
Jewish History
Classical Judaism
66 CE: Jewish War to overcome Romans
70 CE: temple in Jerusalem was destroyed
600 CE: Islam comes to power
Diaspora: dispersion; Jewish people having to live away from their ancestral homeland
Own land at the crossroads of many major empires and have been conquered by many groups
Medieval Judaism
700s-1700s CE
Lived under Muslim rule in Spain and Africa and Christian rule in Europe
Under Muslim regime
Relative peace and prosperity
Still faced harassment, assault, rape
Under Christian regime
Great economic success as bankers
Accused of starting black plague, killing Jesus, killing Christian children
Often harassed/murdered by mobs
Forced conversion
Viewed as a “dangerous influence” to others
Physically tortured
Jewish movement in Europe
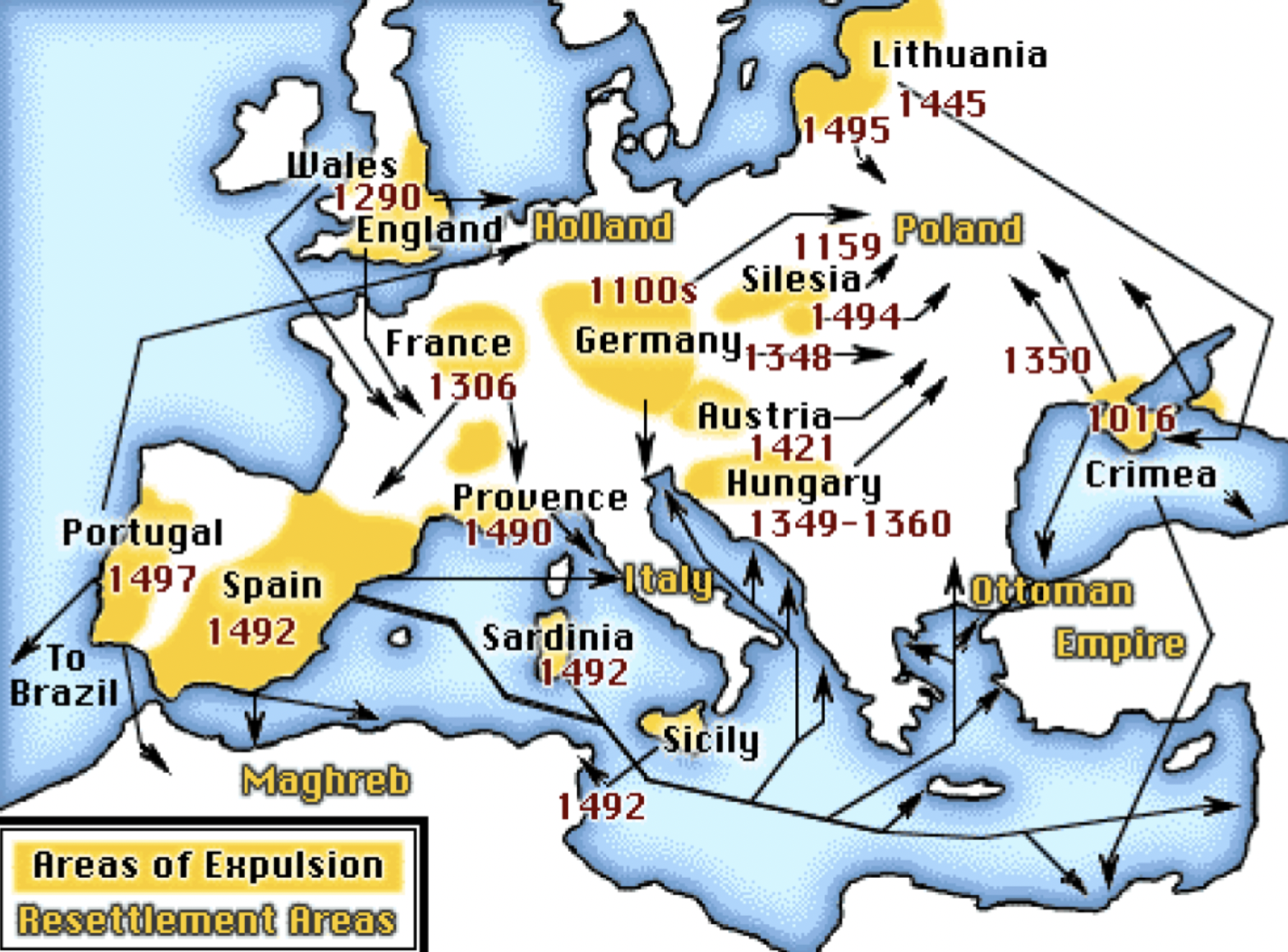
Idea of genocide predates the Holocaust and Jewish history
Despite persecution, Judaism is thriving
Philosophy and Mysticism
Moses Maimonides (1135-1204)
Wrote The Guide to the Perplexed
Created the 13 Principles of Faith
Belief in the existence of God
God’s unity
God’s spirituality and incorporeality
God’s eternity and timelessness
God alone should be the subject of worship and prayer
Revelation through God’s prophets
The preeminence of Moses among the prophets
God’s law was given on Mount Sinai
The immutability of the Torah as God’s Law
God’s foreknowledge of human actions
Reward of good and retribution of evil
The coming of the Jewish Messiah
The resurrection of the dead and human immortality
Kabbalah: a belief that the best way to know God is through the heart and through love
Developed in Spain in the 1200’s
The Torah can be interpreted on multiple levels
Alternative to traditional Judaism
Modern Judaism
Hasidism: pious Judaism which emphasizes mysticism, a personal relationship with Yahweh, and a close community (focus on following Zaddik rather than studying Torah)
Zaddik: a charismatic holy person
Zionist: the belief in re-establishing a Jewish homeland by reclaiming the ancient Jewish ancestral homeland (modern-day Israel and Palestine)
Since 1948, the state of Israel was recognized by the international community and the term refers to those who support Israel
British Empire technically owned the area which would become Israel and gave it to Jewish people following international pressure after the Holocaust
Believed to be needed because of anti-semitism
Anti-Semitism: sentiment against Jewish people deriving from attitudes, exclusion, violence, and/or death
Holocaust: the persecution of Jewish people by Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945
Resulted in the deaths of 6 million Jewish people in Europe
More than exile, inquisition—anything that’s been faced before
Shook the faith of many Jewish people; common questions included
Why did God let this happen?
Some saw it as a punishment for abandoning tradition
Some thought God broke his covenant
One great response—Victor Frankl’s Man’s Search for Meaning
State of Israel
Jews emigrated to Israel before WWI
Was part of the Ottoman Empire
The League of Nations in 1922 recognized the need for a Jewish homeland
Many international treaties before and after reaffirmed this
This land was already occupied
Palestinians and Jews both claim the land as their homeland
Very complicated conflict
Many countries declared war on Israel
Modern Divisions of Judaism
Reform: Jewish people adapt to modern society
Relaxed observance; speak English
~1/3 of Jewish people in the US
Orthodox: follow the Torah
Often live in separate communities
Very strict
Conservative: somewhat open to change, but still fairly strict regarding practices of liturgy and law
Eg. follow the Sabbath
Middle ground between other two branches
Torah
Because you believe, you follow the law/Torah and act accordingly
Daily life is governed by the Torah
Permitted, forbidden, obligated, free, holy, profane (remember Islamic Sharia Law)
Prayer
Takes place three times a day
Yarmulke: a skull cap, sign of respect for God
Reminder that God is above you
Worn after Bar Mitzvah
Tallit: prayer shawl
Tefillin: small boxes with scripture in them
Home and Synagogue
Worship takes place primarily in the home
Mezuzah: parchment in a decorative case which designates the home as Jewish
Food is to be Kosher
Don’t eat pork, shellfish, any combination of meat with dairy
Synagogue is huge since there is no temple
Friday night is the Sabbath (time of rest)
Services are led by Rabbis (religious leaders)
Rabbi: one who has mastered the Talmud
Jewish History
Classical Judaism
66 CE: Jewish War to overcome Romans
70 CE: temple in Jerusalem was destroyed
600 CE: Islam comes to power
Diaspora: dispersion; Jewish people having to live away from their ancestral homeland
Own land at the crossroads of many major empires and have been conquered by many groups
Medieval Judaism
700s-1700s CE
Lived under Muslim rule in Spain and Africa and Christian rule in Europe
Under Muslim regime
Relative peace and prosperity
Still faced harassment, assault, rape
Under Christian regime
Great economic success as bankers
Accused of starting black plague, killing Jesus, killing Christian children
Often harassed/murdered by mobs
Forced conversion
Viewed as a “dangerous influence” to others
Physically tortured
Jewish movement in Europe

Idea of genocide predates the Holocaust and Jewish history
Despite persecution, Judaism is thriving
Philosophy and Mysticism
Moses Maimonides (1135-1204)
Wrote The Guide to the Perplexed
Created the 13 Principles of Faith
Belief in the existence of God
God’s unity
God’s spirituality and incorporeality
God’s eternity and timelessness
God alone should be the subject of worship and prayer
Revelation through God’s prophets
The preeminence of Moses among the prophets
God’s law was given on Mount Sinai
The immutability of the Torah as God’s Law
God’s foreknowledge of human actions
Reward of good and retribution of evil
The coming of the Jewish Messiah
The resurrection of the dead and human immortality
Kabbalah: a belief that the best way to know God is through the heart and through love
Developed in Spain in the 1200’s
The Torah can be interpreted on multiple levels
Alternative to traditional Judaism
Modern Judaism
Hasidism: pious Judaism which emphasizes mysticism, a personal relationship with Yahweh, and a close community (focus on following Zaddik rather than studying Torah)
Zaddik: a charismatic holy person
Zionist: the belief in re-establishing a Jewish homeland by reclaiming the ancient Jewish ancestral homeland (modern-day Israel and Palestine)
Since 1948, the state of Israel was recognized by the international community and the term refers to those who support Israel
British Empire technically owned the area which would become Israel and gave it to Jewish people following international pressure after the Holocaust
Believed to be needed because of anti-semitism
Anti-Semitism: sentiment against Jewish people deriving from attitudes, exclusion, violence, and/or death
Holocaust: the persecution of Jewish people by Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945
Resulted in the deaths of 6 million Jewish people in Europe
More than exile, inquisition—anything that’s been faced before
Shook the faith of many Jewish people; common questions included
Why did God let this happen?
Some saw it as a punishment for abandoning tradition
Some thought God broke his covenant
One great response—Victor Frankl’s Man’s Search for Meaning
State of Israel
Jews emigrated to Israel before WWI
Was part of the Ottoman Empire
The League of Nations in 1922 recognized the need for a Jewish homeland
Many international treaties before and after reaffirmed this
This land was already occupied
Palestinians and Jews both claim the land as their homeland
Very complicated conflict
Many countries declared war on Israel
Modern Divisions of Judaism
Reform: Jewish people adapt to modern society
Relaxed observance; speak English
~1/3 of Jewish people in the US
Orthodox: follow the Torah
Often live in separate communities
Very strict
Conservative: somewhat open to change, but still fairly strict regarding practices of liturgy and law
Eg. follow the Sabbath
Middle ground between other two branches
Torah
Because you believe, you follow the law/Torah and act accordingly
Daily life is governed by the Torah
Permitted, forbidden, obligated, free, holy, profane (remember Islamic Sharia Law)
Prayer
Takes place three times a day
Yarmulke: a skull cap, sign of respect for God
Reminder that God is above you
Worn after Bar Mitzvah
Tallit: prayer shawl
Tefillin: small boxes with scripture in them
Home and Synagogue
Worship takes place primarily in the home
Mezuzah: parchment in a decorative case which designates the home as Jewish
Food is to be Kosher
Don’t eat pork, shellfish, any combination of meat with dairy
Synagogue is huge since there is no temple
Friday night is the Sabbath (time of rest)
Services are led by Rabbis (religious leaders)
Rabbi: one who has mastered the Talmud
 Knowt
Knowt