
AP Environmental Science - Unit 4
Climate and Seasons ⛅️
Climate - long-term patterns
Weather - time-specific occurrences
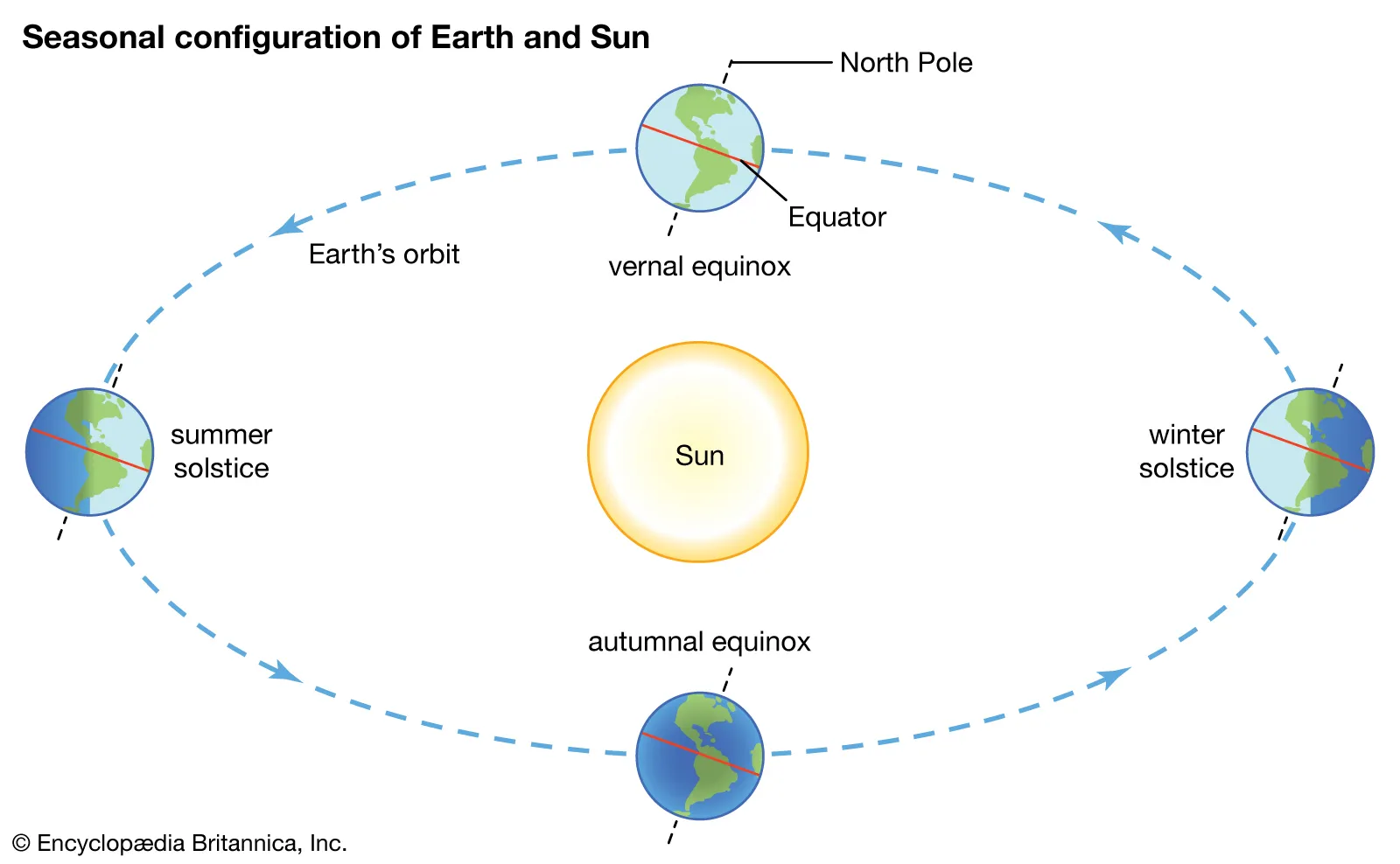
caused by latitude and Earth’s 23.5° Tilt
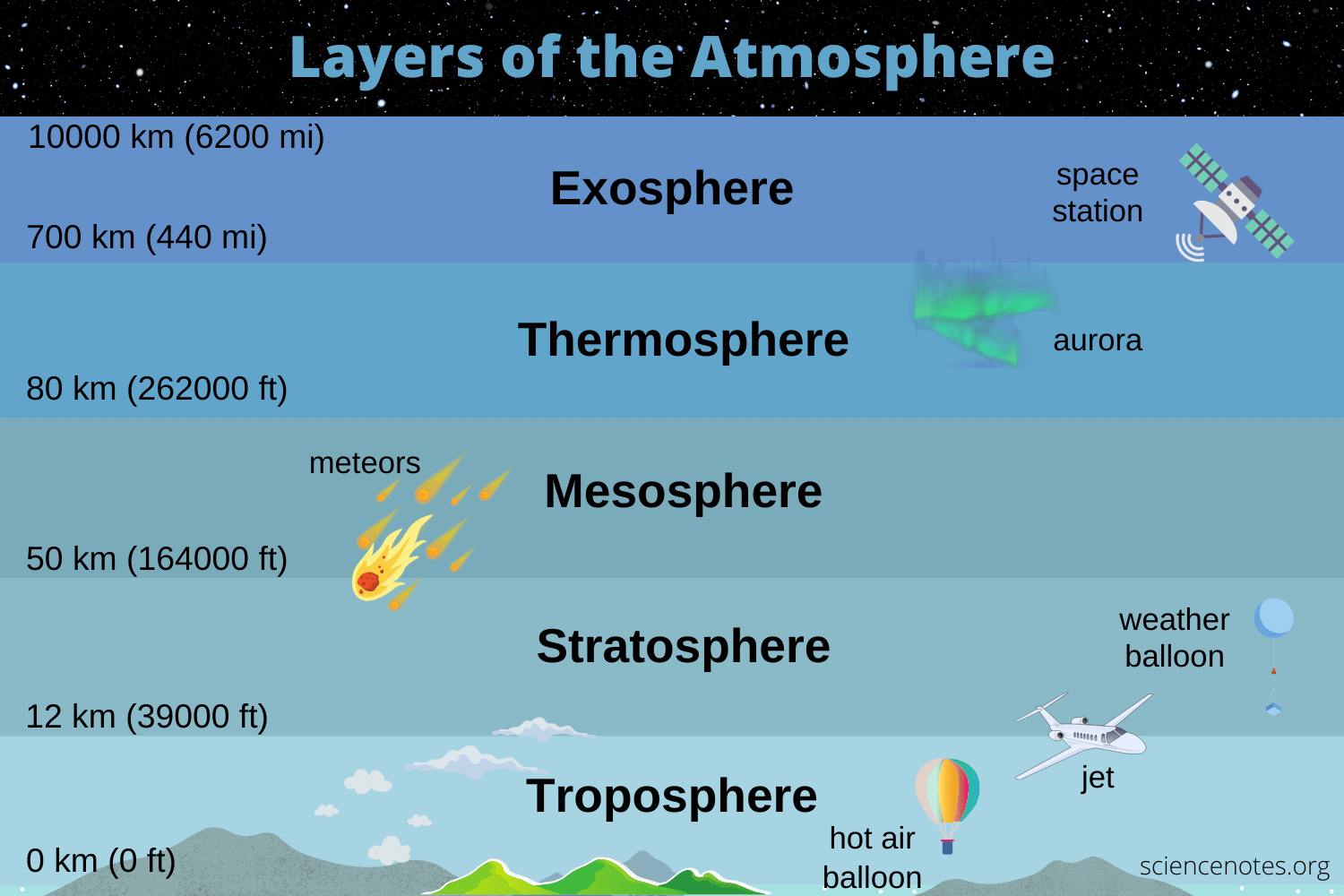
Atmosphere 🌌
Layers -
Troposphere (tropopause causes weather)
Stratosphere (ozone layer)
Mesosphere (middle)
Thermosphere (northern lights)
Exosphere (outer)
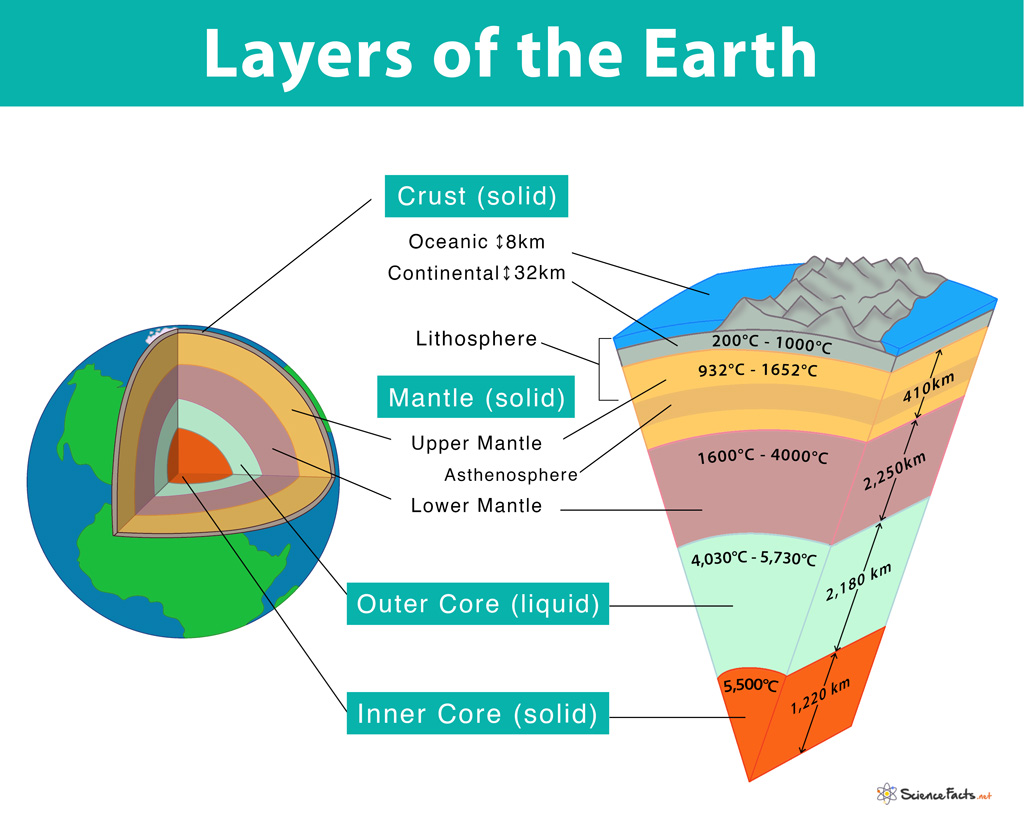
Earth and Plates 🪨
Layers -
Lithosphere (top layer crust; hard solid), part of mantle
Asthenosphere (softer solid), part of mantle
Lower Mantle (hard solid), part of mantle
Outer Core (liquid)
Inner Core (solid)
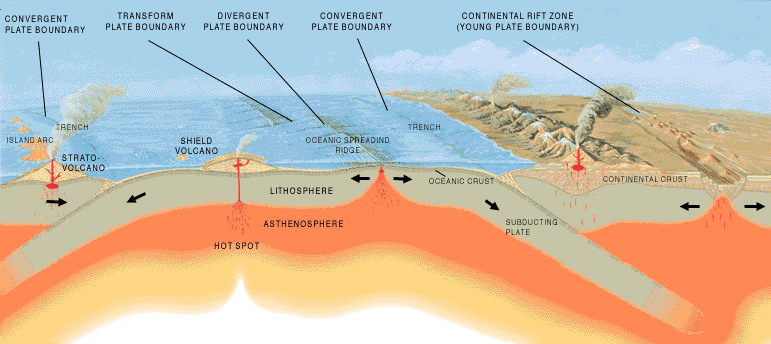
Boundary Types - oceanic/continental, convergent/divergent/transform - cause faults/hotspots (pacific ring of fire)/islands
convergent (pushing together) - volcanoes, islands, mountains
divergent (pushing away) - mountains, rifts, ridges - mid-atlantic ridge
transform (sliding past each other) - earthquakes
Wind Patterns 💨
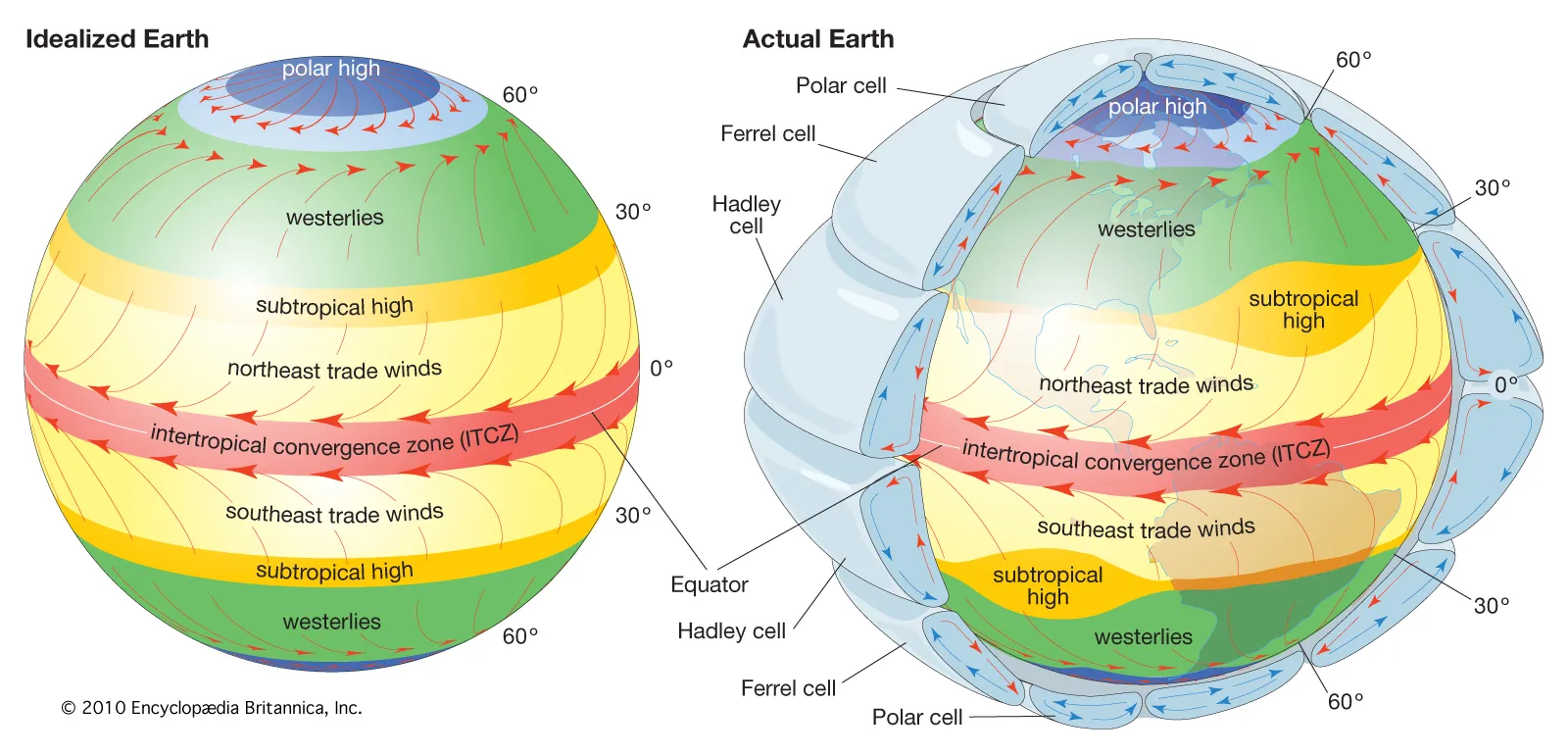
Cells (shown above) lead to currents called jet streams and are caused by convection
Trade Winds (shown above) - the predictable winds at each latitude (affected by the Coriolis effect (tilt causes change in direction))
Sometimes winds are blocked by landforms. One major example is mountains, the windward side is the side experiencing wind, and the leeward side is the other side of the mountain that experiences less wind. This is due to the deflection of wind by the mountain.
El Niño / La Niña 🌬
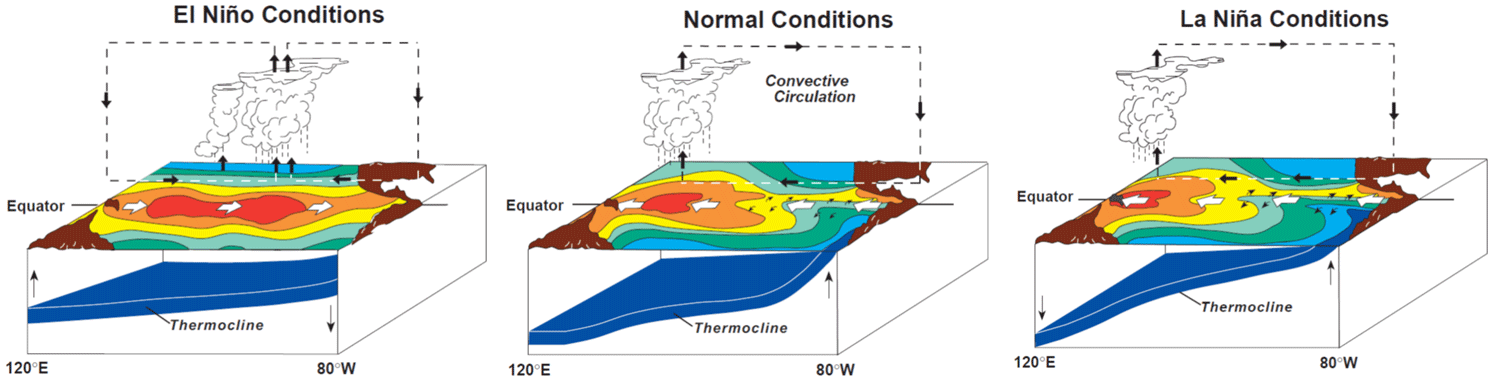
affects agriculture and climate
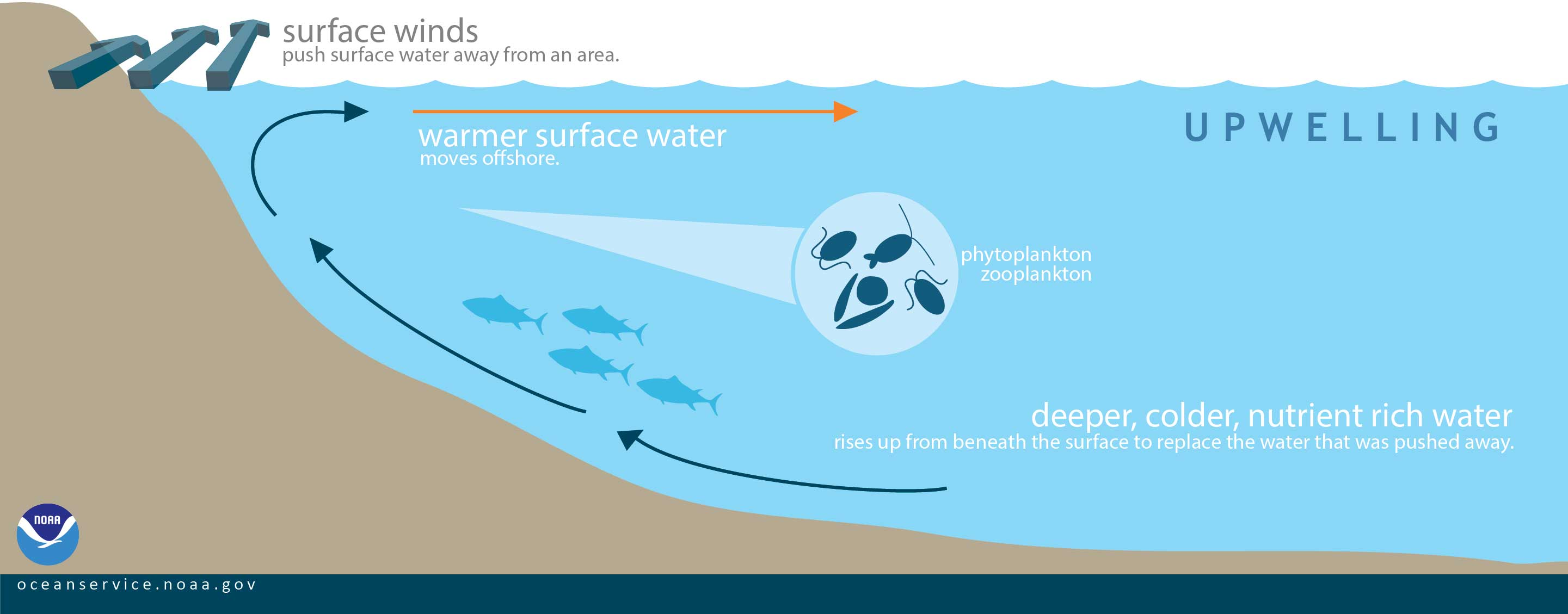
causes upwelling
Soil 🪱
Parent Material - the original substance that soil is made of (rocks)
Weathering - the breakdown of rocks/soil (by wind, water, humans, etc.)
Erosion - the spreading of soil (by wind, water, etc.)
factors - type of parent material, climate, topography (land slope), biological factors, time
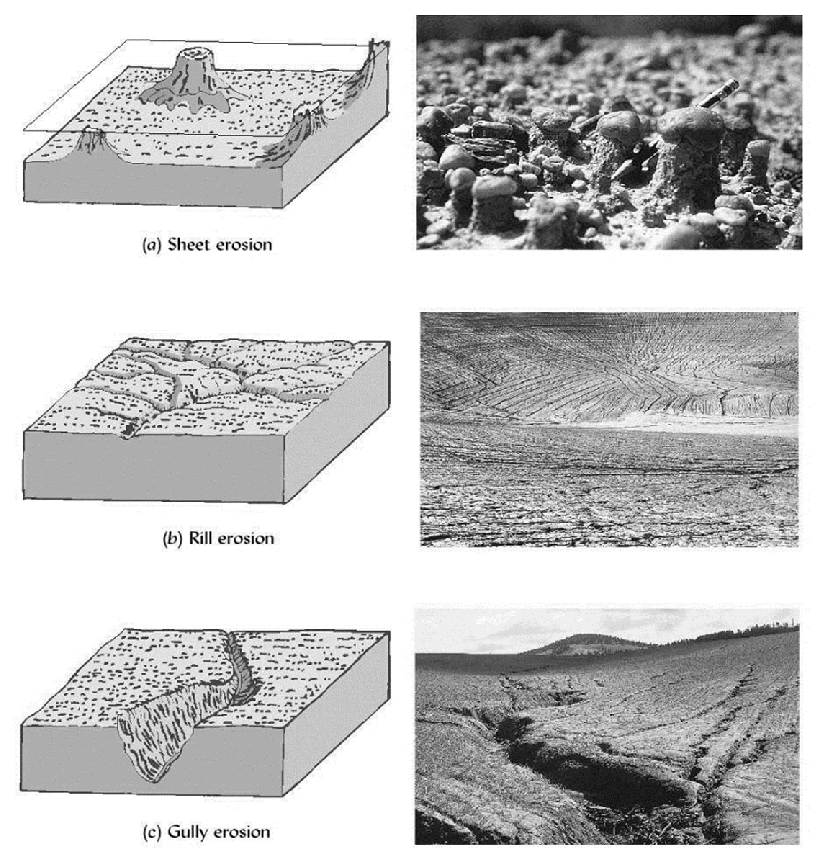
erosion types (and solutions) - sheet erosion (plant cover), rill erosion (strip cropping), gully erosion (diverting water away)
Soil Profile - soil layers (highest - organic matter, surface horizon, subsoil, substrata, bedrock - lowest)
Human Impacts on Soil - deforestation, overgrazing, pesticides/fertilizers, tillage
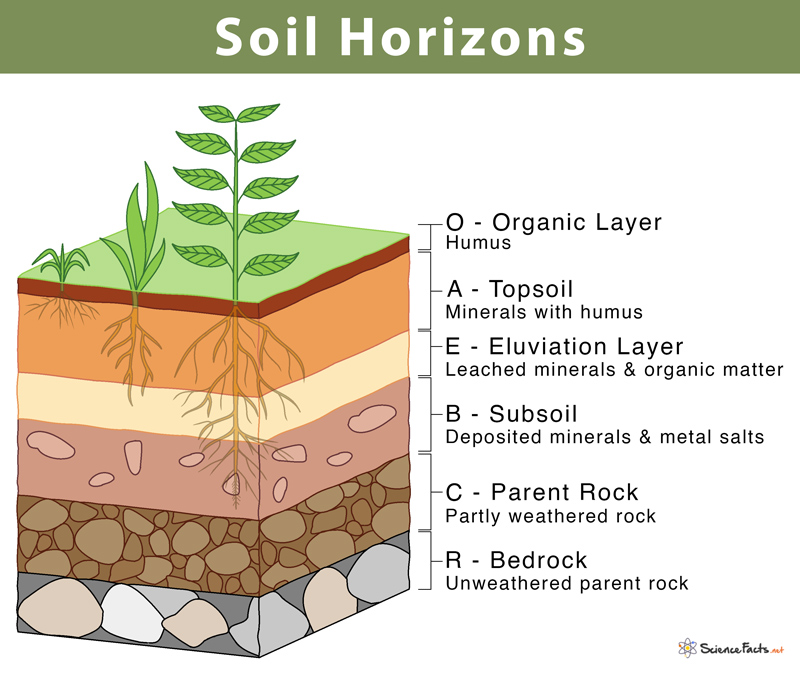
Soil Texture (mixtures of sand, silt, clay)
soil tests - chemical, physical, biological
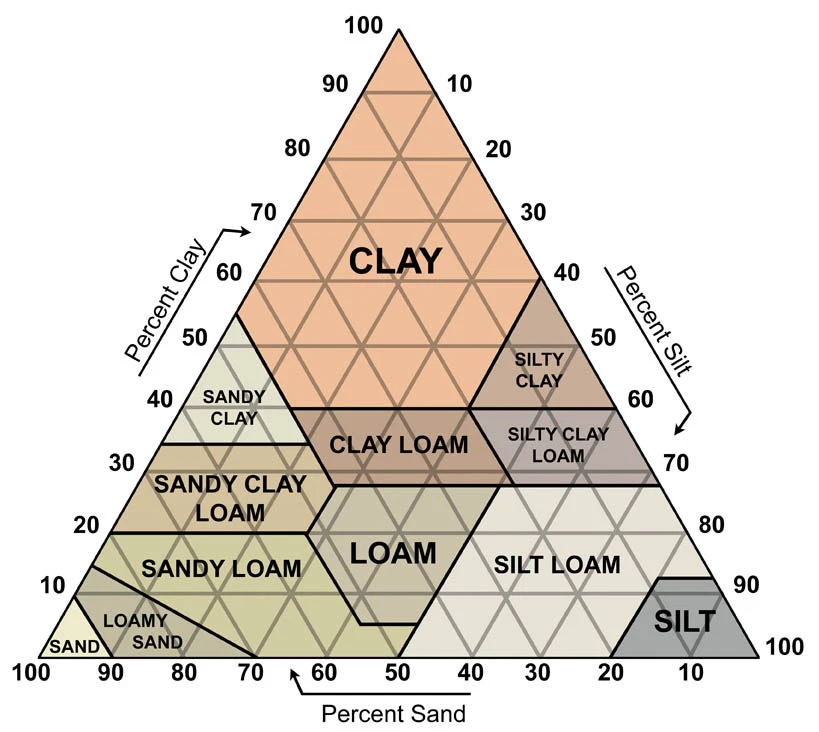
water travels the best through large soil (sand), and the worst through the small soil (clay)
Water 💧
Percolation - water dispersal into the ground
Infiltration - chemical dispersal into the ground
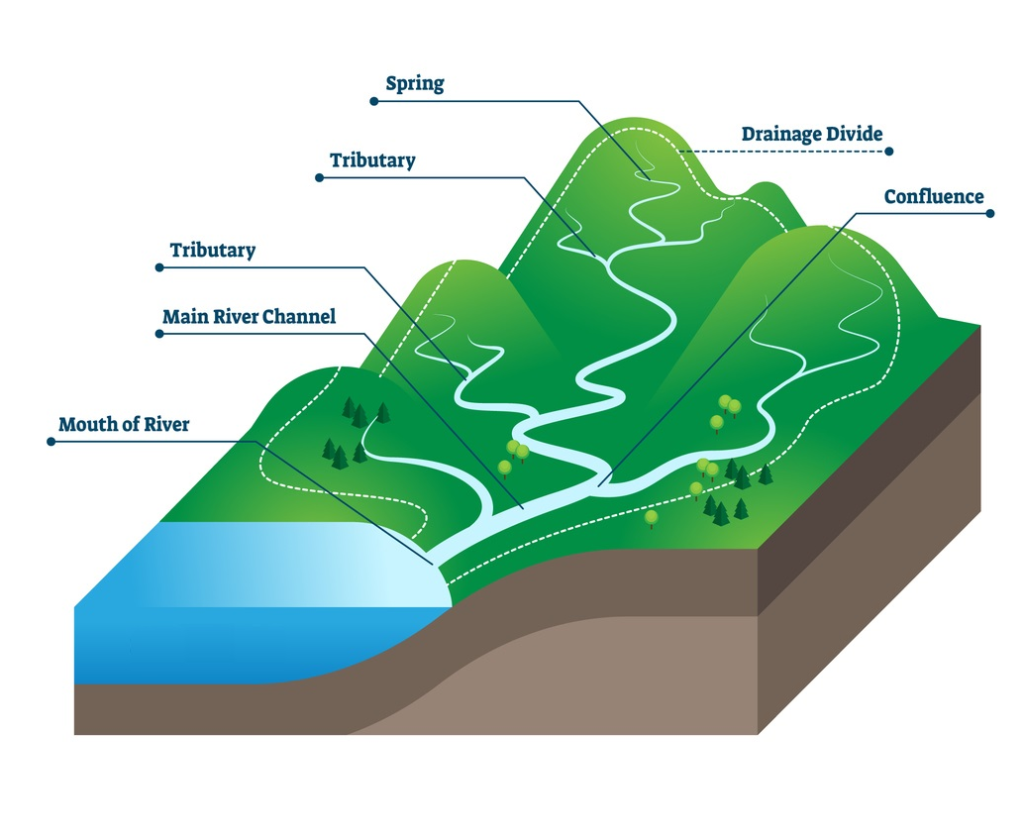
Watershed - geographically flowing water to a point
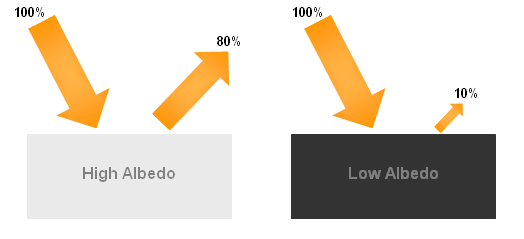
Albedo - the ability to absorb light based on color
AP Environmental Science - Unit 4
Climate and Seasons ⛅️
Climate - long-term patterns
Weather - time-specific occurrences
caused by latitude and Earth’s 23.5° Tilt

Atmosphere 🌌
Layers -
Troposphere (tropopause causes weather)
Stratosphere (ozone layer)
Mesosphere (middle)
Thermosphere (northern lights)
Exosphere (outer)

Earth and Plates 🪨
Layers -
Lithosphere (top layer crust; hard solid), part of mantle
Asthenosphere (softer solid), part of mantle
Lower Mantle (hard solid), part of mantle
Outer Core (liquid)
Inner Core (solid)

Boundary Types - oceanic/continental, convergent/divergent/transform - cause faults/hotspots (pacific ring of fire)/islands
convergent (pushing together) - volcanoes, islands, mountains
divergent (pushing away) - mountains, rifts, ridges - mid-atlantic ridge
transform (sliding past each other) - earthquakes

Wind Patterns 💨

Cells (shown above) lead to currents called jet streams and are caused by convection
Trade Winds (shown above) - the predictable winds at each latitude (affected by the Coriolis effect (tilt causes change in direction))
Sometimes winds are blocked by landforms. One major example is mountains, the windward side is the side experiencing wind, and the leeward side is the other side of the mountain that experiences less wind. This is due to the deflection of wind by the mountain.
El Niño / La Niña 🌬

affects agriculture and climate
causes upwelling

Soil 🪱
Parent Material - the original substance that soil is made of (rocks)
Weathering - the breakdown of rocks/soil (by wind, water, humans, etc.)
Erosion - the spreading of soil (by wind, water, etc.)
factors - type of parent material, climate, topography (land slope), biological factors, time
erosion types (and solutions) - sheet erosion (plant cover), rill erosion (strip cropping), gully erosion (diverting water away)

Soil Profile - soil layers (highest - organic matter, surface horizon, subsoil, substrata, bedrock - lowest)
Human Impacts on Soil - deforestation, overgrazing, pesticides/fertilizers, tillage

Soil Texture (mixtures of sand, silt, clay)
soil tests - chemical, physical, biological

water travels the best through large soil (sand), and the worst through the small soil (clay)
Water 💧
Percolation - water dispersal into the ground
Infiltration - chemical dispersal into the ground
Watershed - geographically flowing water to a point

Albedo - the ability to absorb light based on color

 Knowt
Knowt