
unit 2 | study guide
online study guide (quizizz)
Where is the 90° latitude on Earth?
Both North & South poles
What type of tides would this arrangement of earth-moon-sun create?

Spring tide
A star you observed has an H-alpha line (λo = 345.28nm) at a wavelength of λ = 345.42nm. What speed is this star?
121.64 km/s
Each element on the periodic table can be identified by its
unique spectral “fingerprint”
What measurement is the distance traveled by light in one year?
Light-year
Which type of eclipse is shown in the diagram?
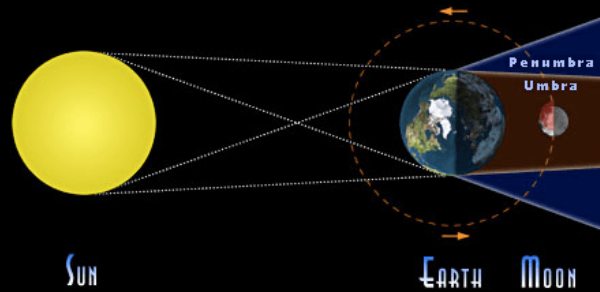
Lunar Eclipse
If two objects in the sky have a different parallax shift what can you conclude from that?
The object with the smaller shift is closer
Where is the 0° latitude on Earth?
Equator
A lunar eclipse only happens during a _____ moon.
Full
A star has a temperature of what if it has a nanometer ranger of 700?
This red star has a temperature of 4286K
What is the difference between solar and sidereal day?
A solar day is the time it takes for the Earth to rotate about its axis so that the Sun appears in the same position in the sky while the sidereal day is the time it takes for the Earth to complete one rotation about its axis with respect to the 'fixed' stars.
The Earth’s axis is tilted ____ degrees.
23.5
What happens when the area in which you live tilts away from the sun?

It is winter.
Which of the following statement/s are correct?
I. The main consequences of Earth's rotation are day and night.
II. The sidereal day has a period of 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds, which is almost 4 minutes shorter than the mean solar day.
III. Earth revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit at an average speed of 107,000 kilometers (66,000 miles) per hour.
I, II, III
The unknown emissions spectra belongs to the element
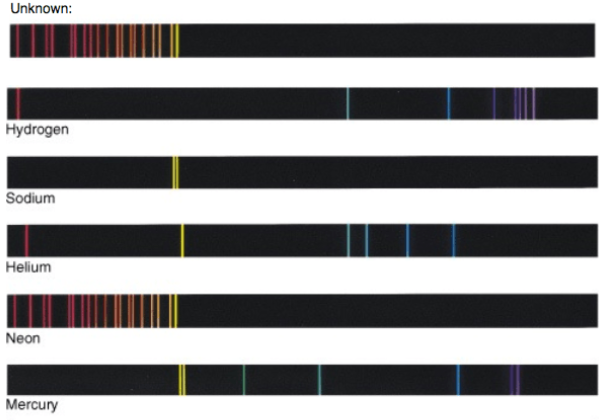

Neon
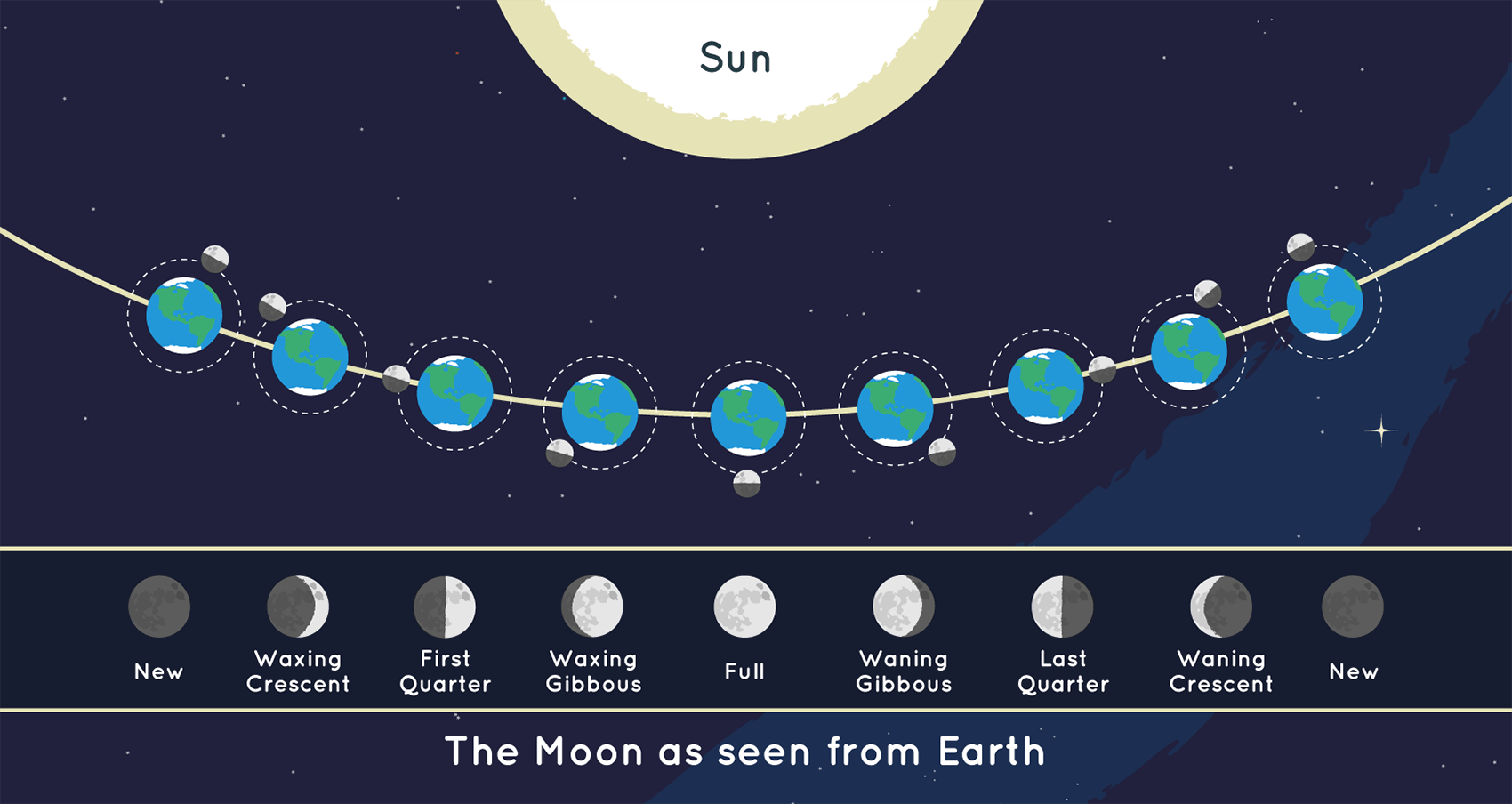
Which of the following causes the phase of the Moon to change each night?
How much of sunlit side of the moon faces Earth
Most places on Earth experience about how many high and low tides in 24 hours?
2 high and 2 low tides
If a star’s frequency has shifted from 430 nm to 500 nm what effect is occurring?
Red Shift
The angle measure upward from the horizon
Altitude
Which of the following is the angle measure from North in the horizontal direction?
Azimuth
Which of the following is NOT true about a total solar eclipse?
It can be viewed from every spot on earth
The unknown emissions spectra belongs to the element

Helium
What are the motions of the Earth?
rotation, revolution, and precession
Is there a dark side of the Moon?
No, since the Moon rotates the Sun illuminates a different part during its cycle
Approximately, how long does the moon completes its cycle around the Earth?
28 days
What type of tide would this arrangement of earth-moon-sun create?

neap tide
If an object like a star is moving away from Earth, the spectral lines are observed to be
wider or broader & red-shifted.
The Earth’s _____ is an imaginary line that goes from the North Pole to the South Pole.
axis
Spectral lines that are observed to be narrower & blue shifted indicates that an object is
moving towards Earth.
Which type of eclipse is shown in this picture?
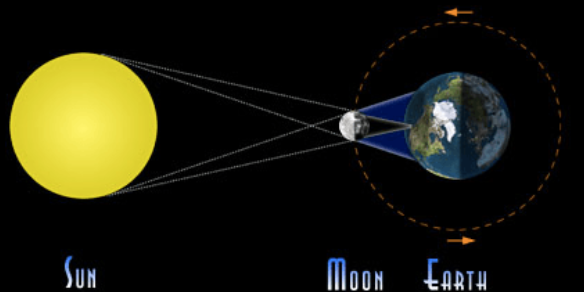
Solar Eclipse
An apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different locations
Parallax
A solar eclipse only happens during a _____ moon.
New
paper study guide
Eclipses
Solar - happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on Earth that either fully or partially blocks the Sun’s light in some areas. occurs on the new moon.
Lunar - happens when Earth is positioned between the Moon and Sun, Earth’s shadow falls upon the surface of the Moon, dimming it and sometimes turns the lunar surface a striking red of the course of a few hours. occurs on full moon. visible from half of Earth.
Seasonal Shift
Cause - due to Earth’s tilted axis (23.5 degrees), which affects the distribution of the sun’s energy across the surface of the planet.
Effect - the seasons, changing vegetation, temperatures, and day length
Three rotations of the Earth
Daily rotation- spinning on axis
creates the day and night cycle (24hrs)
Annual rotation around the Sun
creates the year (~365 days)
Procession of the Equinoxes- Wobble of the Earth on its axis
the position of the Sun on the first day of spring (vernal equinox) slowly shifts westward around the sky, which also moves it around out calendar
Tidal locking of the Moon to the Earth
each time the Moon completes a turn on its axis, it orbits the Earth once, keeping it far side hidden.
Lunar Phases
the cycle of the amount of sunlight illuminated on the moon that is visible on Earth
Tides
High Tides
when water advances to its furthest extend onto the shore line. is closest to the Moon
Low Tides
when water levels have dropped as a result of the Moon’s gravitation pull on Earth. farthest away from the moon.
Spring Tides
formed during new and full moon. moon is aligned with sun. forms a 0° or 180° (straight line)
Neap Tides
occurs during half-moons (1st & 3rd quarter). moon is NOT aligned with sun. forms a 90° with earth.
Diurnal Tides
occurs in locations when the moon is farthest from the equator.
Semi-Diurnal Tides
occurs when the moon is directly over the equator
Mixed Tides
occurs when the moon is extremely far north or extremely far south of the equator
Meteorological Tides
tides affected by wind, barometric pressure (the measurement of air pressure in the atmosphere), rainfall, ice melting, & land drying
Solar and Sidereal days
A solar day is the time it takes for the Earth to rotate about its axis so that the Sun appears in the same position in the sky
The sidereal day is ~4 minutes shorter than the solar day. The sidereal day is the time it takes for the Earth to complete one rotation about its axis with respect to the 'fixed' stars.
Altitude, Azimuth
Altitude is the angular distance of an object above the local horizon. It ranges from 0 degrees at the horizon to 90 degrees at the zenith, the spot directly overhead
Azimuth is the angular distance of an object from the local North, measured along the horizon
Meridian lines
An imaginary line passing from the north of the observer through the zenith and then to the South in the sky
Astronomical Units
major unit to measure space (AU). made from measuring the mean distance from the center of the Earth to the center of the Sun. 1 AU = 1.5 x 10^11 m
Light years
time it takes light to travel one year (lyr). 1lyr = 9.46 x 10^15 m
Parsecs
a unit of distance used in astronomy. one parsec corresponds to the distance at which the mean radius of the Earth’s orbit subtends an angle of one second of arc
1 pc = 3.08 x 10^16 m or 1 pc = 3.26 ly or 1 pc = 206165 AU
Parallax (arcsec)
the angular difference in direct of a celestial body as measured from two points on Earth’s orbit
Wavelength of light, ROYGBIV
every element produces a different set of wavelengths, almost like a fingerprint for that type of gas. the combination of wavelengths emitted by gas when emitting light is called the spectrum of that gas.
Calculations of Temperature/Speed from nanometer range
temperature is the first equation, speed is the last equation. just plug and chug :)

k = temperature
λmax = nanometer
λ = old nanometer
λ0 = new nanometer
Spectrograph data
The spectrum of wavelengths that is produced through the use of a spectrograph. The wavelengths that are produced are individual to the element that is being observed and can be used to identify the element in question.
unit 2 | study guide
online study guide (quizizz)
Where is the 90° latitude on Earth?
Both North & South poles
What type of tides would this arrangement of earth-moon-sun create?

Spring tide
A star you observed has an H-alpha line (λo = 345.28nm) at a wavelength of λ = 345.42nm. What speed is this star?
121.64 km/s
Each element on the periodic table can be identified by its
unique spectral “fingerprint”
What measurement is the distance traveled by light in one year?
Light-year
Which type of eclipse is shown in the diagram?

Lunar Eclipse
If two objects in the sky have a different parallax shift what can you conclude from that?
The object with the smaller shift is closer
Where is the 0° latitude on Earth?
Equator
A lunar eclipse only happens during a _____ moon.
Full
A star has a temperature of what if it has a nanometer ranger of 700?
This red star has a temperature of 4286K
What is the difference between solar and sidereal day?
A solar day is the time it takes for the Earth to rotate about its axis so that the Sun appears in the same position in the sky while the sidereal day is the time it takes for the Earth to complete one rotation about its axis with respect to the 'fixed' stars.
The Earth’s axis is tilted ____ degrees.
23.5
What happens when the area in which you live tilts away from the sun?

It is winter.
Which of the following statement/s are correct?
I. The main consequences of Earth's rotation are day and night.
II. The sidereal day has a period of 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds, which is almost 4 minutes shorter than the mean solar day.
III. Earth revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit at an average speed of 107,000 kilometers (66,000 miles) per hour.
I, II, III
The unknown emissions spectra belongs to the element

Neon
Which of the following causes the phase of the Moon to change each night?
How much of sunlit side of the moon faces Earth
Most places on Earth experience about how many high and low tides in 24 hours?
2 high and 2 low tides
If a star’s frequency has shifted from 430 nm to 500 nm what effect is occurring?
Red Shift
The angle measure upward from the horizon
Altitude
Which of the following is the angle measure from North in the horizontal direction?
Azimuth
Which of the following is NOT true about a total solar eclipse?
It can be viewed from every spot on earth
The unknown emissions spectra belongs to the element

Helium
What are the motions of the Earth?
rotation, revolution, and precession
Is there a dark side of the Moon?
No, since the Moon rotates the Sun illuminates a different part during its cycle
Approximately, how long does the moon completes its cycle around the Earth?
28 days
What type of tide would this arrangement of earth-moon-sun create?

neap tide
If an object like a star is moving away from Earth, the spectral lines are observed to be
wider or broader & red-shifted.
The Earth’s _____ is an imaginary line that goes from the North Pole to the South Pole.
axis
Spectral lines that are observed to be narrower & blue shifted indicates that an object is
moving towards Earth.
Which type of eclipse is shown in this picture?

Solar Eclipse
An apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different locations
Parallax
A solar eclipse only happens during a _____ moon.
New
paper study guide
Eclipses
Solar - happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on Earth that either fully or partially blocks the Sun’s light in some areas. occurs on the new moon.
Lunar - happens when Earth is positioned between the Moon and Sun, Earth’s shadow falls upon the surface of the Moon, dimming it and sometimes turns the lunar surface a striking red of the course of a few hours. occurs on full moon. visible from half of Earth.
Seasonal Shift
Cause - due to Earth’s tilted axis (23.5 degrees), which affects the distribution of the sun’s energy across the surface of the planet.
Effect - the seasons, changing vegetation, temperatures, and day length
Three rotations of the Earth
Daily rotation- spinning on axis
creates the day and night cycle (24hrs)
Annual rotation around the Sun
creates the year (~365 days)
Procession of the Equinoxes- Wobble of the Earth on its axis
the position of the Sun on the first day of spring (vernal equinox) slowly shifts westward around the sky, which also moves it around out calendar
Tidal locking of the Moon to the Earth
each time the Moon completes a turn on its axis, it orbits the Earth once, keeping it far side hidden.
Lunar Phases
the cycle of the amount of sunlight illuminated on the moon that is visible on Earth

Tides
High Tides
when water advances to its furthest extend onto the shore line. is closest to the Moon
Low Tides
when water levels have dropped as a result of the Moon’s gravitation pull on Earth. farthest away from the moon.
Spring Tides
formed during new and full moon. moon is aligned with sun. forms a 0° or 180° (straight line)
Neap Tides
occurs during half-moons (1st & 3rd quarter). moon is NOT aligned with sun. forms a 90° with earth.
Diurnal Tides
occurs in locations when the moon is farthest from the equator.
Semi-Diurnal Tides
occurs when the moon is directly over the equator
Mixed Tides
occurs when the moon is extremely far north or extremely far south of the equator
Meteorological Tides
tides affected by wind, barometric pressure (the measurement of air pressure in the atmosphere), rainfall, ice melting, & land drying
Solar and Sidereal days
A solar day is the time it takes for the Earth to rotate about its axis so that the Sun appears in the same position in the sky
The sidereal day is ~4 minutes shorter than the solar day. The sidereal day is the time it takes for the Earth to complete one rotation about its axis with respect to the 'fixed' stars.
Altitude, Azimuth
Altitude is the angular distance of an object above the local horizon. It ranges from 0 degrees at the horizon to 90 degrees at the zenith, the spot directly overhead
Azimuth is the angular distance of an object from the local North, measured along the horizon
Meridian lines
An imaginary line passing from the north of the observer through the zenith and then to the South in the sky
Astronomical Units
major unit to measure space (AU). made from measuring the mean distance from the center of the Earth to the center of the Sun. 1 AU = 1.5 x 10^11 m
Light years
time it takes light to travel one year (lyr). 1lyr = 9.46 x 10^15 m
Parsecs
a unit of distance used in astronomy. one parsec corresponds to the distance at which the mean radius of the Earth’s orbit subtends an angle of one second of arc
1 pc = 3.08 x 10^16 m or 1 pc = 3.26 ly or 1 pc = 206165 AU
Parallax (arcsec)
the angular difference in direct of a celestial body as measured from two points on Earth’s orbit
Wavelength of light, ROYGBIV
every element produces a different set of wavelengths, almost like a fingerprint for that type of gas. the combination of wavelengths emitted by gas when emitting light is called the spectrum of that gas.
Calculations of Temperature/Speed from nanometer range
temperature is the first equation, speed is the last equation. just plug and chug :)

k = temperature
λmax = nanometer
λ = old nanometer
λ0 = new nanometer
Spectrograph data
The spectrum of wavelengths that is produced through the use of a spectrograph. The wavelengths that are produced are individual to the element that is being observed and can be used to identify the element in question.
 Knowt
Knowt
