
Learning
Conditioning
Acquisition
OC- the strengthening of a reinforced response
CC - when an NS and US are linked so that the NS begins triggering the CR
When the dog begins to salivate in response to the bell
Extinction
OC - when a response is no longer reinforced
CC - diminishing the CR when an US does not follow a CS
A child knows if he throws a tantrum he gets candy but the mom stops giving him candy when he throws tantrums so he stops throwing tantrums.
Operant Conditioning
voluntary behaviors
a type of learning when a behavior is strengthened or punished
Skinner’s pigeons
Positive & Negative, Reinforcement & Punishment
Add something | Remove something | |
|---|---|---|
Increase in Behavior | Positive Reinforcement | Negative Reinforcement |
Decrease in Behavior | Positive Punishment | Negative Punishment |
Examples
PR - Adding a bonus to increase sales
PP - Adding extra work to decrease forgetting homework
NR - Removing chores to increase child’s behavior of completing homework
NP - Removing phone privileges to decrease child’s behavior of staying out late
Reinforcers & Reinforcement
Primary Reinforcers - a stimulus that is inherently rewarding usually satisfies a biological need
food, drink, & pleasure
Conditioned Reinforcers - a stimulus that gets its power through learned association with a primary reinforcer
grades, money
Continuous Reinforcement - desired response is reinforced every time
quick learning but can be lost quickly
Partial Reinforcement - desired response is sometimes reinforced
slow learning and resistant to extinction
Schedules
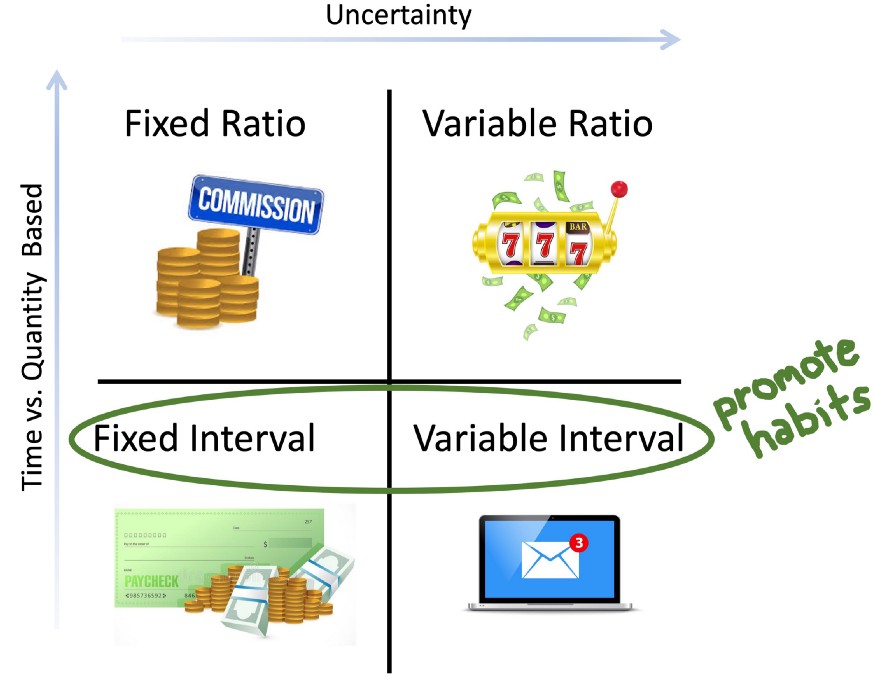
Fixed Ratio - behavior is reinforced after a set number of responses
Commission for every sale
Variable ratio - behavior is reinforced after an unpredictable number of responses
Gambling
Fixed interval - behavior is reinforced after a set period of time
Paycheck every two weeks
Variable interval - behavior is reinforced after varying periods of time
Checking & getting emails
Classical Conditioning
involuntary behaviors
a type of learning when one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
Pavlov’s dogs
Main Points
Neutral Stimulus NS - a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning
Bell
Unconditioned Response UR - naturally occurring response to an US
Salivation
Unconditioned Stimulus US - a stimulus that naturally triggers a response
Food
Conditioned Response CR - a learned response to a previously NS
Salivation in response to the bell
Conditioned Stimulus CS - an originally irrelevant stimulus that comes to trigger a CR
Bell results in salivation
Other
Generalization - the tendency to respond in the same way to a similar but different stimuli
Salivating to a different pitch of bell
Discrimination - learned ability to distinguish between a CS and stimuli that doesn’t signal a US
Different pitches of tones
Higher-order conditioning - the CS is paired with a new NS creating a second, weaker stimulus
Bell and Light produces salivation in addition to Bell and Food
Learning
Insight learning - a sudden realization of a problem’s solution
Latent learning - learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate
mental map of the school
Von Restorff effect - the more something stands out from the crowd the more likely it is to be seen
Associative learning - learning that certain events occur together
hand on hot stove
Habituation - an organism’s decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
Sleeping through an alarm that once was new enough to wake you up
Coping
Problem-focused coping - try to reduce stress directly; altering or removing stressor or changing the way we interact with it
Emotion-focused coping - try to reduce stress by managing our reaction to the stressor but still knowing it exists
Effects
Spacing effect - distributed study or practice yields to better long-term retention
Spreading out studying for a test
Testing effect - enhanced memory after retrieving rather than simply re-reading info
flashcards and visual stimuli
Recency/Primacy Effect
Recency effect - ability to recall the most recent items especially well and quickly
Primacy effect - after delay when attention has shifted, they recall the first items best
Learning
Conditioning
Acquisition
OC- the strengthening of a reinforced response
CC - when an NS and US are linked so that the NS begins triggering the CR
When the dog begins to salivate in response to the bell
Extinction
OC - when a response is no longer reinforced
CC - diminishing the CR when an US does not follow a CS
A child knows if he throws a tantrum he gets candy but the mom stops giving him candy when he throws tantrums so he stops throwing tantrums.
Operant Conditioning
voluntary behaviors
a type of learning when a behavior is strengthened or punished
Skinner’s pigeons
Positive & Negative, Reinforcement & Punishment
Add something | Remove something | |
|---|---|---|
Increase in Behavior | Positive Reinforcement | Negative Reinforcement |
Decrease in Behavior | Positive Punishment | Negative Punishment |
Examples
PR - Adding a bonus to increase sales
PP - Adding extra work to decrease forgetting homework
NR - Removing chores to increase child’s behavior of completing homework
NP - Removing phone privileges to decrease child’s behavior of staying out late
Reinforcers & Reinforcement
Primary Reinforcers - a stimulus that is inherently rewarding usually satisfies a biological need
food, drink, & pleasure
Conditioned Reinforcers - a stimulus that gets its power through learned association with a primary reinforcer
grades, money
Continuous Reinforcement - desired response is reinforced every time
quick learning but can be lost quickly
Partial Reinforcement - desired response is sometimes reinforced
slow learning and resistant to extinction
Schedules
Fixed Ratio - behavior is reinforced after a set number of responses
Commission for every sale
Variable ratio - behavior is reinforced after an unpredictable number of responses
Gambling
Fixed interval - behavior is reinforced after a set period of time
Paycheck every two weeks
Variable interval - behavior is reinforced after varying periods of time
Checking & getting emails

Classical Conditioning
involuntary behaviors
a type of learning when one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
Pavlov’s dogs
Main Points
Neutral Stimulus NS - a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning
Bell
Unconditioned Response UR - naturally occurring response to an US
Salivation
Unconditioned Stimulus US - a stimulus that naturally triggers a response
Food
Conditioned Response CR - a learned response to a previously NS
Salivation in response to the bell
Conditioned Stimulus CS - an originally irrelevant stimulus that comes to trigger a CR
Bell results in salivation
Other
Generalization - the tendency to respond in the same way to a similar but different stimuli
Salivating to a different pitch of bell
Discrimination - learned ability to distinguish between a CS and stimuli that doesn’t signal a US
Different pitches of tones
Higher-order conditioning - the CS is paired with a new NS creating a second, weaker stimulus
Bell and Light produces salivation in addition to Bell and Food
Learning
Insight learning - a sudden realization of a problem’s solution
Latent learning - learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate
mental map of the school
Von Restorff effect - the more something stands out from the crowd the more likely it is to be seen
Associative learning - learning that certain events occur together
hand on hot stove
Habituation - an organism’s decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
Sleeping through an alarm that once was new enough to wake you up
Coping
Problem-focused coping - try to reduce stress directly; altering or removing stressor or changing the way we interact with it
Emotion-focused coping - try to reduce stress by managing our reaction to the stressor but still knowing it exists
Effects
Spacing effect - distributed study or practice yields to better long-term retention
Spreading out studying for a test
Testing effect - enhanced memory after retrieving rather than simply re-reading info
flashcards and visual stimuli
Recency/Primacy Effect
Recency effect - ability to recall the most recent items especially well and quickly
Primacy effect - after delay when attention has shifted, they recall the first items best
 Knowt
Knowt
