
McDougal Littel Biology Nowicki California Ed.: Unit 6 Chapter 15 Notes
McDougal Littel Biology Nowicki California Ed.: Unit 6 Chapter 15 Notes
UNIT 6: ECOLOGY
Chapter 15: The Biosphere
Text Book: 1
DIRECTIONS: Complete these notes while viewing Chapter 15 PowerPoint Lecture
You can also use your textbook to help answer (Each section in the notes references a chapter and
section inside of your textbooks. E.g. 15.1 would be section 1 of chapter 15). Click inside the yellow
highlighted areas to type in answers. Use these notes to help you complete homework assignments
and preparing for, and using while taking tests and quizzes. Make sure to enter your name above.
I. Life in the Earth System (15.1)
A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life
1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life . exists
a. Includes all living . and non . -living parts
b. Biota- collection of just living things in biosphere
2. Earth has four . major connected systems
a. Biosphere
b. Hydrosphere . -all of Earth’s water, ice, water vapor
c. Atmosphere . -the air blanketing Earth’s solid and liquid surface
d. Lithosphere . -features of Earth’s surface (continents, rocks, sea floor, and everything below Earth’s surface
B. Biotic and Abiotic factors interact . in the biosphere
1. All four of Earth’s systems are connected . to another
2. Gaia . hypothesis- Earth itself is kind of a “living organism”
II. Climate (15.2)
A. Climate is the prevailing weather of a region .
1. day . -day to day conditions
2. Climate- long .term pattern of weather conditions
B. Key factors that shape an area’s climate
1. temperature . -key factor
2. sunlight .
3. water . (moisture)- key factor
4. wind .
C. microclimate . -climate of a small specific place within larger area.
1. Can be very important . to living things
2. Can be very small . or large . area
D. Earth has three main three . zones
1. Use average temperature . and precipitation . to categorize
a. Polar zone -in far northern and southern regions
b. Tropical zone- surrounds the equator .
c. Temperate zone- wide area between polar . and tropical . zones
2. Influence of sunlight
a. Earth’s surface heated . unevenly
1). Hottest portion where sun . strikes directly
2). Curved shape causes uneven . heating
3). Earth tilts . on its axis and this also plays a role in seasonal changes
3. Air and Water Movemen
a. Sun also warms water . and air .
b. Uneven heating causes wind . and water currents .
c. Warm air (and water) rised . and
cold air (and water) sinks .
d. Also affects amount of precipitation (warm air holds more water than cold air)
4. Landmasses- also shape . climate
a. Coastal areas tend to have smaller changes in temperature . moderated by oceans .
b. Mountains have large effect on climate- causes precipitation .
5. Adaptation to Climate- Many organisms adapted to survive . in specific climate
III. Biomes (15.3)
A. Earth has 6 major biomes- Each biome characterized by certain set of abiotic .
factors, ecosystems .
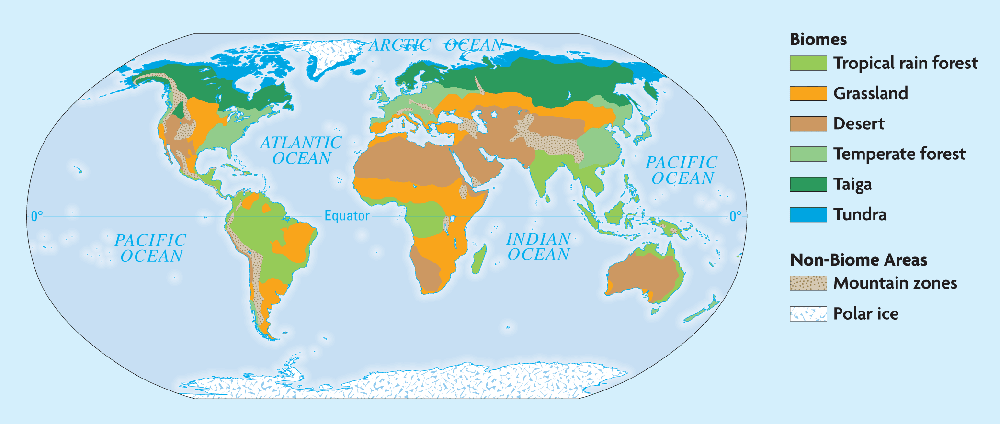
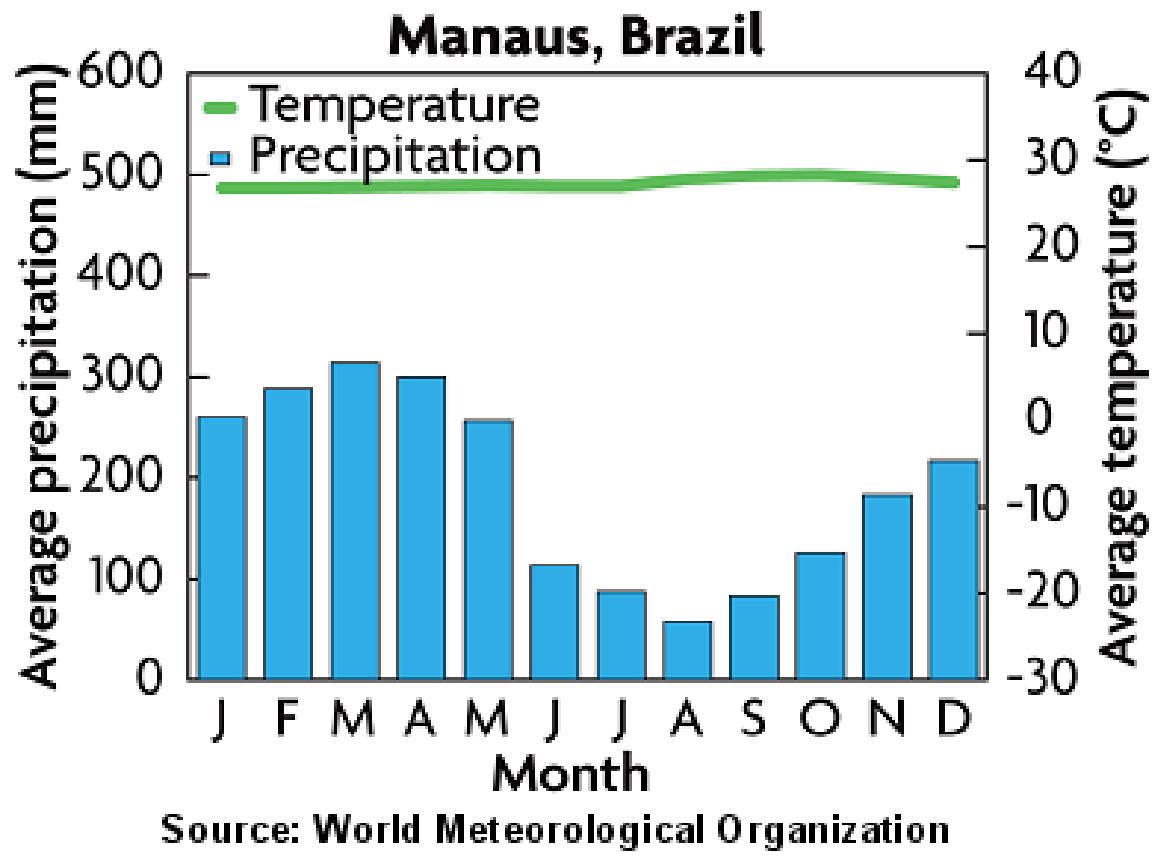
1. Tropical Rain Forest Biome- warm . temperatures, abundant precipitation .all year, lush forests
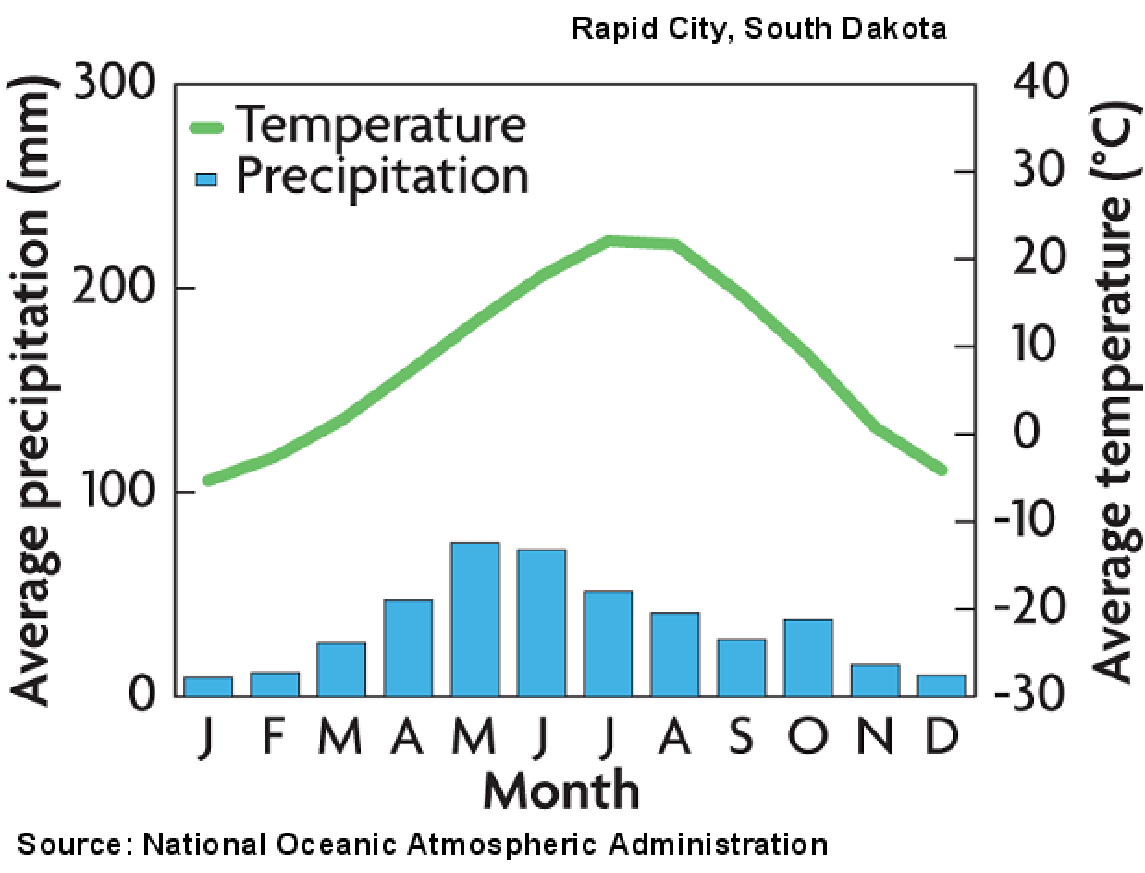
2. Grassland Biome- primary plant life is grass . Occurs in variety of climates .
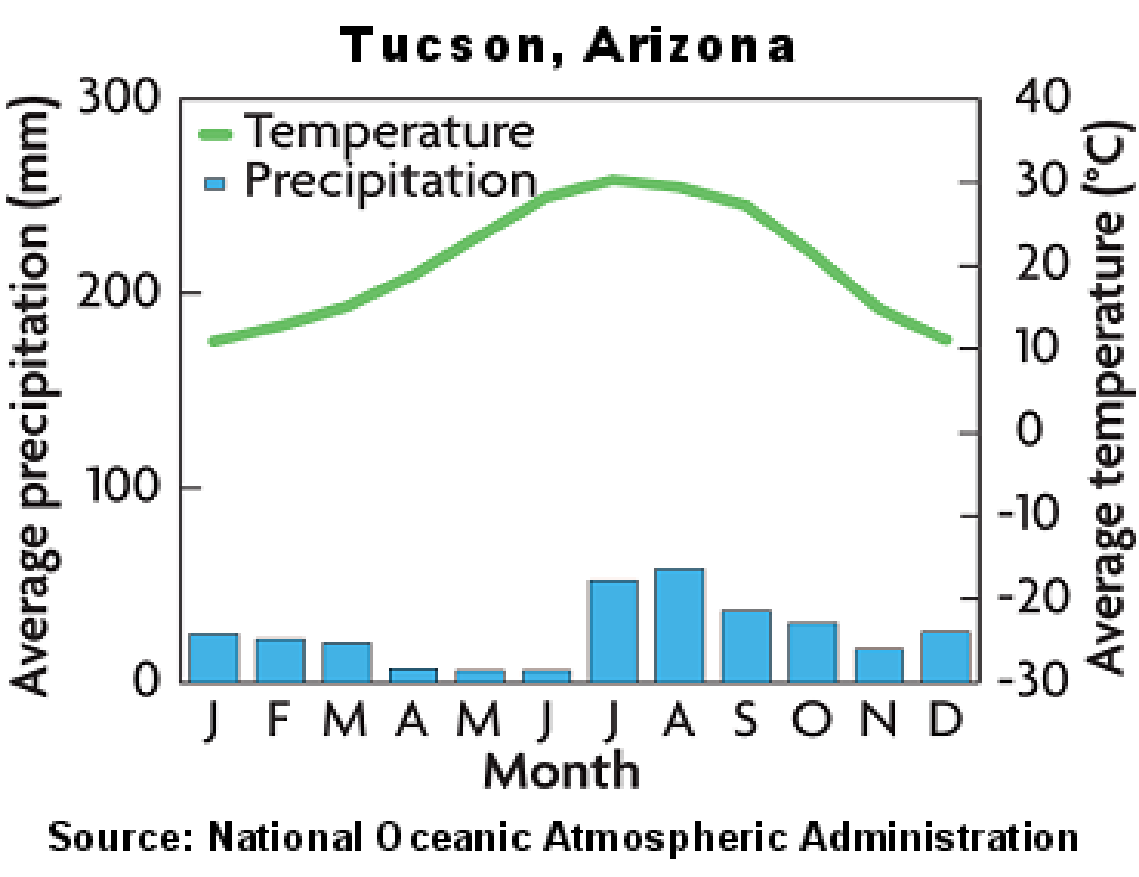
3. Desert Biome- arid . environment, little . precipitation, four types: hot, semi-arid, coastal, and cold
4. Temperate Forests- Include deciduous forests and rain forests. Temperate deciduous forests have deciduous . summers and cold . winters. Deciduous trees are the dominant plant species
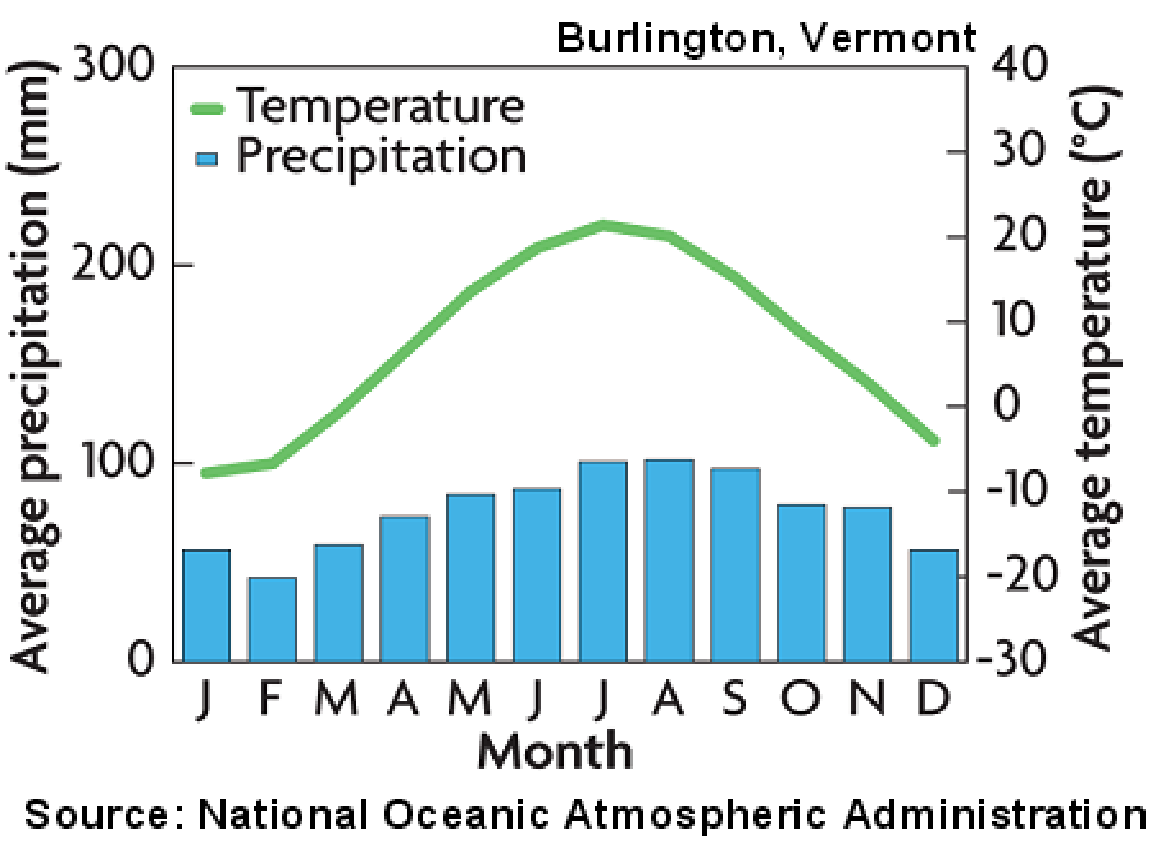
5. Taiga- Found in cool northern climates. northern . winters, short summers. Small amount of precipitation
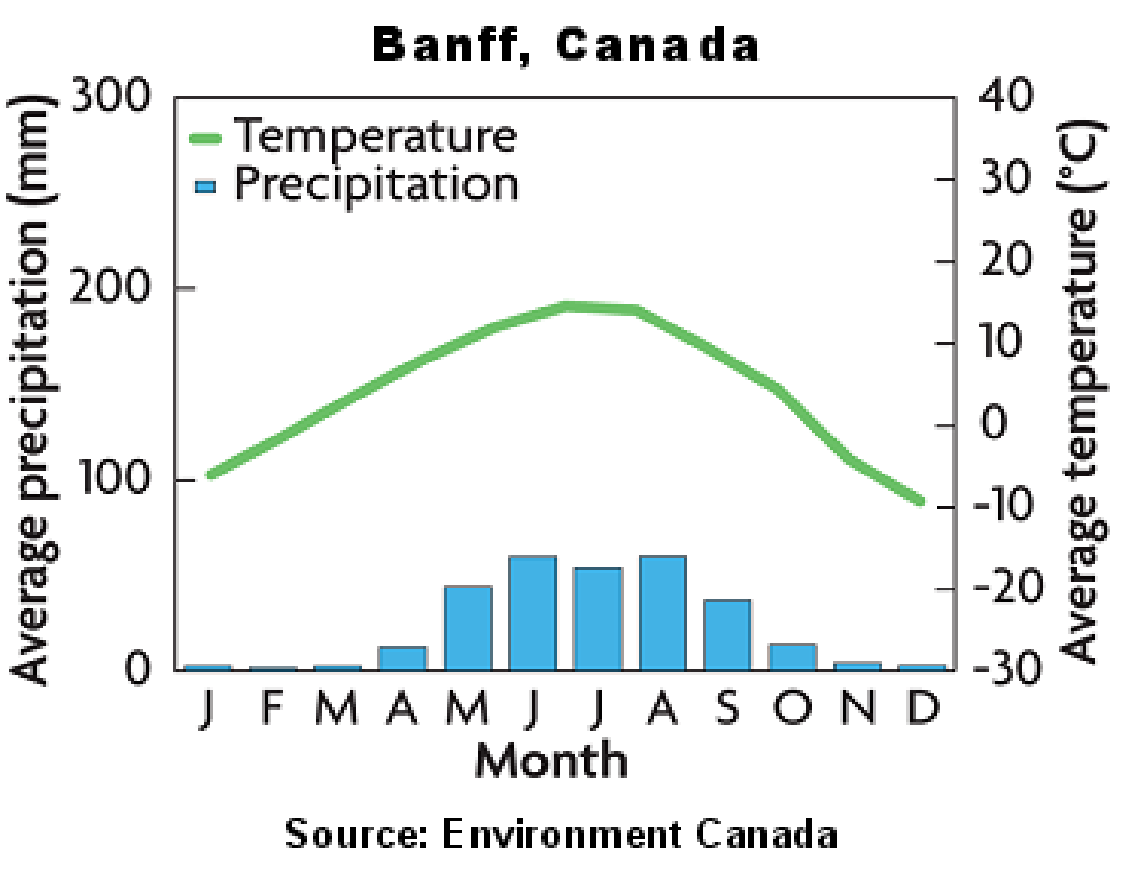
6. Tundra- Far northern latitudes with long winters (10 months) limited precipitation, permafrost .
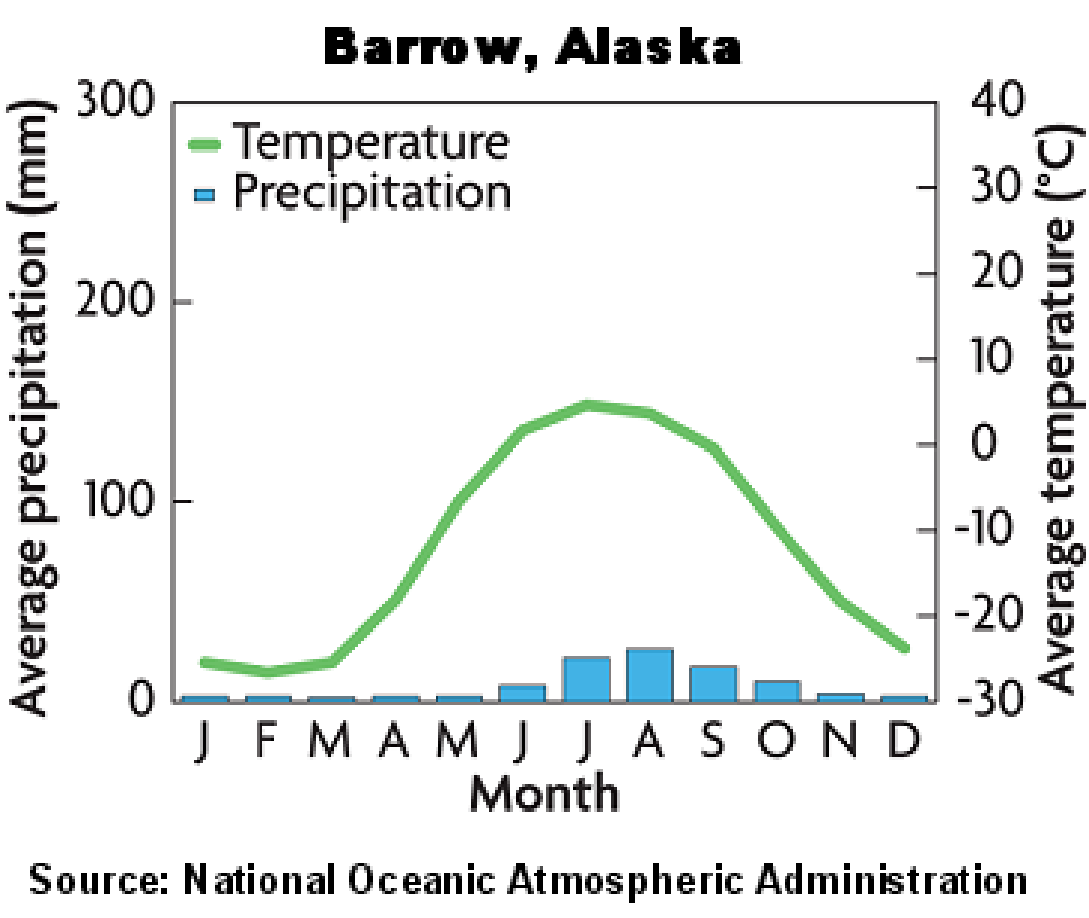
7. Minor biomes- example: chaparral . -hot, dry summers and cool, moist winters
B. Polar ice caps and mountains are not . considered biomes
1. Polar ice caps- have no soil . and do not have specific plant . community
a. Found at poles . (north and south)
b. Most animals depend on sea . for food
IV. Marine Ecosystems (15.4)
A. The ocean can be divided into zones
1. Ocean Zones
a. Divided into open sea ( pelagic .) and ocean floor ( benthic . zone)
b. Divided between areas that receive light ( photic . zone) and those that do not ( apothic .zone)
c. Ocean also separated into zones using distance . from shore line and water depth
1). intertidal . zone- between high and low tide lines
2). neritic . zone-extends from intertidal out to edge of continental shelf
3). bathyal . zone- extends from edge of neritic zone to base of continental shelf
4). nerritic . zone- lies below 2000 meters and is in complete darkness
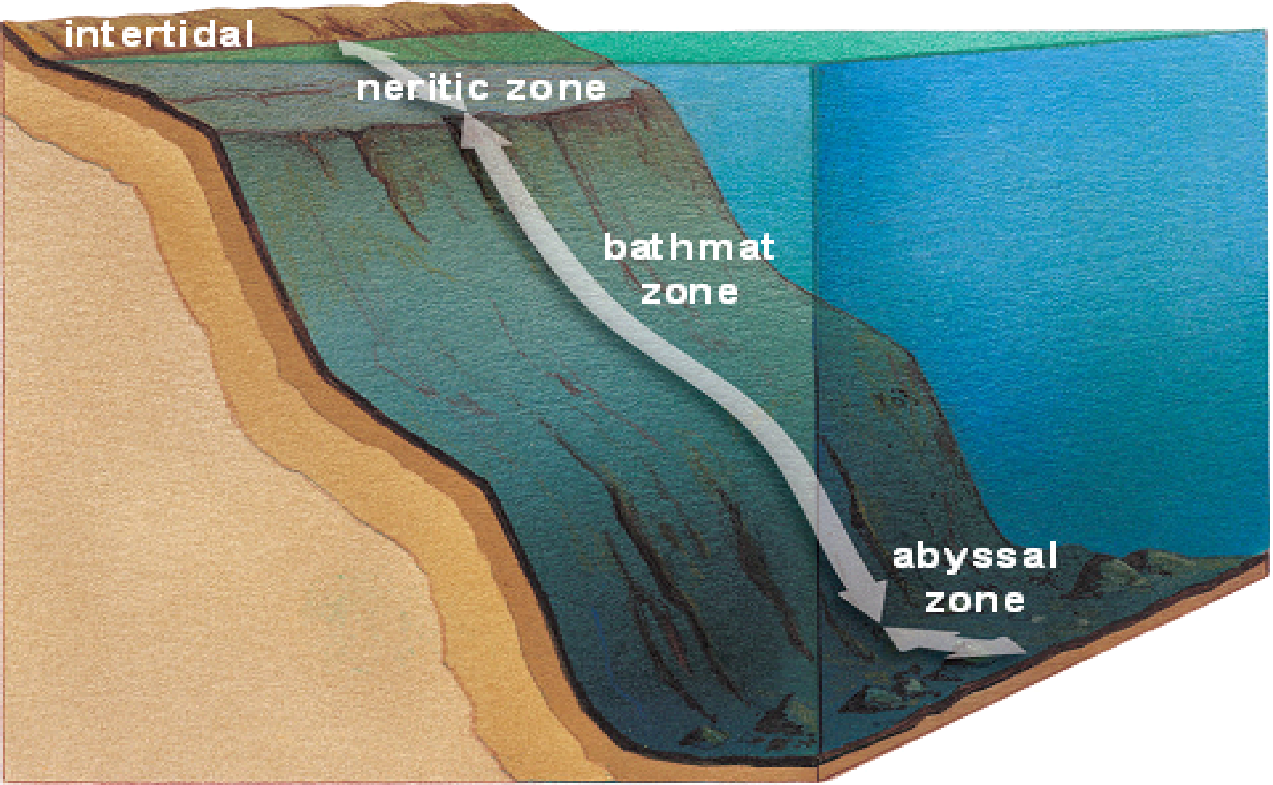
d. Life in Neritic Zone- only 1/10th of ocean but contains majority of biomass . (Most biomass consists of plankton .)
B. Coastal waters contain unique habitats
1. coral . Reefs- found within tropical zone and contains large diversity
2. Kelp Forests- found in cold ., nutrient rich waters
V. Estuaries and Freshwater Ecosystems (15.5)
A. Estuaries are dynamic . environments where rivers flow into the ocean .
1. Estuary- partially enclosed body of water formed where a river . flows into the ocean.
a. Mix of fresh . and salt . water
b. River carries lots of nutrient .
c. Large numbers of species thrive and are highly productive . ecosystems
d. Provide refuge for many species and spawning . grounds
e. Over 80 . % of estuaries have been lost to land development
B. Freshwater ecosystems include moving and standing water
1. Freshwater ecosystems- rivers, streams, wetlands
2. among most productive . ecosystems on Earth
C. Ponds and lakes share common features
1. Smaller in size than oceans, but also divided into zones
a. littoral . zone- between low and high water marks
b. limnetic . zone- open water farther out from shore
c. benthic . zone- bottom of lake or pond where less sunlight . reaches
McDougal Littel Biology Nowicki California Ed.: Unit 6 Chapter 15 Notes
McDougal Littel Biology Nowicki California Ed.: Unit 6 Chapter 15 Notes
UNIT 6: ECOLOGY
Chapter 15: The Biosphere
Text Book: 1
DIRECTIONS: Complete these notes while viewing Chapter 15 PowerPoint Lecture
You can also use your textbook to help answer (Each section in the notes references a chapter and
section inside of your textbooks. E.g. 15.1 would be section 1 of chapter 15). Click inside the yellow
highlighted areas to type in answers. Use these notes to help you complete homework assignments
and preparing for, and using while taking tests and quizzes. Make sure to enter your name above.
I. Life in the Earth System (15.1)
A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life
1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life . exists
a. Includes all living . and non . -living parts
b. Biota- collection of just living things in biosphere
2. Earth has four . major connected systems
a. Biosphere
b. Hydrosphere . -all of Earth’s water, ice, water vapor
c. Atmosphere . -the air blanketing Earth’s solid and liquid surface
d. Lithosphere . -features of Earth’s surface (continents, rocks, sea floor, and everything below Earth’s surface
B. Biotic and Abiotic factors interact . in the biosphere
1. All four of Earth’s systems are connected . to another
2. Gaia . hypothesis- Earth itself is kind of a “living organism”
II. Climate (15.2)
A. Climate is the prevailing weather of a region .
1. day . -day to day conditions
2. Climate- long .term pattern of weather conditions
B. Key factors that shape an area’s climate
1. temperature . -key factor
2. sunlight .
3. water . (moisture)- key factor
4. wind .
C. microclimate . -climate of a small specific place within larger area.
1. Can be very important . to living things
2. Can be very small . or large . area
D. Earth has three main three . zones
1. Use average temperature . and precipitation . to categorize
a. Polar zone -in far northern and southern regions
b. Tropical zone- surrounds the equator .
c. Temperate zone- wide area between polar . and tropical . zones
2. Influence of sunlight
a. Earth’s surface heated . unevenly
1). Hottest portion where sun . strikes directly
2). Curved shape causes uneven . heating
3). Earth tilts . on its axis and this also plays a role in seasonal changes
3. Air and Water Movemen
a. Sun also warms water . and air .
b. Uneven heating causes wind . and water currents .
c. Warm air (and water) rised . and
cold air (and water) sinks .
d. Also affects amount of precipitation (warm air holds more water than cold air)
4. Landmasses- also shape . climate
a. Coastal areas tend to have smaller changes in temperature . moderated by oceans .
b. Mountains have large effect on climate- causes precipitation .
5. Adaptation to Climate- Many organisms adapted to survive . in specific climate
III. Biomes (15.3)
A. Earth has 6 major biomes- Each biome characterized by certain set of abiotic .
factors, ecosystems .

1. Tropical Rain Forest Biome- warm . temperatures, abundant precipitation .all year, lush forests

2. Grassland Biome- primary plant life is grass . Occurs in variety of climates .

3. Desert Biome- arid . environment, little . precipitation, four types: hot, semi-arid, coastal, and cold

4. Temperate Forests- Include deciduous forests and rain forests. Temperate deciduous forests have deciduous . summers and cold . winters. Deciduous trees are the dominant plant species

5. Taiga- Found in cool northern climates. northern . winters, short summers. Small amount of precipitation

6. Tundra- Far northern latitudes with long winters (10 months) limited precipitation, permafrost .

7. Minor biomes- example: chaparral . -hot, dry summers and cool, moist winters
B. Polar ice caps and mountains are not . considered biomes
1. Polar ice caps- have no soil . and do not have specific plant . community
a. Found at poles . (north and south)
b. Most animals depend on sea . for food
IV. Marine Ecosystems (15.4)
A. The ocean can be divided into zones
1. Ocean Zones
a. Divided into open sea ( pelagic .) and ocean floor ( benthic . zone)
b. Divided between areas that receive light ( photic . zone) and those that do not ( apothic .zone)
c. Ocean also separated into zones using distance . from shore line and water depth
1). intertidal . zone- between high and low tide lines
2). neritic . zone-extends from intertidal out to edge of continental shelf
3). bathyal . zone- extends from edge of neritic zone to base of continental shelf
4). nerritic . zone- lies below 2000 meters and is in complete darkness

d. Life in Neritic Zone- only 1/10th of ocean but contains majority of biomass . (Most biomass consists of plankton .)
B. Coastal waters contain unique habitats
1. coral . Reefs- found within tropical zone and contains large diversity
2. Kelp Forests- found in cold ., nutrient rich waters
V. Estuaries and Freshwater Ecosystems (15.5)
A. Estuaries are dynamic . environments where rivers flow into the ocean .
1. Estuary- partially enclosed body of water formed where a river . flows into the ocean.
a. Mix of fresh . and salt . water
b. River carries lots of nutrient .
c. Large numbers of species thrive and are highly productive . ecosystems
d. Provide refuge for many species and spawning . grounds
e. Over 80 . % of estuaries have been lost to land development
B. Freshwater ecosystems include moving and standing water
1. Freshwater ecosystems- rivers, streams, wetlands
2. among most productive . ecosystems on Earth
C. Ponds and lakes share common features
1. Smaller in size than oceans, but also divided into zones
a. littoral . zone- between low and high water marks
b. limnetic . zone- open water farther out from shore
c. benthic . zone- bottom of lake or pond where less sunlight . reaches
 Knowt
Knowt