
Stress
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
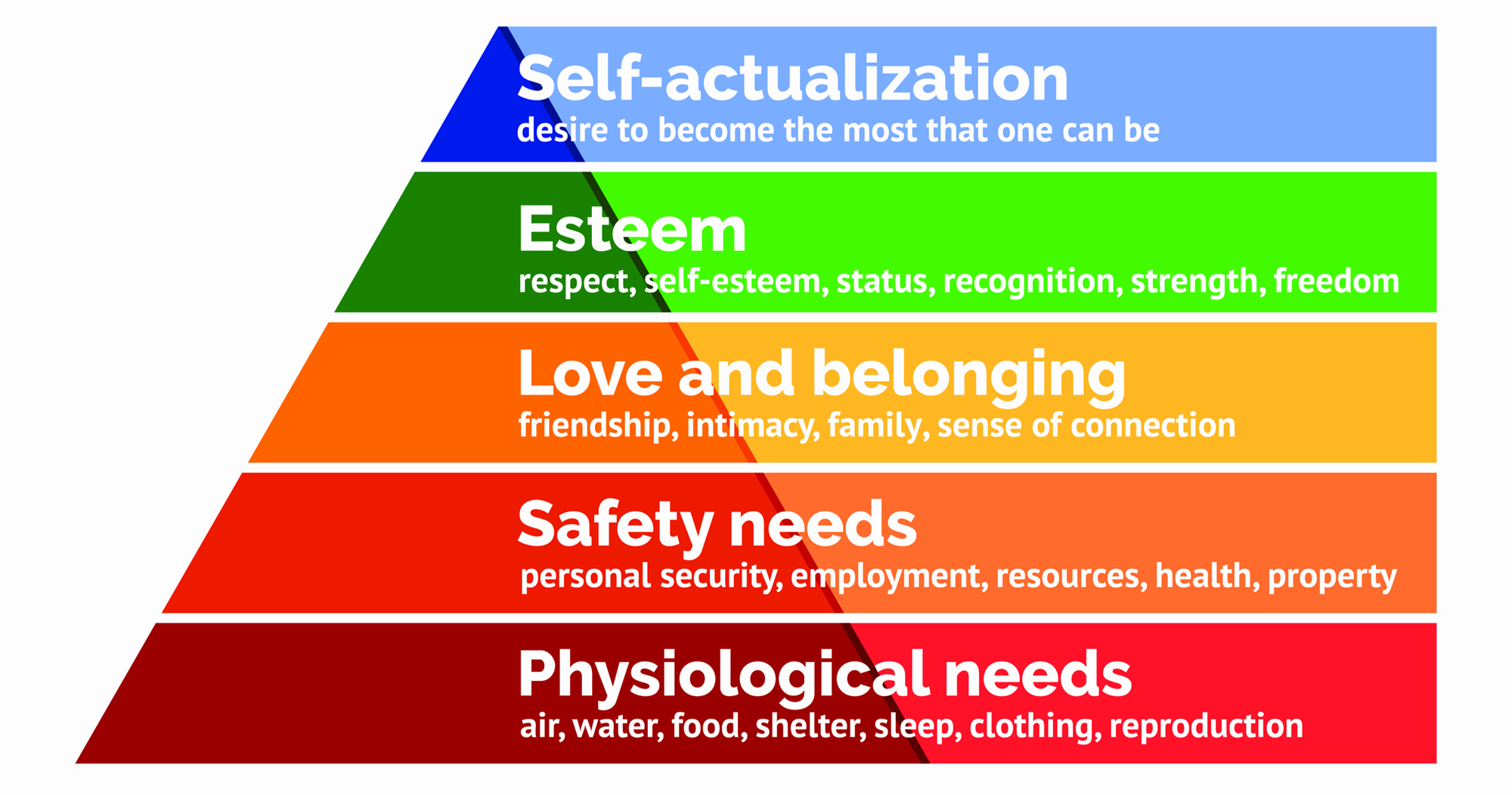
self actualization — realizing one’s fullest potential; what do you want to be?
esteem — also includes achievement
stress
stress: the body’s response to a demand
stressor: the demand put on the body
eustress: manageable stress that can lead to growth
distress: uncontrolled, overwhelming stress that is destructive and negative
general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
alarm = fight or flight response
also includes tertiary “freeze” response
resistance = body attempts to return to normal
exhaustion = “wear and tear,” illness may occur
physical symptoms of stress
headaches, diarrhea, dizziness, loss of appetite, increase in appetite, dry mouth, heartburn
positive ways to handle stress (examples, not a conclusive list)
hobbies
exercise
deep breathing
taking breaks
relaxation and meditation
talking through problems
negative ways to handle stress (examples, not a conclusive list)
violence
procrastination
destruction
addiction
taking anger out on others
denial
over eating
under eating
defense mechanism: a strategy used to cope with a stressful situation
can be positive or negative, or dependent on the situation
positive mechanisms relieve stress whereas negative mechanisms add to stress
most mechanisms can be both
sublimation: positive; the direction of energy into a useful rather than unacceptable goal
identification: may be positive or negative; assuming the qualities of someone you admire
compensation: positive; making up for weakness in one area by excelling in another area
rationalization: negative; making excuses for actions or feelings
daydreaming: may be positive or negative; fantasizing to escape unpleasant realities
displacement: negative; transforming emotions or thoughts from the original source to another
regression: negative; reverting to immature behavior to express emotions
projection: negative; putting your own faults onto someone else
denial: negative; refusing to recognize or otherwise acknowledge an emotion or problem
Stress
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs

self actualization — realizing one’s fullest potential; what do you want to be?
esteem — also includes achievement
stress
stress: the body’s response to a demand
stressor: the demand put on the body
eustress: manageable stress that can lead to growth
distress: uncontrolled, overwhelming stress that is destructive and negative
general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
alarm = fight or flight response
also includes tertiary “freeze” response
resistance = body attempts to return to normal
exhaustion = “wear and tear,” illness may occur
physical symptoms of stress
headaches, diarrhea, dizziness, loss of appetite, increase in appetite, dry mouth, heartburn
positive ways to handle stress (examples, not a conclusive list)
hobbies
exercise
deep breathing
taking breaks
relaxation and meditation
talking through problems
negative ways to handle stress (examples, not a conclusive list)
violence
procrastination
destruction
addiction
taking anger out on others
denial
over eating
under eating
defense mechanism: a strategy used to cope with a stressful situation
can be positive or negative, or dependent on the situation
positive mechanisms relieve stress whereas negative mechanisms add to stress
most mechanisms can be both
sublimation: positive; the direction of energy into a useful rather than unacceptable goal
identification: may be positive or negative; assuming the qualities of someone you admire
compensation: positive; making up for weakness in one area by excelling in another area
rationalization: negative; making excuses for actions or feelings
daydreaming: may be positive or negative; fantasizing to escape unpleasant realities
displacement: negative; transforming emotions or thoughts from the original source to another
regression: negative; reverting to immature behavior to express emotions
projection: negative; putting your own faults onto someone else
denial: negative; refusing to recognize or otherwise acknowledge an emotion or problem
 Knowt
Knowt
