
Ch 4. Telecommunications, the Internet, Intranets, and Extranets
Supply chain management might use telecommunications and networks the most among all business functions
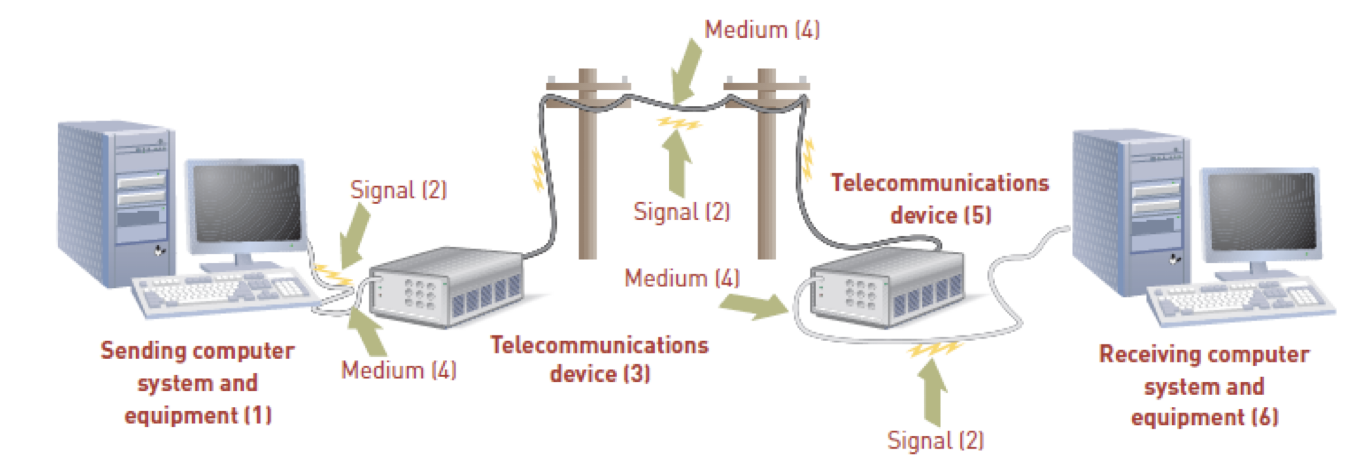
Telecommunications are electronic transmission of signals for communications
telecommunications medium: any material substance that carries an electronic signal to support communications between a sending and receiving device
Telecommunications devices relay signals between computer systems and transmission media
Channel Bandwidth: is the rate at which data is exchanged.
Broadband communications are telecommunication systems that can exchange data very quickly
Communications Media: are the means of delivering and receiving data or information
Guided transmission media types include:
Wireless technologies
Microwave transmission
3G/4G wireless communications
Worldwide interoperability for microwave access (WiMAX)
Wireless technologies: Wireless telecommunications involves the broadcast of communications in one of three frequency ranges → microwave, radio, and infrared
Microwave transmission: high frequency (300MHz-300GHz) signal sent through the air
3G wireless communications: supports wireless voice broadband speed data communications in a mobile environment
4G wireless communications: 4G will also provide increased data transmission rates in the 20-40 Mbps range
Worldwide interoperability for microwave access (WiMAX)
Operated like wifi, only over greater distances and at faster transmission speeds
Telecommunications Hardware: Smartphones:
Have their own software operating systems
Applications are developed by: manufacturers, operators of the communications network on which they operate, third-party software developers
Modem, Fax modem, Multiplexer, PBX, Front-end processor, Switch, Bridge, Router
Networks and Distributed Processing
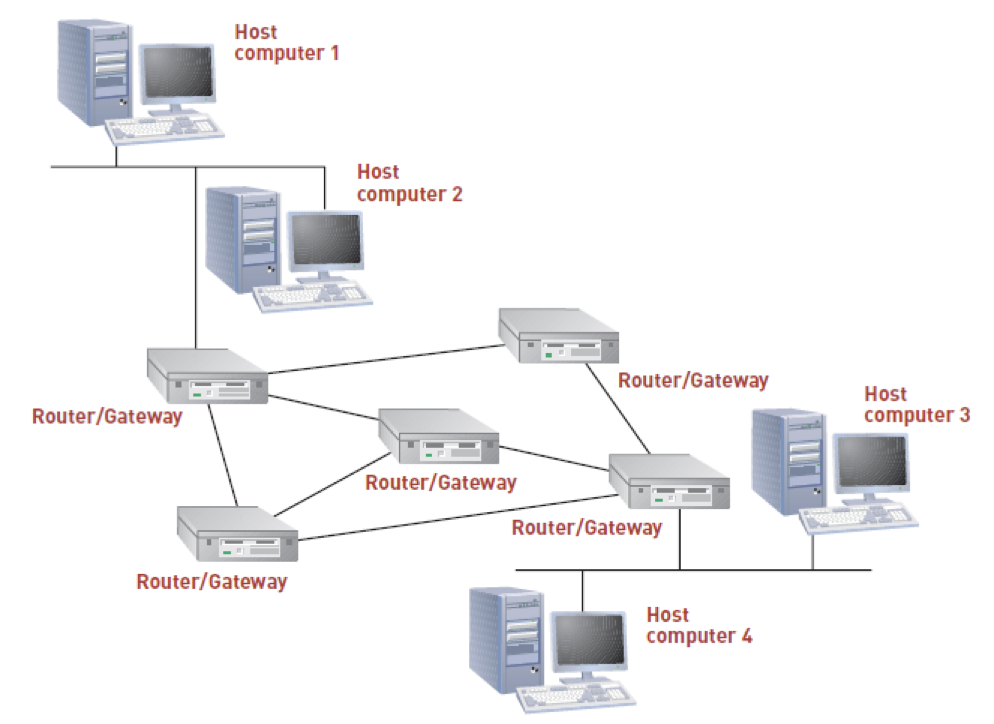
Computer network: consists of communications media, devices, and software needed to connect two or more computer systems or devices
Can transmit and receive information to improve organisation effectiveness and efficiency
Network types:
Personal area networks (PAN): support interconnection of information technology within a range of about 33 feet
Local area network (LAN): connect computer systems and devices within a small area (office/home)
Metropolitan area networks (MAN): connect users and their devices in a geographical area that spans a campus or city
Wide area networks (WAN): connect large geographic regions
In a typical LAN, all network users within an office can connect to each other's devices for rapid communication.
Distributed Processing:
Centralised processing: all processing occurs in a single location or facility
Decentralised processing: processing devices are places at various remote locations
Distributed processing: processing devices are placed at remote locations but are connected to each other via a network
Client/server systems:
Client/server Architecture: multiple computer programs are dedicated to special functions
Server: distributes programs and data to other computer (clients) on the network as they request them
Telecommunications software
Network Operating system (NOS): systems software that controls the computer systems and devices on a network
Network management software: protects software from being copied, modified, or downloaded illegally
Located telecommunications errors and potential network problems
Use of the Internet/How it works:
ARPANET: ancestor of the internet
Internet Protocol (IP): enables computers to route communications traffic from one network to another
IP Protocol: set of rules to pass packets from one host to another
IP Address: 64-bit number that identifies a computer on the internet
Uniform Resource Locator (URL): web address that specific the exact location of a web page
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN):
Responsible for managing IP addresses and the internet domain names
Has authority to resolve domain name disputes
Domain Name ID: The internet routes data packets over the network backbone from route to route to reach their destinations
Com → business sites
Gov → government sites
Net → networking sites
Edu → educational sites
Org → non-profit organisation sites
Mobi → mobile-compatible sites for smartphones
Accessing the Internet: access method determined by the size and capability of your organisation or system
Connect via LAN server: business LAN servers are typically connected to their internet at very fast data rates
Connecting via internet service providers: an ISP is any organisation that provides internet access to people
Cloud Computing: Computer environment in which software and storage are provided as an internet service and accessed with a web browser
Extremely scalable and often takes advantage of virtualisation technologies
Advantages to businesses:
Businesses can save on system design, installation, and maintenance
Employees can access corporate systems from any internet-connected computer
World Wide Web & How it Works: Originally created as an internal document management system, and has become:
Primary source of information and news
Indispensable conduit for commerce
A popular hub for social interaction, entertainment, and communication
The Internet: made up of computers, network hardware such as routers and fiber-optic cables, software, and the TCP/IP protocol
The Web: consists of server and client software, the hypertext transfer protocol (http), and mark-up languages that combine to deliver information and services over the internet
It works using:
Hyperlink: highlighted text or graphics in a web document that, when clicked, opens a new web page
Web browser: web client software such as internet explorer, firefox, and safari used to view web pages
Hypertext markup language (HTML): standard page description language for web pages
HTML tags: tell the web browser how to format text
Extensible markup language (XML): markup language for web documents containing structured information
Cascading style sheet (CSS): markup language that defines the visual appearance of content in a web page
Web Programming Languages:
Java:
Object oriented programming language from sun microsystems based on C++
Allows small programs (applets) to be embedded within an HTML document
Other documents: JavaScript, VBScript, ActiveX
Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP)
Web services: Standards and tools that streamline and simplify communication among web sites
XML: the key to web services
Developing Web Content:
Web publishing tools: .NET, Bubbler, Homestead QuickSites, and JobSpot
Mashup: named for the process of mixing two or more hip-hop sings into one song
Popular uses for the Internet and Web:
Publishing information
Assisting users in finding information
Supporting communication and collaboration
Building online community
Providing software applications
Providing a platform for expressing ideas
Delivering media of all types
Providing a platform for commerce
Supporting travel and navigation
Online Information Sources:
Business information: businesses often use internet and web-based systems for knowledge management
Search Engines: enable you to find information on the web by specifying keywords (example: google)
Rich Internet Applications: software that has the functionality and complexity of traditional application software but does not require local installation and runs in a web browser
Result of continuously improving programming languages and platforms designed for the web
Intranet: internal corporate network built using internet and world wide web standards and technologies
Extranet: network that links selected resources of a company’s intranet with its customers, suppliers, or other business partners
Ch 4. Telecommunications, the Internet, Intranets, and Extranets
Supply chain management might use telecommunications and networks the most among all business functions
Telecommunications are electronic transmission of signals for communications
telecommunications medium: any material substance that carries an electronic signal to support communications between a sending and receiving device
Telecommunications devices relay signals between computer systems and transmission media
Channel Bandwidth: is the rate at which data is exchanged.
Broadband communications are telecommunication systems that can exchange data very quickly
Communications Media: are the means of delivering and receiving data or information
Guided transmission media types include:
Wireless technologies
Microwave transmission
3G/4G wireless communications
Worldwide interoperability for microwave access (WiMAX)

Wireless technologies: Wireless telecommunications involves the broadcast of communications in one of three frequency ranges → microwave, radio, and infrared
Microwave transmission: high frequency (300MHz-300GHz) signal sent through the air
3G wireless communications: supports wireless voice broadband speed data communications in a mobile environment
4G wireless communications: 4G will also provide increased data transmission rates in the 20-40 Mbps range
Worldwide interoperability for microwave access (WiMAX)
Operated like wifi, only over greater distances and at faster transmission speeds
Telecommunications Hardware: Smartphones:
Have their own software operating systems
Applications are developed by: manufacturers, operators of the communications network on which they operate, third-party software developers
Modem, Fax modem, Multiplexer, PBX, Front-end processor, Switch, Bridge, Router
Networks and Distributed Processing
Computer network: consists of communications media, devices, and software needed to connect two or more computer systems or devices
Can transmit and receive information to improve organisation effectiveness and efficiency
Network types:
Personal area networks (PAN): support interconnection of information technology within a range of about 33 feet
Local area network (LAN): connect computer systems and devices within a small area (office/home)
Metropolitan area networks (MAN): connect users and their devices in a geographical area that spans a campus or city
Wide area networks (WAN): connect large geographic regions
In a typical LAN, all network users within an office can connect to each other's devices for rapid communication.
Distributed Processing:
Centralised processing: all processing occurs in a single location or facility
Decentralised processing: processing devices are places at various remote locations
Distributed processing: processing devices are placed at remote locations but are connected to each other via a network
Client/server systems:
Client/server Architecture: multiple computer programs are dedicated to special functions
Server: distributes programs and data to other computer (clients) on the network as they request them
Telecommunications software
Network Operating system (NOS): systems software that controls the computer systems and devices on a network
Network management software: protects software from being copied, modified, or downloaded illegally
Located telecommunications errors and potential network problems
Use of the Internet/How it works:
ARPANET: ancestor of the internet
Internet Protocol (IP): enables computers to route communications traffic from one network to another
IP Protocol: set of rules to pass packets from one host to another
IP Address: 64-bit number that identifies a computer on the internet
Uniform Resource Locator (URL): web address that specific the exact location of a web page
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN):
Responsible for managing IP addresses and the internet domain names
Has authority to resolve domain name disputes
Domain Name ID: The internet routes data packets over the network backbone from route to route to reach their destinations
Com → business sites
Gov → government sites
Net → networking sites
Edu → educational sites
Org → non-profit organisation sites
Mobi → mobile-compatible sites for smartphones

Accessing the Internet: access method determined by the size and capability of your organisation or system
Connect via LAN server: business LAN servers are typically connected to their internet at very fast data rates
Connecting via internet service providers: an ISP is any organisation that provides internet access to people
Cloud Computing: Computer environment in which software and storage are provided as an internet service and accessed with a web browser
Extremely scalable and often takes advantage of virtualisation technologies
Advantages to businesses:
Businesses can save on system design, installation, and maintenance
Employees can access corporate systems from any internet-connected computer
World Wide Web & How it Works: Originally created as an internal document management system, and has become:
Primary source of information and news
Indispensable conduit for commerce
A popular hub for social interaction, entertainment, and communication
The Internet: made up of computers, network hardware such as routers and fiber-optic cables, software, and the TCP/IP protocol
The Web: consists of server and client software, the hypertext transfer protocol (http), and mark-up languages that combine to deliver information and services over the internet
It works using:
Hyperlink: highlighted text or graphics in a web document that, when clicked, opens a new web page
Web browser: web client software such as internet explorer, firefox, and safari used to view web pages
Hypertext markup language (HTML): standard page description language for web pages
HTML tags: tell the web browser how to format text
Extensible markup language (XML): markup language for web documents containing structured information
Cascading style sheet (CSS): markup language that defines the visual appearance of content in a web page
Web Programming Languages:
Java:
Object oriented programming language from sun microsystems based on C++
Allows small programs (applets) to be embedded within an HTML document
Other documents: JavaScript, VBScript, ActiveX
Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP)
Web services: Standards and tools that streamline and simplify communication among web sites
XML: the key to web services
Developing Web Content:
Web publishing tools: .NET, Bubbler, Homestead QuickSites, and JobSpot
Mashup: named for the process of mixing two or more hip-hop sings into one song
Popular uses for the Internet and Web:
Publishing information
Assisting users in finding information
Supporting communication and collaboration
Building online community
Providing software applications
Providing a platform for expressing ideas
Delivering media of all types
Providing a platform for commerce
Supporting travel and navigation
Online Information Sources:
Business information: businesses often use internet and web-based systems for knowledge management
Search Engines: enable you to find information on the web by specifying keywords (example: google)
Rich Internet Applications: software that has the functionality and complexity of traditional application software but does not require local installation and runs in a web browser
Result of continuously improving programming languages and platforms designed for the web
Intranet: internal corporate network built using internet and world wide web standards and technologies
Extranet: network that links selected resources of a company’s intranet with its customers, suppliers, or other business partners
 Knowt
Knowt
