
Chapter 15 - Spending, income & GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP): measuring the nation’s output
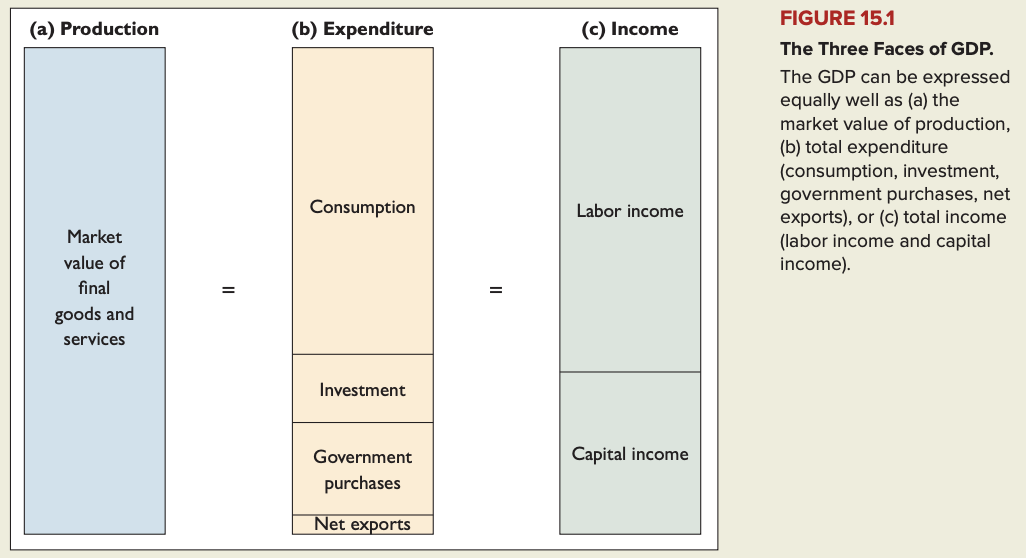
Gross domestic product (GDP): market value of the final goods and services produced in a country during a given period.
Market value: selling prices of goods and services in the open market.
Final goods/services: goods/services consumed by the ultimate user; because they are the end products of the production process, they are counted as part of GDP.
Intermediate goods/services: goods/services used up in the production of final goods and services and therefore not counted as part of GDP.
Capital good: long-lived good that is used in the production of other goods and services.
Value added: for any firm, the market value of its product/service minus the cost of inputs purchased from other firms.
The expenditure method for measuring GDP
Consumption expenditure (or consumption): spending by households on goods and services such as food, clothing, and entertainment.
Investment: spending by firms on final goods and services, primarily capital goods.
Government purchases: purchases by federal, state and local governments of final goods and services; government purchases do not include transfer payments, which are payments made by the government in return for which no current goods or services are received, nor do they include interest paid on the government debt.
Net exports: exports minus imports.
Nominal GDP vs real GDP
Nominal GDP: measure of GDP in which the quantities produced are valued at current-year prices; nominal GDP measures the current dollar value of production.
Real GDP: measure of GDP in which the quantities produced are valued at the prices in a base year rather than at current prices; real GDP measures the actual physical volume of production.
Chapter 15 - Spending, income & GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP): measuring the nation’s output
Gross domestic product (GDP): market value of the final goods and services produced in a country during a given period.
Market value: selling prices of goods and services in the open market.
Final goods/services: goods/services consumed by the ultimate user; because they are the end products of the production process, they are counted as part of GDP.
Intermediate goods/services: goods/services used up in the production of final goods and services and therefore not counted as part of GDP.
Capital good: long-lived good that is used in the production of other goods and services.
Value added: for any firm, the market value of its product/service minus the cost of inputs purchased from other firms.
The expenditure method for measuring GDP
Consumption expenditure (or consumption): spending by households on goods and services such as food, clothing, and entertainment.
Investment: spending by firms on final goods and services, primarily capital goods.
Government purchases: purchases by federal, state and local governments of final goods and services; government purchases do not include transfer payments, which are payments made by the government in return for which no current goods or services are received, nor do they include interest paid on the government debt.
Net exports: exports minus imports.

Nominal GDP vs real GDP
Nominal GDP: measure of GDP in which the quantities produced are valued at current-year prices; nominal GDP measures the current dollar value of production.
Real GDP: measure of GDP in which the quantities produced are valued at the prices in a base year rather than at current prices; real GDP measures the actual physical volume of production.
 Knowt
Knowt