
Photosynthesis
1) Which molecule stores more than 90 times the energy of an ATP molecule?
-glucose
2) All organisms get the energy they need to regenerate ATP from___
-foods like glucose
ATP consists of ribose, sugar, adenine, and 3 phosphate groups.
ADP forms when ATP loses a phosphate and releases energy.
ATP provides energy for active transport in cells
What is it called? | Definition | 2 examples |
|---|---|---|
Autotroph | organisms that make their own foods. | Cynobacteria, plants, algea |
heterotroph | organisms that obtain energy from food they eat. | Animals, fungi |
What is the ultimate source of energy autotrophs use to produce food?
-the sun
Pigments:
Light green: chlorophyll B
Dark green: Chlorophyll A
Orange: Carotenoids
How do we see color? how does that apply to black and white?
Our eyes pick up the color reflected by objects that are not absorbed.
White- reflects all light
Black- absorbs all light
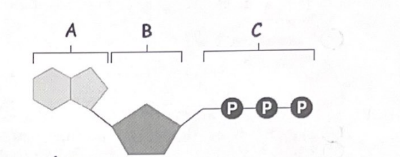 A= adenine
A= adenine
B= ribose
C= phosphate group
Name 3 cellular activities/work that use energy to stored in ATP
Chemical
Mechanical
Transport
Chlorophyll absorbs light well in the blue-violet and red regions of the visible spectrum
6H2O+ 6CO2+ Light —> C6H12O2 + O2
QUESTIONS:
If a plant is kept under green-colored light for an extended period of time, what will happen to the rate of photosynthesis?
The plant is not absorbing any light necessary for Light Dependant reactions.
Why are carotenoid colors present in leaves during fall and not other times?
This is because as days shorten, temperature cools. Chlorophyll is broken down into accesory pigments that are used to absorb higher energy light waves.
Photosystem one and two are part of the thylakoid membrane
why does the space inside the thylakoid become positively charged during the light-dependant reactions?
H+ ions build up as water splits.
Where does the calvin cycle occur in?
the stroma
Write an equation that shows NADP+ become NADPH
NADP+ + H+ + 2e- —> NADPH
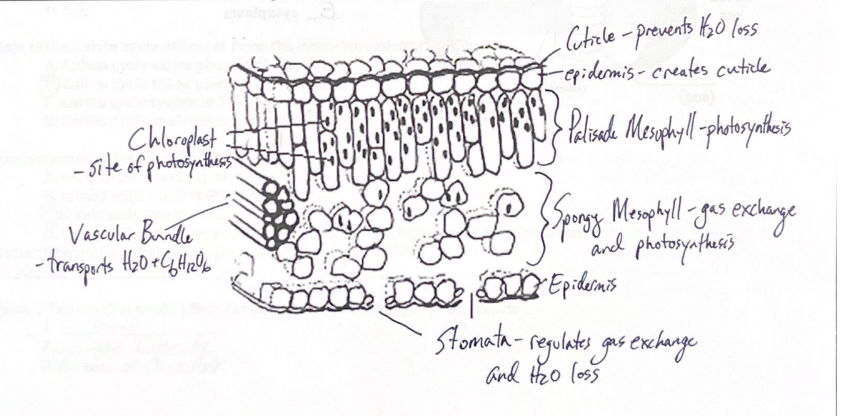
Flashcards-
Chloroplast- site of photosynthesis
Cuticle- prevents H2O loss
Vascular bundle transports H2O and C6H12O6
Palisade Mesophyll: photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll: gas exchange and photosynthesis.
Stomata- regulates gas exchange H2O loss
epidermis- hydrophobic, doesn’t let water out of the leaf.
first stage of calvin cycle- carbon fixation
second stage of calvin cycle- reduction
3rd stage of calvin cycle- regeneration
Rubisco- an enzyme that combines RUBP and CO2
PSII- where light first hits to excite the electrons.
Photo excitation- (step 1) when the elctrons become excited
Electron transport chain- (step 2) when the excited protein from PSII goes through a bunch of different membrane proteins.
Photolysis- (step 3) the process of splitting water, from H2O to H+, O2, and e-, this electron replaces the one in photosystem 2
Chemiosmosis- (step 4) when the H+ ions go through the ATP synthase.
reduction in LDP- when ADP turns into ATP, and NADP+ turns into NADPH
Photosynthesis
1) Which molecule stores more than 90 times the energy of an ATP molecule?
-glucose
2) All organisms get the energy they need to regenerate ATP from___
-foods like glucose
ATP consists of ribose, sugar, adenine, and 3 phosphate groups.
ADP forms when ATP loses a phosphate and releases energy.
ATP provides energy for active transport in cells
What is it called? | Definition | 2 examples |
|---|---|---|
Autotroph | organisms that make their own foods. | Cynobacteria, plants, algea |
heterotroph | organisms that obtain energy from food they eat. | Animals, fungi |
What is the ultimate source of energy autotrophs use to produce food?
-the sun
Pigments:
Light green: chlorophyll B
Dark green: Chlorophyll A
Orange: Carotenoids
How do we see color? how does that apply to black and white?
Our eyes pick up the color reflected by objects that are not absorbed.
White- reflects all light
Black- absorbs all light
 A= adenine
A= adenine
B= ribose
C= phosphate group
Name 3 cellular activities/work that use energy to stored in ATP
Chemical
Mechanical
Transport
Chlorophyll absorbs light well in the blue-violet and red regions of the visible spectrum
6H2O+ 6CO2+ Light —> C6H12O2 + O2
QUESTIONS:
If a plant is kept under green-colored light for an extended period of time, what will happen to the rate of photosynthesis?
The plant is not absorbing any light necessary for Light Dependant reactions.
Why are carotenoid colors present in leaves during fall and not other times?
This is because as days shorten, temperature cools. Chlorophyll is broken down into accesory pigments that are used to absorb higher energy light waves.
Photosystem one and two are part of the thylakoid membrane
why does the space inside the thylakoid become positively charged during the light-dependant reactions?
H+ ions build up as water splits.
Where does the calvin cycle occur in?
the stroma
Write an equation that shows NADP+ become NADPH
NADP+ + H+ + 2e- —> NADPH

Flashcards-
Chloroplast- site of photosynthesis
Cuticle- prevents H2O loss
Vascular bundle transports H2O and C6H12O6
Palisade Mesophyll: photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll: gas exchange and photosynthesis.
Stomata- regulates gas exchange H2O loss
epidermis- hydrophobic, doesn’t let water out of the leaf.
first stage of calvin cycle- carbon fixation
second stage of calvin cycle- reduction
3rd stage of calvin cycle- regeneration
Rubisco- an enzyme that combines RUBP and CO2
PSII- where light first hits to excite the electrons.
Photo excitation- (step 1) when the elctrons become excited
Electron transport chain- (step 2) when the excited protein from PSII goes through a bunch of different membrane proteins.
Photolysis- (step 3) the process of splitting water, from H2O to H+, O2, and e-, this electron replaces the one in photosystem 2
Chemiosmosis- (step 4) when the H+ ions go through the ATP synthase.
reduction in LDP- when ADP turns into ATP, and NADP+ turns into NADPH
 Knowt
Knowt