
Chapter 6 - Plant Nutrition
Types of nutrition
Plants follow autotrophic nutrition
Inorganic substances: carbon dioxide, water, minerals, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins
Organic substances: Bread, Vegetables, Fruits
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light.
Photosynthesis(light manufacture)
Sunlight and chlorophyll are need for chemical process to take place
Carbon dioxide + Water ———> Glucose + Oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O ———> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Chlorophyll is a green pigment in plants which helps in photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are the organelles in which photosynthesis takes place
Leaves
Leaves is a factory for making carbohydrates
Leaf structure:
The top coat is called the lamina
joined to the plant by Petiole or leaf stalk
vascular bundles, veins in leaf
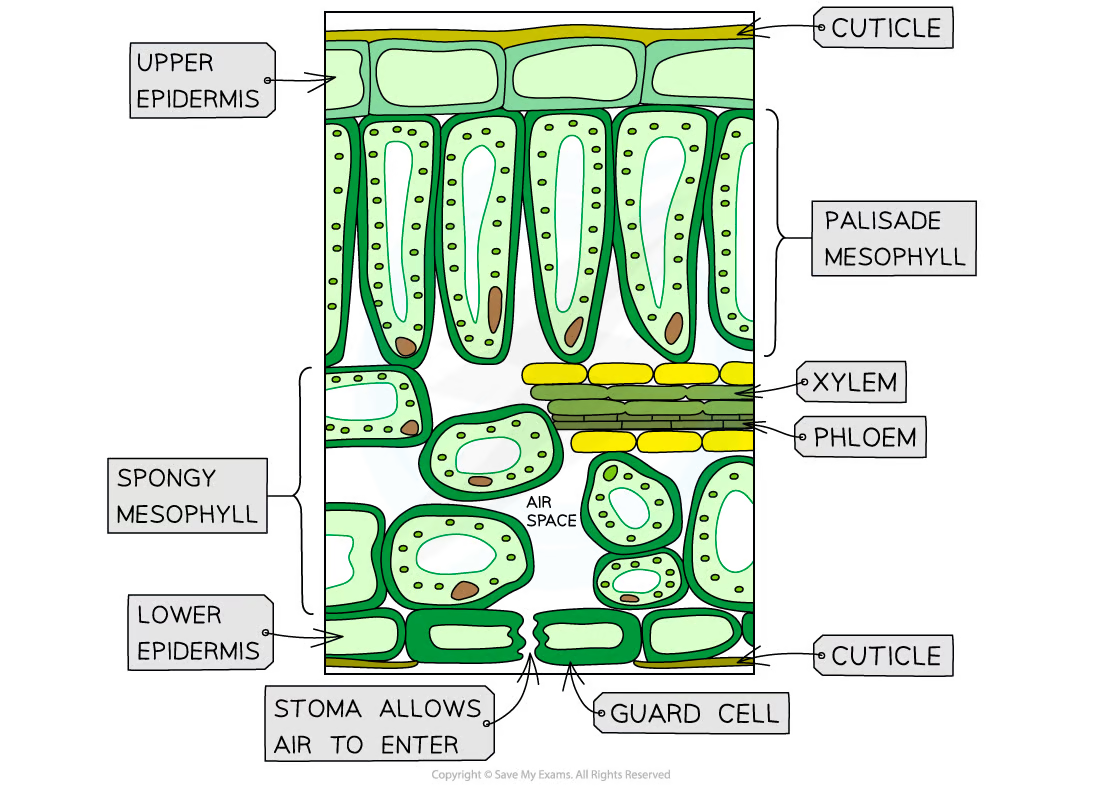
stomata: exchange of gases, transpiration
waxy substance cuticle
mesophyll contain chloroplasts
palisade layer performs photosynthesis
xylem vessel for carrying water
phloem tubes carry sucrose and other substances
Leaf Adaptations:
adapted to obtain carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
Carbon Dioxide:
spongy mesophyll cells need carbon dioxide
enters through stomata by diffusion
diffuses to all the cells in the plant through air spaces between mesophyll cells
Water:
obtained from soil and absorbed by root hairs
carried to the leaf through the xylem
to the mesophyll cell by osmosis
Sunlight:
the flat surface absorbs light
spongy mesophyll cells and palisade cells need sunlight
the thinness allows light to penetrate
Uses of Glucose
Uses of Energy:
energy is released from glucose
Stored as Starch:
glucose is stored as starch in the leaf
glucose is reactive and would dissolve in water around the plant cell
when dissolved it could cause damage from the concentration
Chapter 6 - Plant Nutrition
Types of nutrition
Plants follow autotrophic nutrition
Inorganic substances: carbon dioxide, water, minerals, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins
Organic substances: Bread, Vegetables, Fruits
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light.
Photosynthesis(light manufacture)
Sunlight and chlorophyll are need for chemical process to take place
Carbon dioxide + Water ———> Glucose + Oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O ———> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Chlorophyll is a green pigment in plants which helps in photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are the organelles in which photosynthesis takes place
Leaves
Leaves is a factory for making carbohydrates
Leaf structure:
The top coat is called the lamina
joined to the plant by Petiole or leaf stalk
vascular bundles, veins in leaf

stomata: exchange of gases, transpiration
waxy substance cuticle
mesophyll contain chloroplasts
palisade layer performs photosynthesis
xylem vessel for carrying water
phloem tubes carry sucrose and other substances
Leaf Adaptations:
adapted to obtain carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
Carbon Dioxide:
spongy mesophyll cells need carbon dioxide
enters through stomata by diffusion
diffuses to all the cells in the plant through air spaces between mesophyll cells
Water:
obtained from soil and absorbed by root hairs
carried to the leaf through the xylem
to the mesophyll cell by osmosis
Sunlight:
the flat surface absorbs light
spongy mesophyll cells and palisade cells need sunlight
the thinness allows light to penetrate
Uses of Glucose
Uses of Energy:
energy is released from glucose
Stored as Starch:
glucose is stored as starch in the leaf
glucose is reactive and would dissolve in water around the plant cell
when dissolved it could cause damage from the concentration
 Knowt
Knowt