
Ch 6 - Information and decision support systems
Management Information System: is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualisation of information in an organisation.
Provide routine information to managers in the functional areas
Provide information in exception reports and ad hoc (demand) reports
MIS used to have everything to do with IT and IS, however, it is now used for the report system.
MIS Reports Types:
Scheduled Reports:
Produced periodically, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. For example, a production manager could use a weekly summary report listing total payroll costs to monitor and control labour and job costs.
monthly bills are examples of scheduled reports
Key-indicator report:
Summarises previous day’s critical activities and is available at the beginning of each work day
Used by managers and executives to take quick, corrective action on significant aspects of the business
summarise inventory levels , production activity, and sales volume.
Demand Reports:
Demand reports are developed to provide certain information upon request
Are produced on demand rather than a schedule
Demand report can be generated to provide requested information by querying the company’s database
Come from an organisation’s database system. They are generated from the internet or by using cloud computing. The software can also generate useful graphics, including pie charts and bar graphs
Exception Reports:
Reports that are automatically produced when a situation is unusual or requires management action
This report would only contain items with fewer than five days of sales in inventory
Drill-down reports:
Provide increasingly detailed data about a situation. Analysts can see data at:
A high level first (such as sales for the entire company)
At a more detailed level (sales for one department of the company)
At a very detailed level (sales for one sales representative)
Decision Support Systems: a set of related computer programs and the data required to assist with analysis and decision-making within an organisation.
Support for problem-solving phases:
Different decision frequencies: One-time: ad hoc DSS Repetitive: institutional DSS
DIfferent Problem Structures: Highly structured vs. semi or unstructured
Support for various decision-making levels: Operational, tactical, strategic
DSS model:
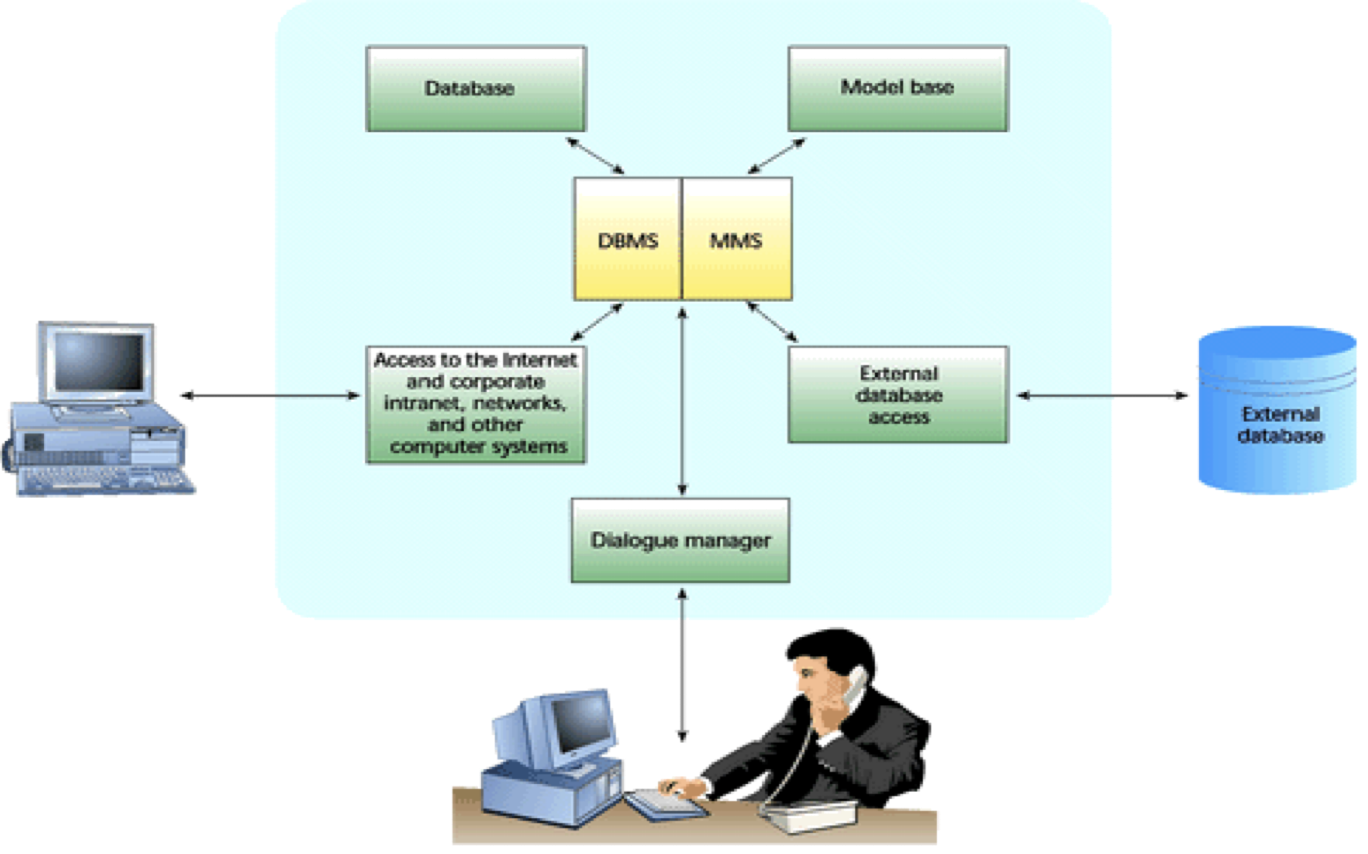
Components of a DSS: At the core of a DSS are a database and a model base.
The database management system: software that handles the storage, retrieval, and updating of data in a computer system
Allows managers and decision makers to perform qualitative analysis on the company’s vast stores of data in databases , data warehouses, and data marts.
A data-driven DSS primarily performs qualitative analysis based on the company’s databases
The model base: allows managers and decision makers to perform qualitative analysis on both internal and external data
A model driven DSS primarily performs mathematical or quantitative analysis
Model Management System (MMS): is a component of DSS architecture which provides for the creation, storage, manipulation, and access of models
Can coordinate the use of models in a DSS, including financial, statistical analysis, graphical, and project-management models
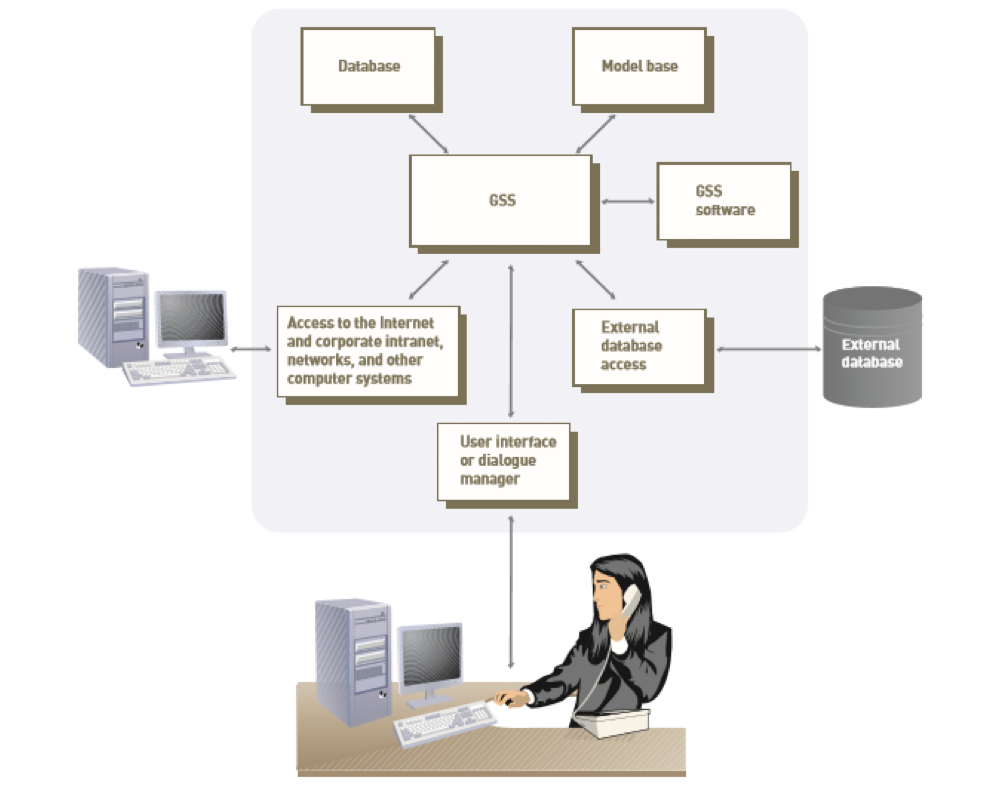
Group Support System
A group support system (GSS), or group decision support system and a computerised collaborative work system, consists of most of the elements in a DSS, plus software to provide effective support in group decision-making settings
GSS alternative:
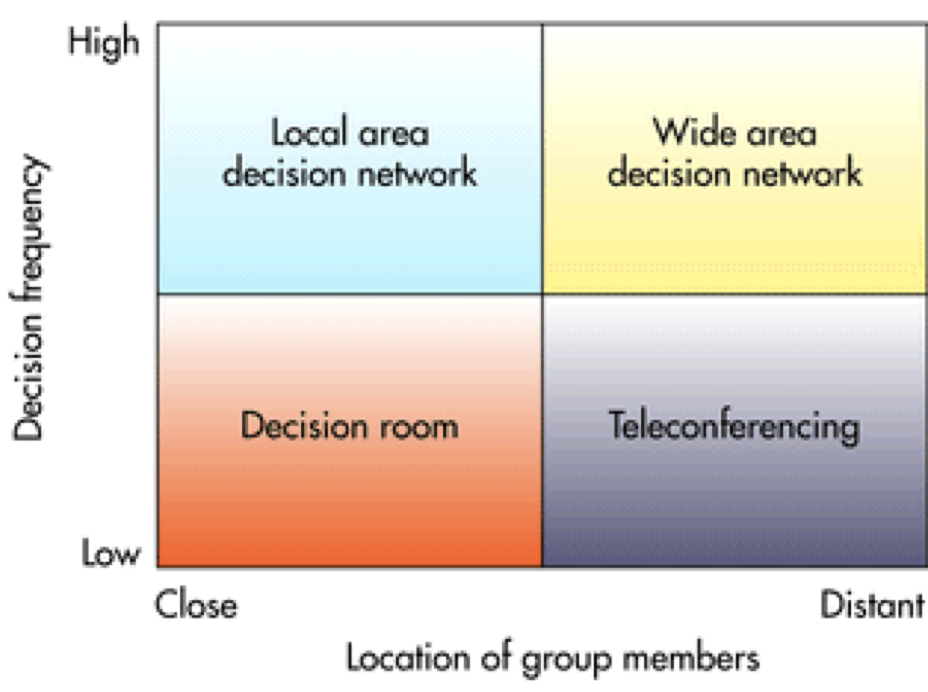
Characteristics of GSS:
Special design: Ease of use, Reduction of negative group behaviour
Flexibility: parallel communication, decision-making support
Anonymous input: automated record keeping
Executive support system (ESS): specialised DSS that includes all the hardware, software, data, procedures, and people used to assist senior-level executives within an organisation.
ESS, also called Executive Information Systems (EIS), supports decision making of members of the board of directors, who are responsible to stockholders
Capabilities of Executive Support Systems:
Defining an overall vision
Strategic planning
Strategic organising and staffing
Strategic control
Crisis management
Ch 6 - Information and decision support systems
Management Information System: is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualisation of information in an organisation.
Provide routine information to managers in the functional areas
Provide information in exception reports and ad hoc (demand) reports
MIS used to have everything to do with IT and IS, however, it is now used for the report system.
MIS Reports Types:
Scheduled Reports:
Produced periodically, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. For example, a production manager could use a weekly summary report listing total payroll costs to monitor and control labour and job costs.
monthly bills are examples of scheduled reports
Key-indicator report:
Summarises previous day’s critical activities and is available at the beginning of each work day
Used by managers and executives to take quick, corrective action on significant aspects of the business
summarise inventory levels , production activity, and sales volume.
Demand Reports:
Demand reports are developed to provide certain information upon request
Are produced on demand rather than a schedule
Demand report can be generated to provide requested information by querying the company’s database
Come from an organisation’s database system. They are generated from the internet or by using cloud computing. The software can also generate useful graphics, including pie charts and bar graphs
Exception Reports:
Reports that are automatically produced when a situation is unusual or requires management action
This report would only contain items with fewer than five days of sales in inventory
Drill-down reports:
Provide increasingly detailed data about a situation. Analysts can see data at:
A high level first (such as sales for the entire company)
At a more detailed level (sales for one department of the company)
At a very detailed level (sales for one sales representative)
Decision Support Systems: a set of related computer programs and the data required to assist with analysis and decision-making within an organisation.
Support for problem-solving phases:
Different decision frequencies: One-time: ad hoc DSS Repetitive: institutional DSS
DIfferent Problem Structures: Highly structured vs. semi or unstructured
Support for various decision-making levels: Operational, tactical, strategic
DSS model:

Components of a DSS: At the core of a DSS are a database and a model base.
The database management system: software that handles the storage, retrieval, and updating of data in a computer system
Allows managers and decision makers to perform qualitative analysis on the company’s vast stores of data in databases , data warehouses, and data marts.
A data-driven DSS primarily performs qualitative analysis based on the company’s databases
The model base: allows managers and decision makers to perform qualitative analysis on both internal and external data
A model driven DSS primarily performs mathematical or quantitative analysis
Model Management System (MMS): is a component of DSS architecture which provides for the creation, storage, manipulation, and access of models
Can coordinate the use of models in a DSS, including financial, statistical analysis, graphical, and project-management models
Group Support System
A group support system (GSS), or group decision support system and a computerised collaborative work system, consists of most of the elements in a DSS, plus software to provide effective support in group decision-making settings
GSS alternative:

Characteristics of GSS:
Special design: Ease of use, Reduction of negative group behaviour
Flexibility: parallel communication, decision-making support
Anonymous input: automated record keeping

Executive support system (ESS): specialised DSS that includes all the hardware, software, data, procedures, and people used to assist senior-level executives within an organisation.
ESS, also called Executive Information Systems (EIS), supports decision making of members of the board of directors, who are responsible to stockholders
Capabilities of Executive Support Systems:
Defining an overall vision
Strategic planning
Strategic organising and staffing
Strategic control
Crisis management
 Knowt
Knowt
