
Biological Molecules
Monomers - sub-units of larger molecules that can be bonded together in a chain to form polymers.
There are four main biological molecules:
Carbohydrates - monomers are known as monosaccharides.
they are a fast source of energy
Lipids (fats) - formed by fatty acids and glycerol. Lipids are not polymers.
they are good as insulators within cells
they are a long-term source of energy
the make up cell membranes
Proteins - monomers are known as amino acids.
they are good for muscle building
they strengthen the immune system
Nucleic acids - monomers are known as nucleotides.
they code for proteins
Biological Molecule | Elements it contains |
|---|---|
Carbohydrate | C, H, O |
Lipid | C, H, O |
Protein | C, H, O, N |
Nucleic Acid | C, H, O, N, P |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is the process of breaking polymers into their respective monomers using water.
“Hydro“ = water, “lysis“ = splitting
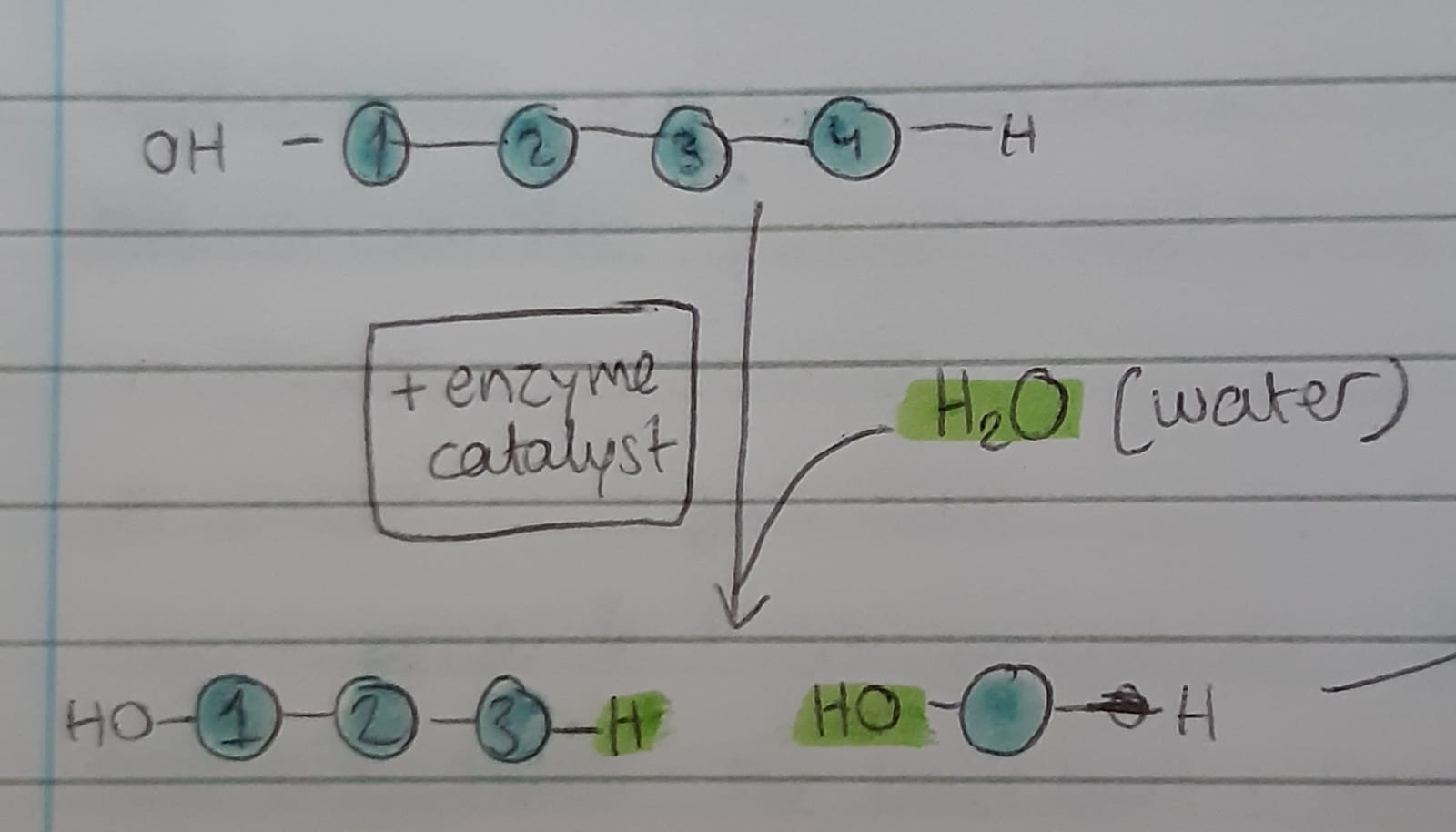
Above: a polymer being split into two sub-sections using water and an enzyme catalyst. This is a hydrolysis reaction.
Condensation
The opposite of a hydrolysis reaction is a condensation reaction. This is when two monomers are combined to form a polymer, which also gives water as a product.
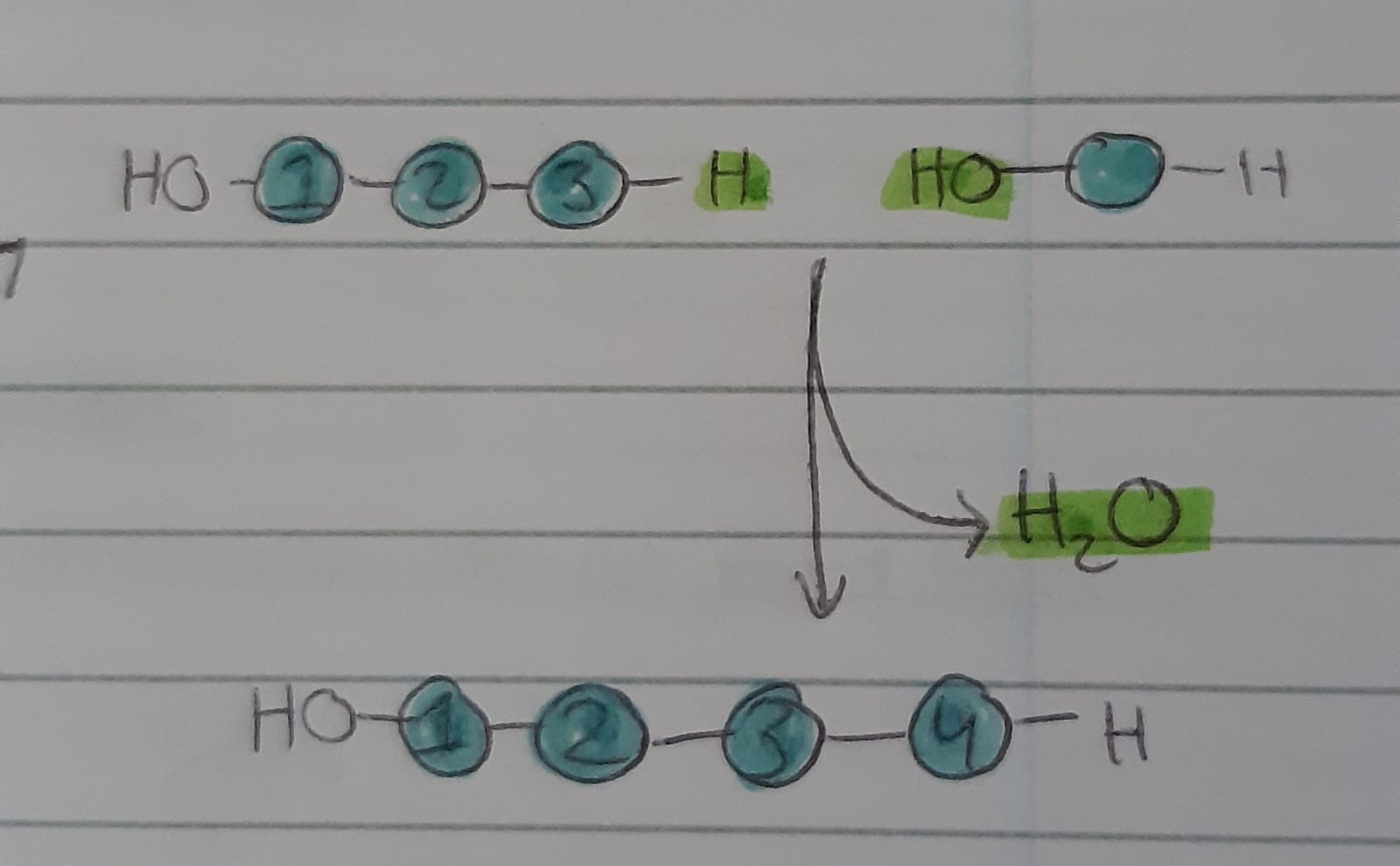
Q: Which type of reaction would form a molecule of starch?
A: A condensation reaction.
Q: Which type of reaction would form molecules of glucose?
A: a hydrolysis reaction.
Biological Molecules as evidence for evolution
all living organisms contain carbon
DNA is present in all living organisms and code for the same amino acids
This suggests a common ancestor.
Biological Molecules
Monomers - sub-units of larger molecules that can be bonded together in a chain to form polymers.
There are four main biological molecules:
Carbohydrates - monomers are known as monosaccharides.
they are a fast source of energy
Lipids (fats) - formed by fatty acids and glycerol. Lipids are not polymers.
they are good as insulators within cells
they are a long-term source of energy
the make up cell membranes
Proteins - monomers are known as amino acids.
they are good for muscle building
they strengthen the immune system
Nucleic acids - monomers are known as nucleotides.
they code for proteins
Biological Molecule | Elements it contains |
|---|---|
Carbohydrate | C, H, O |
Lipid | C, H, O |
Protein | C, H, O, N |
Nucleic Acid | C, H, O, N, P |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is the process of breaking polymers into their respective monomers using water.
“Hydro“ = water, “lysis“ = splitting

Above: a polymer being split into two sub-sections using water and an enzyme catalyst. This is a hydrolysis reaction.
Condensation
The opposite of a hydrolysis reaction is a condensation reaction. This is when two monomers are combined to form a polymer, which also gives water as a product.

Q: Which type of reaction would form a molecule of starch?
A: A condensation reaction.
Q: Which type of reaction would form molecules of glucose?
A: a hydrolysis reaction.
Biological Molecules as evidence for evolution
all living organisms contain carbon
DNA is present in all living organisms and code for the same amino acids
This suggests a common ancestor.
 Knowt
Knowt