routes, and resources (oil + natural gas), so northern countries such as Canada, Greenland/Denmark, Russia, USA, Norway, and Iceland have all claimed territory there
Problems with border
continental shelf
new claims
fight over resources
fight to exert power/influence
Russia has strong territoriality over the Arctic
Funding Coal Mining
actually losses money, but gives Russia a claim over the Arctic
roots to claim resources
Continental Shelf claim
flag under N Pole
visually ties Russia to the Arctic
Tourist spectacle
Barensburg tourists
visually ties Russia to the Arctic
Military coasts
Renovate outposts
military exercises
Supranational Organization
Supranational - alliances of multiple states/countries
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
European Union (EU)
United Nations (UN)
They take away some sovereignty because all members have to abide by the regulations of the supranational organization
→ Less control over tariffs, currency, borders, engaging in war
However, they unite for a political, economic, military, or environmental goal that is hard to achieve independently
→ Having more allies, protection, helping the environment, selling more goods
European Union
Benefits
Freedom of movement
citizens can live/work in any EU country
trading goods over borders
Common currency (Euro)
Centripetal to the EU as a whole
Drawbacks
membership dues
can’t control who passes the border
Can’t choose the currency (Euro)
lose pol./eco. sovereignty
centrifugal to individual states - lose national identity
Schengen Area - “meh“ borders, no border officers, stroll from countries
Eurozone - creates free trade and common currency
Other Resources -
8.1 and 8.2 Quizlet
https://quizlet.com/358492121/hug-chapter-8-key-issues-1-2-flash-cards/
8.3 and 8.4 Quizlet
https://quizlet.com/363422270/hug-chapter-8-key-issues-3-and-4-flash-cards/
Key Terms
https://knowt.io/flashcards/57e62b6b-e439-433f-bfb2-c61864fff61b
2017 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 6 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/ap/pdf/ap17-sg-human-geo.pdf

2015 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 2 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap15_human_geography_sg.pdf

2014 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 5 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap14_human_geography_scoring_guidelines.pdf

2010 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 3 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/apc/ap10_human_geo_scoring_guidelines.pdf

2005 Released FRQ
Rubric Page 2 - https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/apc/_ap05_sg_human_geogra_46637.pdf

 Knowt
Knowt