
Thermal Energy, Endothermic and Exothermic
Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Formulas
Celsius to Kelvin: 0°C + 273.15 = 273.15K
Celsius to Fahrenheit: (0°C × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F
Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C
You can convert to K and °F easily from there
Difference between temperature and thermal energy
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of moving particles of matter
Thermal energy is a measure of the total kinetic energy of moving particles of matter
Kinetic energy is a measurement of movement; anything that moves has kinetic energy
The slower the particles are moving, the less kinetic energy they have, therefore the less thermal energy they have
A 20 gallon tub of water at 30°C has a lower temperature than a drop of water at 50°C
However, the same tub has higher thermal energy than the same drop of water because its mass is larger
Thermal energy depends on:
mass
temperature
number of particles

Specific Heat - the amount of energy needed to raise the temp. of 1 g of a substance by 1°C
Different for each substance
Specific heat of liquid water - 4.186 J/g°C
one thermochemical (small/lowercase) calorie is also equal to 4.186 Joules
Formula°C
heat (J) = specific heat (J/g°C) × mass (g) × temp. change (°C)
Don’t forget to convert the units in practice problems
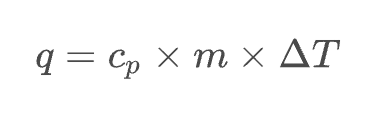
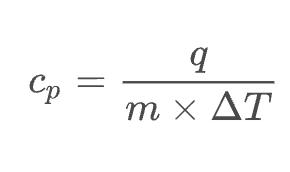
Sample Problem


Vocabulary
system - a specified portion of matter in a given region of space that has been selected for study during an experiment or observation
usually where a chemical reaction is taking place; the reactants and products of a chemical reaction
surrounding - the area around the system; everything but the system itself
endothermic - absorbing heat
exothermic - releasing heat (exo = exit)
How many Joules are in one…
UNIT | AMOUNT |
|---|---|
Joule | 1 J |
calorie (small) | 4.184 J |
Calorie (large/kilocalorie) | 4184 J |
kilowatt/hour | 3.6 × 10⁶ J |
Example: convert 10 calories (small) to Joules
1 calorie = 4.184 J
10 calories = 41.84 J
Example 2: convert 4184 Joules to calories (small)
4184/4.184 = 1000 calories
Molar mass
Example: the molar mass of Substance 1 is 10 g/mol. How many grams are in 2 moles of Substance 1?
The answer is 20 g. Multiply the # of moles given by the molar mass (2 moles * 10 g/mol = 20 g).
Thermal Energy, Endothermic and Exothermic
Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Formulas
Celsius to Kelvin: 0°C + 273.15 = 273.15K
Celsius to Fahrenheit: (0°C × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F
Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C
You can convert to K and °F easily from there
Difference between temperature and thermal energy
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of moving particles of matter
Thermal energy is a measure of the total kinetic energy of moving particles of matter
Kinetic energy is a measurement of movement; anything that moves has kinetic energy
The slower the particles are moving, the less kinetic energy they have, therefore the less thermal energy they have
A 20 gallon tub of water at 30°C has a lower temperature than a drop of water at 50°C
However, the same tub has higher thermal energy than the same drop of water because its mass is larger
Thermal energy depends on:
mass
temperature
number of particles

Specific Heat - the amount of energy needed to raise the temp. of 1 g of a substance by 1°C
Different for each substance
Specific heat of liquid water - 4.186 J/g°C
one thermochemical (small/lowercase) calorie is also equal to 4.186 Joules
Formula°C
heat (J) = specific heat (J/g°C) × mass (g) × temp. change (°C)
Don’t forget to convert the units in practice problems
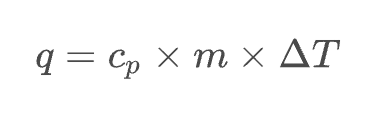
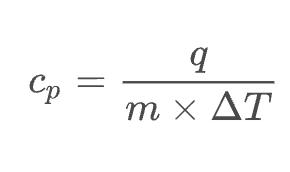
Sample Problem


Vocabulary
system - a specified portion of matter in a given region of space that has been selected for study during an experiment or observation
usually where a chemical reaction is taking place; the reactants and products of a chemical reaction
surrounding - the area around the system; everything but the system itself
endothermic - absorbing heat
exothermic - releasing heat (exo = exit)
How many Joules are in one…
UNIT | AMOUNT |
|---|---|
Joule | 1 J |
calorie (small) | 4.184 J |
Calorie (large/kilocalorie) | 4184 J |
kilowatt/hour | 3.6 × 10⁶ J |
Example: convert 10 calories (small) to Joules
1 calorie = 4.184 J
10 calories = 41.84 J
Example 2: convert 4184 Joules to calories (small)
4184/4.184 = 1000 calories
Molar mass
Example: the molar mass of Substance 1 is 10 g/mol. How many grams are in 2 moles of Substance 1?
The answer is 20 g. Multiply the # of moles given by the molar mass (2 moles * 10 g/mol = 20 g).
 Knowt
Knowt
