
Fission and Fusion
Nuclear fission-splitting a large, unstable nucleus
Nuclear fission is a type of nuclear reaction used to release energy from large and unstable atoms by splitting them into smaller atoms
Spontaneous fission rarely happens. Usually, the nucleus has to absorb a neutron before it will split
When the atom splits it forms two new lighter elements that are roughly the same size
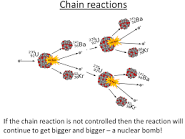
Two or three neutrons are also released when an atom splits. If any of these neutrons are moving slow enough to be absorbed by another nucleus, they cause more fission to occur, which is a chain reaction
The energy not transferred to the kinetic energy is carried away by gamma rays
Energy carried away can be used to heat water making steam to turn turbines and generators
The amount of energy produced by fission in a nuclear reactor is controlled by changing how quickly the chain reaction can occur, which is done by control rods
Uncontrolled chain reactions quickly lead to lots of energy being released as an explosion-this is how nuclear weapons work
Nuclear fusion-joining small nuclei
Nuclear fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission
Two light nuclei collide at high speed and join to create larger, heavier nucleus
Heavier nucleus produced does not have as much mass as the two separate light nuclei did. Some of the mass is converted to energy, which is released as radiation
Fusion released a lot of energy
Scientists haven’t found a way of using fusion to generate energy, and would be to hard and expensive to do at the moment
Fission and Fusion
Nuclear fission-splitting a large, unstable nucleus
Nuclear fission is a type of nuclear reaction used to release energy from large and unstable atoms by splitting them into smaller atoms
Spontaneous fission rarely happens. Usually, the nucleus has to absorb a neutron before it will split
When the atom splits it forms two new lighter elements that are roughly the same size
Two or three neutrons are also released when an atom splits. If any of these neutrons are moving slow enough to be absorbed by another nucleus, they cause more fission to occur, which is a chain reaction

The energy not transferred to the kinetic energy is carried away by gamma rays
Energy carried away can be used to heat water making steam to turn turbines and generators
The amount of energy produced by fission in a nuclear reactor is controlled by changing how quickly the chain reaction can occur, which is done by control rods
Uncontrolled chain reactions quickly lead to lots of energy being released as an explosion-this is how nuclear weapons work
Nuclear fusion-joining small nuclei
Nuclear fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission
Two light nuclei collide at high speed and join to create larger, heavier nucleus
Heavier nucleus produced does not have as much mass as the two separate light nuclei did. Some of the mass is converted to energy, which is released as radiation
Fusion released a lot of energy
Scientists haven’t found a way of using fusion to generate energy, and would be to hard and expensive to do at the moment
 Knowt
Knowt
