
Body Systems
Nervous System receives incoming information (senses). Sends messages to the body about how to react.
Central Nervous System (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous system are the body nerves that connect to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Connects the central nervous system to the body's organs and limbs.
the Autonomic Nervous System controls involuntary bodily functions (not consciously controlled), such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes
the Somatic Nervous System controls voluntary bodily functions (consciously controlled), such as controlling skeletal muscles
Stimulus are things that initiate nerve impulses (ex. hot room) and the Effector is the response (ex. Sweating)
Motor Functions are complex muscle-and-nerve acts that produce movement (walking, writing, typing running etc.)
the Synapse is where the nerve impulse is sent (connection of 2 neurons).
Action Potential changes the charge of the synapse (causes electricity) and Neurotransmitters are sent.
the Myelin Sheath covers Schwann Cells and speeds up nerve impulses.
Axons are the long threadlike part of a nerve cell that carry the nerve impulse.
Dendrites are nranch like extensions on a neuron that GET signals and connect to the synapse.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another 'target' neuron.
Multipolar Neurons make up most of the brain/spinal cord and these neurons are mylinated.
Bipolar Neurons are found in eyes, nose, and ears. Classified as an "interneuron" and connects PNS to CNS.
Interneurons are nerve cells that serve as that connection between Peripheral Nerves to Central Nervous System.
Unipolar Neurons help accept sensory messages (feelings & senses) and are found outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Sensory Neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, smell, sound etc.)
Bipolar shaped Neurons Motor Neuron Nerve cells responsible for making an action or movement happen.
Multipolar Shaped Neurons Sodium Potassium Pump A protein on the outside membrane of a neuron at the Synapse.
Changes the charge (aka. polarity) of the neuron.
Moves sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane to change the "electricity" of the neuron. The order of events during an Action Potential caused by the Sodium Potassium Pump
1.) Sodium Channel Opens 2.) Sodium Channel Closes 3.) Potassium Channel Opens 4.) Potassium Channel Closes Depolarization During nerve impulse, electrical charge increases to Action Potential (30mV) Repolarization During nerve impulse (Action Potential), electrical charge decreases to Resting Potential (-70mV)
5 milliseconds Time it takes to send a nerve impulse (Action Potential of Sodium Potassium Pump)
4 Major Brain Structures 1. Cerebellum 2. Cerebrum 3. Diencephalon 4. Brainstem Cerebrum "Brain" area
Divided into Right and left hemispheres, connected by the Corpus Callosum Diencephalon "Middle of brain"- in between Cerebrum & Brain Stem
Consists of:
Hypothalamus
Thalamus Cerebellum Coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance, coordination, and speech, resulting in smooth, balanced muscular activity Brain Stem Connects brain to spinal cord
Made up of the Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata
Right Cerebral Hemisphere Controls left body,
Creative, Visual, facial recognition, visual, and musical traits Left Cerebral Hemisphere Controls Right Body
Logical, Math, Calculations, Organized traits Corpus Callosum Connects the left and right hemispheres(sides) of the brain Gyri Brain ridges or Brain wrinkles Sulcus Shallow wrinkles of the brain Fissure Deep groove of the brain Frontal Lobe Controls your logic, decision making, concentration, and personality Parietal Lobe Touch, pressure, temperature, pain Temporal Lobe Controls your hearing & memory. Occipital Lobe Controls vision/sight Brocas & Wernicke's Area Controls Language and Speech
Brocas: hearing and interpreting speech
Wernickes's: writing Hippocampus Controls Memory
important in forming new memories and connecting emotions and senses, such as smell and sound, to memories. Thalamus Accepts sensory messages Hypothalamus Takes messages from the Thalamus and sends signals to glands.
Helps regulate body temperature, certain metabolic processes and other autonomic activities Amygdala Controls Emotions "almond" shaped Limbic System (and the organs that make up the Limbic System) Controls Emotion.
Includes: 1.Thalamus & Hypothalamus 2. Amygdala 3. Hippocampus 4. Olfactory bulbs. Midbrain A portion of the Central Nervous System controls reflexes Medulla Oblongata Transfers messages along the spinal cord.
Located below the pons
Controls some autonomic functions (ex. breathing, swallowing) Autonomic functions Regulate involuntary actions like the intestines, heart, and glands. Reticular Formation Mediates the overall level of consciousness Excitatory Neurtransmitters Starts up (stimulates the brain) Inhibitory Neurotransmitters Calms the brain and helps create balance Acetylcholine Neurotransmitter, skeletal muscle contractions Endorphins Neurotransmitter, Reduces pain, fight or flight Norepinephrine Neurotransmitter, feel good
(low amounts: depression) Dopamine Neurotransmitter, feel good
Regulates attention, cognition, movement, pleasure, and hormonal processes
(Low amounts: Parkinson's) Serotonin Neurotransmitter, that causes the feeling of sleepiness
(Low amounts: Aggression) Olfactory Bulb Sense Smell
Linked to the Hippocampus (the reason why smell is so related to memory)
Skeletal System provides shape and structure to the body, allows for movement, protects vital organs, and produces blood cells.
Integumentary System protects the body from invaders by providing a tough protective layer. Warms and Cools the body.
Muscular System allows for movement of the body, keeps head in position, and provides heat.
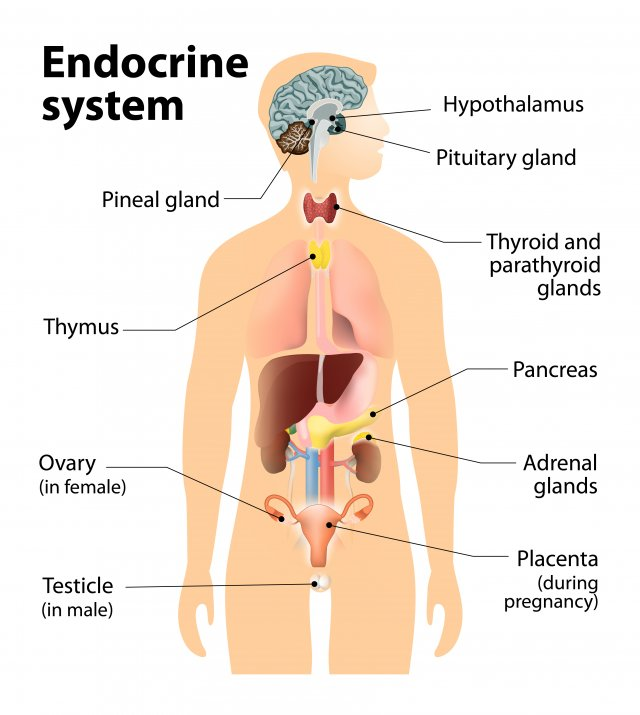
Endocrine System controls body functions using chemical messengers called hormones, it acts with the nervous system to coordinate functions of all other body systems; releases hormones (mediators); Hormones act on target cells which are cells that have the specific hormone receptor; slower and longer lasting response
Endocrine Glands
Pituitary, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Pineal, Adrenal.
Endocrine Tissues
Hypothalamus, Thymus, Pancreas, Ovaries/Testes, Kidneys, Placenta, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine.
Anterior Pituitary
Adenohyophysis; composed of epithelial tissue; produces and secretes hormones
Posterior Pituitary
Neurophypophysis; composed of neural tissue; secretes two hormone
Endocrine Hormones:
Glucagon raises blood sugar, stimulates liver to release glycogen.
Insulin decreases blood sugar PTH regulates calcium and phosphates stimulates kidneys.
A way to remember if glucagon or insulin is needed, think about the word. GlucaGON(E) is when glucose is GONE (or is too low), and Insulin is when there is extra glucose.
Thyroxine/Triiodothyronine regulate metabolism Growth Hormone (GH) regulates the growth of the body.
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is produced by the pituitary gland when the body is dehydrated, it causes the kidneys to reabsorb more water into the blood making the urine more concentrated.
Adrenaline is released into the bloodstream in response to physical or mental stress.
Corticosteroids are a group of hormones, including cortisol, released by the adrenal glands at times of stress (long term)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates the adrenal cortex
Releasing Factors are hormones transmitted from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary that stimulate release of some other hormones
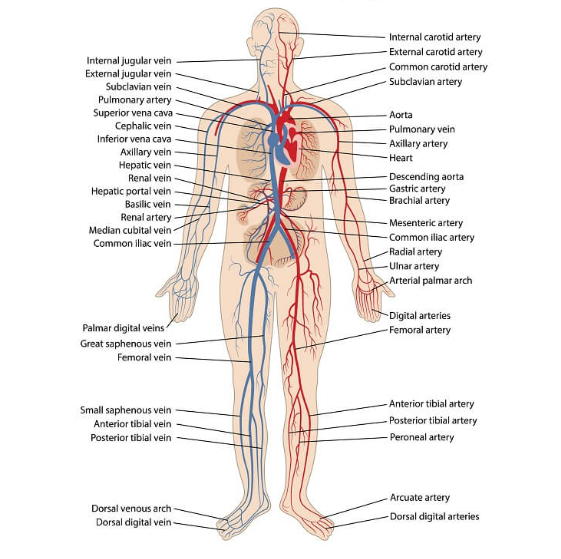
Circulatory System transports oxygen, waste, nutrients, hormones, and other things all around the body, also known as the body’s transportation system.
the Heart pumps blood throughout the body in the circulatory system, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues, and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes.
Cardiac Muscle is the type of muscle that makes up the heart.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart and are muscular, elastic, thick “walls”.
Aorta is the largest artery in the body.
Veins carry blood back to the heart, thin walls, contains valves.
Vena Cava is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood into the heart.
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels.
Arterioles are the smallest arteries that connect with the capillaries.
Venules are small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins.
Systole is the __top/highe__r number on a blood pressure reading when the heart is contracted.
Diastole is the bottom/lower number on a blood pressure reading when the heart is relaxed.
Four Parts of Blood include Plasma, Platlets, White Blood Cells, and Red Blood Cells.
Plasma is the liquid part of blood (around 55%).
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) are nonnucleated biconcave disks, and contain hemoglobin.
A Blood Type contains A antigen and B antibody.
B Blood Type contains B antigens and A antibodies.
O Blood Type is a universal donor; no antigens present both antibodies.
AB Blood Type is a universal recipient, A and B antigens, no antibodies.
Hemoglobin Oxygen carries pigments in red blood cells.
Agglutination is the clumping of red blood cells.
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) fight infections.
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off viral infections.
Platelets (Thrombcytes) is the part of blood responsible for clotting.
Urinary System cleans the blood, rids the body of wastes, and maintains salt and water balance.
Respiratory System brings oxygen into the body and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
Immune System fights diseases, helps your body stay healthy. You would be dead within minutes if you didn’t have this system as there are billions of bacteria and other little viruses that are dealt with easily by the immune system.
Digestive System breaks down food into smaller molecules and absorbs nutrients into the body.
Reproductive System produces sex cells (sperm and eggs) and produces sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen), nurtures the unborn baby (fetus) in women.
Excretory System removes excess/unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. Wastes such as stool or urine are removed by this system, and the urinary system is associated with the excretory system.
Body Systems
Nervous System receives incoming information (senses). Sends messages to the body about how to react.
Central Nervous System (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous system are the body nerves that connect to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Connects the central nervous system to the body's organs and limbs.
the Autonomic Nervous System controls involuntary bodily functions (not consciously controlled), such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes
the Somatic Nervous System controls voluntary bodily functions (consciously controlled), such as controlling skeletal muscles
Stimulus are things that initiate nerve impulses (ex. hot room) and the Effector is the response (ex. Sweating)
Motor Functions are complex muscle-and-nerve acts that produce movement (walking, writing, typing running etc.)
the Synapse is where the nerve impulse is sent (connection of 2 neurons).
Action Potential changes the charge of the synapse (causes electricity) and Neurotransmitters are sent.
the Myelin Sheath covers Schwann Cells and speeds up nerve impulses.
Axons are the long threadlike part of a nerve cell that carry the nerve impulse.
Dendrites are nranch like extensions on a neuron that GET signals and connect to the synapse.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another 'target' neuron.
Multipolar Neurons make up most of the brain/spinal cord and these neurons are mylinated.
Bipolar Neurons are found in eyes, nose, and ears. Classified as an "interneuron" and connects PNS to CNS.
Interneurons are nerve cells that serve as that connection between Peripheral Nerves to Central Nervous System.
Unipolar Neurons help accept sensory messages (feelings & senses) and are found outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Sensory Neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, smell, sound etc.)
Bipolar shaped Neurons Motor Neuron Nerve cells responsible for making an action or movement happen.
Multipolar Shaped Neurons Sodium Potassium Pump A protein on the outside membrane of a neuron at the Synapse.
Changes the charge (aka. polarity) of the neuron.
Moves sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane to change the "electricity" of the neuron. The order of events during an Action Potential caused by the Sodium Potassium Pump
1.) Sodium Channel Opens 2.) Sodium Channel Closes 3.) Potassium Channel Opens 4.) Potassium Channel Closes Depolarization During nerve impulse, electrical charge increases to Action Potential (30mV) Repolarization During nerve impulse (Action Potential), electrical charge decreases to Resting Potential (-70mV)
5 milliseconds Time it takes to send a nerve impulse (Action Potential of Sodium Potassium Pump)
4 Major Brain Structures 1. Cerebellum 2. Cerebrum 3. Diencephalon 4. Brainstem Cerebrum "Brain" area
Divided into Right and left hemispheres, connected by the Corpus Callosum Diencephalon "Middle of brain"- in between Cerebrum & Brain Stem
Consists of:
Hypothalamus
Thalamus Cerebellum Coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance, coordination, and speech, resulting in smooth, balanced muscular activity Brain Stem Connects brain to spinal cord
Made up of the Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata
Right Cerebral Hemisphere Controls left body,
Creative, Visual, facial recognition, visual, and musical traits Left Cerebral Hemisphere Controls Right Body
Logical, Math, Calculations, Organized traits Corpus Callosum Connects the left and right hemispheres(sides) of the brain Gyri Brain ridges or Brain wrinkles Sulcus Shallow wrinkles of the brain Fissure Deep groove of the brain Frontal Lobe Controls your logic, decision making, concentration, and personality Parietal Lobe Touch, pressure, temperature, pain Temporal Lobe Controls your hearing & memory. Occipital Lobe Controls vision/sight Brocas & Wernicke's Area Controls Language and Speech
Brocas: hearing and interpreting speech
Wernickes's: writing Hippocampus Controls Memory
important in forming new memories and connecting emotions and senses, such as smell and sound, to memories. Thalamus Accepts sensory messages Hypothalamus Takes messages from the Thalamus and sends signals to glands.
Helps regulate body temperature, certain metabolic processes and other autonomic activities Amygdala Controls Emotions "almond" shaped Limbic System (and the organs that make up the Limbic System) Controls Emotion.
Includes: 1.Thalamus & Hypothalamus 2. Amygdala 3. Hippocampus 4. Olfactory bulbs. Midbrain A portion of the Central Nervous System controls reflexes Medulla Oblongata Transfers messages along the spinal cord.
Located below the pons
Controls some autonomic functions (ex. breathing, swallowing) Autonomic functions Regulate involuntary actions like the intestines, heart, and glands. Reticular Formation Mediates the overall level of consciousness Excitatory Neurtransmitters Starts up (stimulates the brain) Inhibitory Neurotransmitters Calms the brain and helps create balance Acetylcholine Neurotransmitter, skeletal muscle contractions Endorphins Neurotransmitter, Reduces pain, fight or flight Norepinephrine Neurotransmitter, feel good
(low amounts: depression) Dopamine Neurotransmitter, feel good
Regulates attention, cognition, movement, pleasure, and hormonal processes
(Low amounts: Parkinson's) Serotonin Neurotransmitter, that causes the feeling of sleepiness
(Low amounts: Aggression) Olfactory Bulb Sense Smell
Linked to the Hippocampus (the reason why smell is so related to memory)
Skeletal System provides shape and structure to the body, allows for movement, protects vital organs, and produces blood cells.
Integumentary System protects the body from invaders by providing a tough protective layer. Warms and Cools the body.
Muscular System allows for movement of the body, keeps head in position, and provides heat.
Endocrine System controls body functions using chemical messengers called hormones, it acts with the nervous system to coordinate functions of all other body systems; releases hormones (mediators); Hormones act on target cells which are cells that have the specific hormone receptor; slower and longer lasting response
Endocrine Glands
Pituitary, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Pineal, Adrenal.
Endocrine Tissues
Hypothalamus, Thymus, Pancreas, Ovaries/Testes, Kidneys, Placenta, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine.
Anterior Pituitary
Adenohyophysis; composed of epithelial tissue; produces and secretes hormones
Posterior Pituitary
Neurophypophysis; composed of neural tissue; secretes two hormone
Endocrine Hormones:
Glucagon raises blood sugar, stimulates liver to release glycogen.
Insulin decreases blood sugar PTH regulates calcium and phosphates stimulates kidneys.
A way to remember if glucagon or insulin is needed, think about the word. GlucaGON(E) is when glucose is GONE (or is too low), and Insulin is when there is extra glucose.
Thyroxine/Triiodothyronine regulate metabolism Growth Hormone (GH) regulates the growth of the body.
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is produced by the pituitary gland when the body is dehydrated, it causes the kidneys to reabsorb more water into the blood making the urine more concentrated.
Adrenaline is released into the bloodstream in response to physical or mental stress.
Corticosteroids are a group of hormones, including cortisol, released by the adrenal glands at times of stress (long term)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates the adrenal cortex
Releasing Factors are hormones transmitted from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary that stimulate release of some other hormones

Circulatory System transports oxygen, waste, nutrients, hormones, and other things all around the body, also known as the body’s transportation system.
the Heart pumps blood throughout the body in the circulatory system, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues, and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes.
Cardiac Muscle is the type of muscle that makes up the heart.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart and are muscular, elastic, thick “walls”.
Aorta is the largest artery in the body.
Veins carry blood back to the heart, thin walls, contains valves.
Vena Cava is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood into the heart.
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels.
Arterioles are the smallest arteries that connect with the capillaries.
Venules are small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins.
Systole is the __top/highe__r number on a blood pressure reading when the heart is contracted.
Diastole is the bottom/lower number on a blood pressure reading when the heart is relaxed.
Four Parts of Blood include Plasma, Platlets, White Blood Cells, and Red Blood Cells.
Plasma is the liquid part of blood (around 55%).
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) are nonnucleated biconcave disks, and contain hemoglobin.
A Blood Type contains A antigen and B antibody.
B Blood Type contains B antigens and A antibodies.
O Blood Type is a universal donor; no antigens present both antibodies.
AB Blood Type is a universal recipient, A and B antigens, no antibodies.
Hemoglobin Oxygen carries pigments in red blood cells.
Agglutination is the clumping of red blood cells.
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) fight infections.
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off viral infections.
Platelets (Thrombcytes) is the part of blood responsible for clotting.

Urinary System cleans the blood, rids the body of wastes, and maintains salt and water balance.
Respiratory System brings oxygen into the body and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
Immune System fights diseases, helps your body stay healthy. You would be dead within minutes if you didn’t have this system as there are billions of bacteria and other little viruses that are dealt with easily by the immune system.
Digestive System breaks down food into smaller molecules and absorbs nutrients into the body.
Reproductive System produces sex cells (sperm and eggs) and produces sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen), nurtures the unborn baby (fetus) in women.
Excretory System removes excess/unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. Wastes such as stool or urine are removed by this system, and the urinary system is associated with the excretory system.
 Knowt
Knowt